
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Correct IUPAC name for the structure given has to be written.
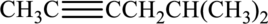
Concept Introduction:
A common nomenclature of naming organic compounds has been developed by IUPAC. By usage of this nomenclature or rules, memorizing of names of organic compounds is not necessary.
IUPAC rules for naming
There are about five rules that has to be followed for naming an alkene and an alkyne. They are,
- The longest continuous carbon chain in the compound that contains double bond or triple has to be identified. This is known as parent compound.
- Suffix “–ane” (in name of
alkane ) is replaced with “-ene” for alkene or “-yne” for alkyne. - Numbering has to be done so that the lowest number is given to the double or triple bond.
- Naming and numbering has to be given for each atom or group that is attached to the parent chain. Numbering has to be done in a way that substituents get the least numbering.
- If the alkenes have more than one double bond they are called as alkadienes (two double bonds) or alkatrienes (three double bonds). Appropriate suffix has to be used depending on the number of multiple bonds present in the compound.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound and IUPAC name is.
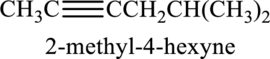
IUPAC name given is wrong as the triple bond is not given the least numbering. Correct IUPAC name for the given structure can be given as shown below.
Longest carbon chain with triple bond is found to contain six carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane is hexane. As a triple bond is present, the alkyne name is hexyne.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the triple bond gets the least numbering. In this case, triple bond is present between carbon-2 and carbon-3. Therefore, the parent alkyne is 2-hexyne.
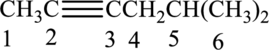
The substituent present in the given structure are a methyl group on carbon-5. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of alkene as 5-methyl-2-hexyne.
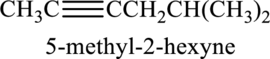
Longest carbon chain containing triple bond is hexane. Position of triple bond is 2-hexyne. Substituent present in the chain is 5-methyl. Correct IUPAC name of the structure given is 5-methyl-2-hexyne.
(b)
Interpretation:
Correct IUPAC name for the structure given has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
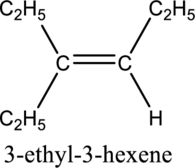
Given compound and IUPAC name is.
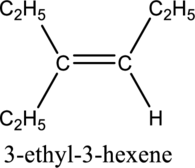
Longest carbon chain with double bond is found to contain six carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane is hexane. As a double bond is present, the alkene name is hexene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the triple bond gets the least numbering. In this case, triple bond is present between carbon-3 and carbon-4. Therefore, the parent alkyne is 3-hexene.
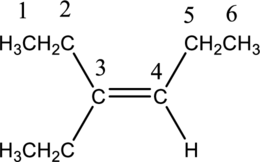
The substituent present in the given structure are an ethyl group on carbon-3. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of alkene as 3-ethyl-3-hexene.
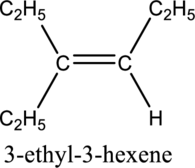
Longest carbon chain containing double bond is hexene. Position of double bond is 3-hexene. Substituent present in the chain is 3-ethyl. IUPAC name of the structure given is 3-methyl-3-hexene. Therefore, the given name is correct.
(c)
Interpretation:
Correct IUPAC name for the structure given has to be written.
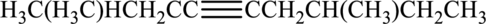
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound and IUPAC name is.
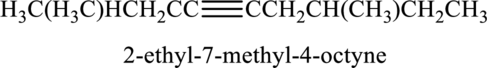
IUPAC name given is wrong as the parent chain considered and the substituents are not given correctly. Correct IUPAC name for the given structure can be given as shown below.
Longest carbon chain with triple bond is found to contain nine carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane is nonane. As a triple bond is present, the alkyne name is nonyne.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the triple bond gets the least numbering. In this case, triple bond is present between carbon-4 and carbon-5. Therefore, the parent alkyne is 4-nonyne.
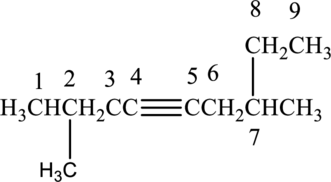
The substituent present in the given structure two methyl groups, each on carbon-2 and carbon-7. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of alkyne as 2,7-dimethyl-4-nonyne.
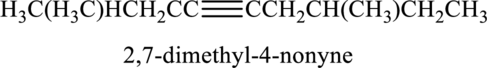
Longest carbon chain containing triple bond is nonane. Position of triple bond is 4-nonyne. Substituent present in the chain is 2,7-dimethyl. Correct IUPAC name of the structure given is 2,7-dimethyl-4-nonyne.
(d)
Interpretation:
Correct IUPAC name for the structure given has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
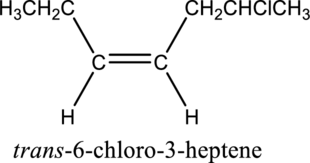
Given compound and IUPAC name is.
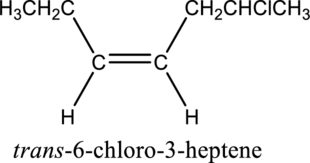
The configuration given in the IUPAC name is wrong as both hydrogen atoms are present on same side of the double bond. Correct IUPAC name can be given as shown below.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the double bond gets the least numbering. In this case, double bond is present between carbon-3 and carbon-4. Therefore, the parent alkyne is 3-heptene.
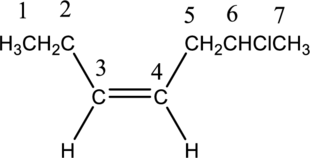
The substituent present in the given structure is a chloro group. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of alkene as 6-chloro-3-heptene. Looking into the stereo information, there are hydrogen atoms present on the same side of the double bond. Hence, the structure given is in cis conformation. Therefore, the name of the structure can be given as cis-6-chloro-3-heptene.
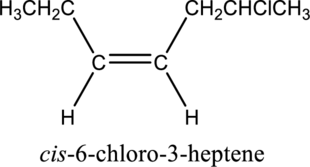
Longest carbon chain containing double bond is heptene. Position of double bond is 3-heptene. Substituent present in the chain is 6-chloro. Configuration is “cis”. Correct IUPAC name of the structure given is cis-6-chloro-3-heptene.
(e)
Interpretation:
Correct IUPAC name for the structure given has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(e)
Explanation of Solution
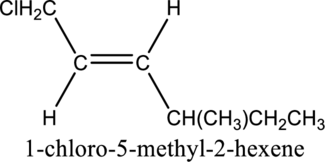
Given compound and IUPAC name is.
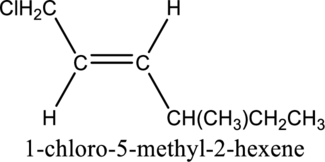
The configuration given in the IUPAC name is wrong as configuration is not given and the position of methyl substituent is wrong. Correct IUPAC name can be given as shown below.
Parent carbon chain is found to contain six carbon atoms. Therefore, the alkane is hexane.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the double bond gets the least numbering. In this case, double bond is present between carbon-2 and carbon-3. Therefore, the parent alkyne is 2-hexene.
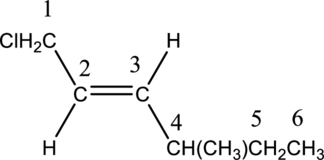
The substituent present in the given structure are a chloro group and a methyl group. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of alkene as 1-chloro-4-methyl. Looking into the stereo information, there are hydrogen atoms present on opposite side of the double bond. Hence, the structure given is in trans conformation. Therefore, the name of the structure can be given as trans-1-chloro-4-methyl2-hexene.
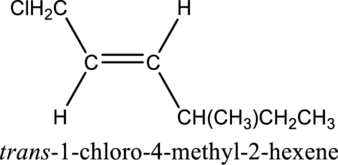
Longest carbon chain containing double bond is hexene. Position of double bond is 2-hexene. Substituent present in the chain is 1-chloro-4-methyl. Configuration is “trans”. Correct IUPAC name of the structure given is trans-1-chloro-4-methyl-2-hexene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIOCHEMISTRY(LL)-PKG
- 5) Confidence interval. Berglund and Wichardt investigated the quantitative determination of Cr in high-alloy steels using a potentiometric titration of Cr(VI). Before the titration, samples of the steel were dissolved in acid and the chromium oxidized to Cr(VI) using peroxydisulfate. Shown here are the results (as %w/w Cr) for the analysis of a reference steel. 16.968, 16.922, 16.840, 16.883, 16.887, 16.977, 16.857, 16.728 Calculate the mean, the standard deviation, and the 95% confidence interval about the mean. What does this confidence interval mean?arrow_forwardIn the Nitrous Acid Test for Amines, what is the observable result for primary amines? Group of answer choices nitrogen gas bubbles form a soluble nitrite salt yellow oily layer of nitrosoaminearrow_forward3. a. Use the MS to propose at least two possible molecular formulas. For an unknown compound: 101. 27.0 29.0 41.0 50.0 52.0 55.0 57.0 100 57.5 58.0 58.5 62.0 63.0 64.0 65.0 74.0 40 75.0 76.0 20 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 m/z 99.5 68564810898409581251883040 115.0 116.0 77404799 17417M 117.0 12.9 118.0 33.5 119.0 36 133 0 1.2 157.0 2.1 159.0 16 169.0 219 170.0 17 171.0 21.6 172.0 17 181.0 1.3 183.0 197.0 100.0 198.0 200. 784 Relative Intensity 2 2 8 ō (ppm) 6 2arrow_forward
- Solve the structure and assign each of the following spectra (IR and C-NMR)arrow_forward1. For an unknown compound with a molecular formula of C8H100: a. What is the DU? (show your work) b. Solve the structure and assign each of the following spectra. 8 6 2 ō (ppm) 4 2 0 200 150 100 50 ō (ppm) LOD D 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 HAVENUMBERI -11arrow_forward16. The proton NMR spectral information shown in this problem is for a compound with formula CioH,N. Expansions are shown for the region from 8.7 to 7.0 ppm. The normal carbon-13 spec- tral results, including DEPT-135 and DEPT-90 results, are tabulated: 7 J Normal Carbon DEPT-135 DEPT-90 19 ppm Positive No peak 122 Positive Positive cus и 124 Positive Positive 126 Positive Positive 128 No peak No peak 4° 129 Positive Positive 130 Positive Positive (144 No peak No peak 148 No peak No peak 150 Positive Positive してしarrow_forward
- 3. Propose a synthesis for the following transformation. Do not draw an arrow-pushing mechanism below, but make sure to draw the product of each proposed step (3 points). + En CN CNarrow_forwardShow work..don't give Ai generated solution...arrow_forwardLabel the spectrum with spectroscopyarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





