
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The general trend in ionization energy should be summarized and the relation of ionization energy with valence electrons in an element should be discussed.
Concept introduction:
Ionization energy is the amount of energy required in order to remove the valence electron from an isolated neutral gaseous atom.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
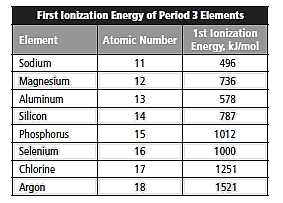
The given data is entered in excel spreadsheet and the following plot is obtained where x -axis represents
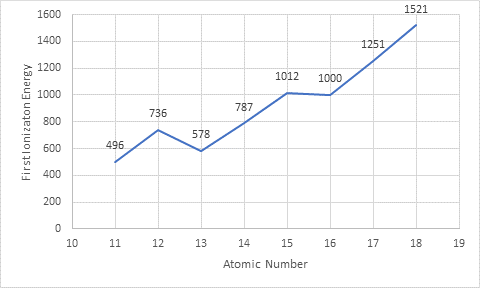
The given elements are present in period 3 of the periodic table and the trend in plot shows an increase in first ionization energy on moving from left to right in the period.
From the given data, the element that has lowest first ionization energy is sodium that means an atom possess low ionization energy when it is easy to remove an electron from it thus, it will form positive ion easily whereas the element that has highest ionization energy is argon that means an atom possess high ionization energy when it is harder to remove an electron from it thus, it will not form positive ion easily. As the number of valence electrons increases from sodium to argon (1 to 8) so, the ionization energy is greater for the atoms having more valence electrons.
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Microbiology: An Introduction
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Draw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with one pen and all in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the oxidation of 3-bromo-cyclohexan-1-ol.arrow_forwardConvert the following Fischer projection to Haworth projections. show work and show the arrows please.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the substitution reaction converting an alcohol into an alkyl halide. If chirality is important to the reaction include it.arrow_forwardWrite, in words three different reactions we can use to make an alcohol.arrow_forwardDraw the reduction mechanism for the reduction of the aldehyde.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





