
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach ( 9th International Edition ) ISBN:9781260092684
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781260048667
Author: Yunus A. Cengel Dr.; Michael A. Boles
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.9, Problem 61P
Repeat Prob. 10–60, but replace the open feedwater heater with a closed feedwater heater. Assume that the feedwater leaves the heater at the condensation temperature of the extracted steam and that the extracted steam leaves the heater as a saturated liquid and is pumped to the line carrying the feedwater.
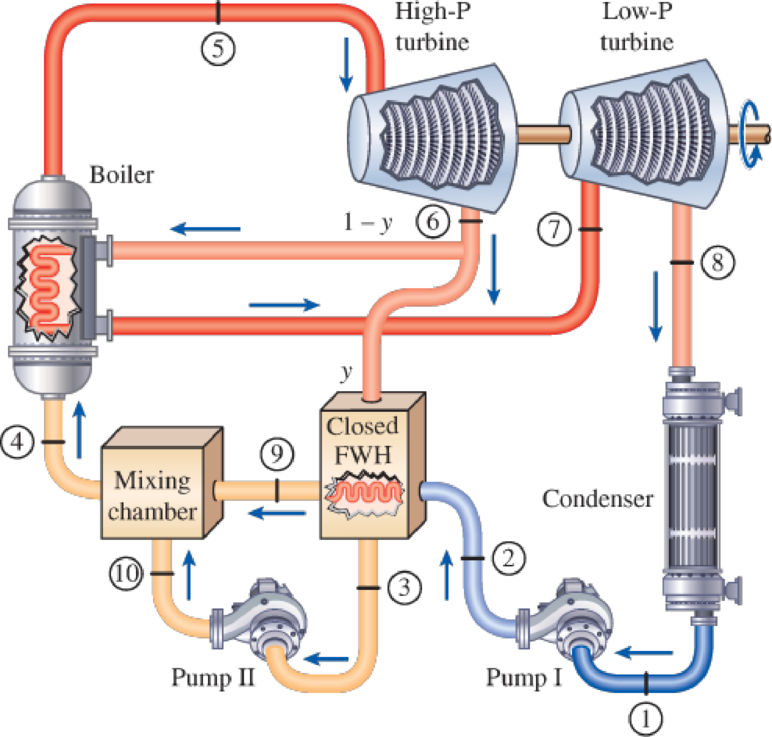
FIGURE P10–61
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1- Determine the following: 1- RSHF? 2- C.C.C in tons-ref. 3- Mass
of supply air?
Fresh
Spray chilled
water
S
air
100% RH
To 34 C db & 26 wbt
S
Operation
fan
room I
Exhaust
air
Ti 22 C db & 50% RH
How do I solve this task
A weight for a lift is suspended using an adapter. The counterweight is held up with 4 screws. The weight F is 3200kg.
The screws have a strength class of 8.8. Safety factor 3
Which is the smallest bunch size that can be used?+_Sr/Fm =0,16Gr=0,71ơ=800·0.8=640 MPaAs=?Fmax= As·ơ·GrFs=ơs·AsFFm= Fs· GFSF =SF / FFm · FFm Fpreload =Fload / SF → Fload /3Fpreload per screw =Fload / SF → Fload /4As=Fpreload per screw /ơ·Gr → As= Fpreload per screw / 640· 0.71
The correct answer should be M12 with As=84.3mm²
...
TELEGRAM
ديسمبر
۲۰۲ عند الساعة
سوأل الوجه البينة
۲۷
- Find the equivalent resistance between
A and B
bellows
For the circuit shown.
• All resistances in Ohms.
2
C
2
A
4
B
www
4
E
5
www
ww
8
bar K.
Dr. Abduljabbo
Hammade
27/12/2024
Chapter 10 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach ( 9th International Edition ) ISBN:9781260092684
Ch. 10.9 - Why is the Carnot cycle not a realistic model for...Ch. 10.9 - Why is excessive moisture in steam undesirable in...Ch. 10.9 - A steady-flow Carnot cycle uses water as the...Ch. 10.9 - A steady-flow Carnot cycle uses water as the...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steady-flow Carnot cycle with water as...Ch. 10.9 - Water enters the boiler of a steady-flow Carnot...Ch. 10.9 - What four processes make up the simple ideal...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a simple ideal Rankine cycle with fixed...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a simple ideal Rankine cycle with fixed...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a simple ideal Rankine cycle with fixed...
Ch. 10.9 - How do actual vapor power cycles differ from...Ch. 10.9 - Compare the pressures at the inlet and the exit of...Ch. 10.9 - The entropy of steam increases in actual steam...Ch. 10.9 - Is it possible to maintain a pressure of 10 kPa in...Ch. 10.9 - A simple ideal Rankine cycle with water as the...Ch. 10.9 - A simple ideal Rankine cycle with water as the...Ch. 10.9 - A simple ideal Rankine cycle which uses water as...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a solar-pond power plant that operates on...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a 210-MW steam power plant that operates...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a 210-MW steam power plant that operates...Ch. 10.9 - A simple ideal Rankine cycle with water as the...Ch. 10.9 - A simple ideal Rankine cycle with water as the...Ch. 10.9 - A steam Rankine cycle operates between the...Ch. 10.9 - A steam Rankine cycle operates between the...Ch. 10.9 - A simple Rankine cycle uses water as the working...Ch. 10.9 - The net work output and the thermal efficiency for...Ch. 10.9 - A binary geothermal power plant uses geothermal...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a coal-fired steam power plant that...Ch. 10.9 - Show the ideal Rankine cycle with three stages of...Ch. 10.9 - Is there an optimal pressure for reheating the...Ch. 10.9 - How do the following quantities change when a...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a simple ideal Rankine cycle and an ideal...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on the...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on the...Ch. 10.9 - An ideal reheat Rankine cycle with water as the...Ch. 10.9 - Steam enters the high-pressure turbine of a steam...Ch. 10.9 - An ideal reheat Rankine cycle with water as the...Ch. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal reheat...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on a...Ch. 10.9 - Repeat Prob. 1041 assuming both the pump and the...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 43PCh. 10.9 - Prob. 44PCh. 10.9 - How do open feedwater heaters differ from closed...Ch. 10.9 - How do the following quantities change when the...Ch. 10.9 - Cold feedwater enters a 200-kPa open feedwater...Ch. 10.9 - In a regenerative Rankine cycle. the closed...Ch. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal...Ch. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal...Ch. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal...Ch. 10.9 - Consider an ideal steam regenerative Rankine cycle...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on the...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on the...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on the...Ch. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal...Ch. 10.9 - Repeat Prob. 1060, but replace the open feedwater...Ch. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal...Ch. 10.9 - A simple ideal Rankine cycle with water as the...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 64PCh. 10.9 - An ideal reheat Rankine cycle with water as the...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on a...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 67PCh. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal...Ch. 10.9 - The schematic of a single-flash geothermal power...Ch. 10.9 - What is the difference between cogeneration and...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 71PCh. 10.9 - Prob. 72PCh. 10.9 - Consider a cogeneration plant for which the...Ch. 10.9 - Steam is generated in the boiler of a cogeneration...Ch. 10.9 - A large food-processing plant requires 1.5 lbm/s...Ch. 10.9 - An ideal cogeneration steam plant is to generate...Ch. 10.9 - Steam is generated in the boiler of a cogeneration...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a cogeneration power plant modified with...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 80PCh. 10.9 - Why is the combined gassteam cycle more efficient...Ch. 10.9 - The gas-turbine portion of a combined gassteam...Ch. 10.9 - A combined gassteam power cycle uses a simple gas...Ch. 10.9 - Reconsider Prob. 1083. An ideal regenerator is...Ch. 10.9 - Reconsider Prob. 1083. Determine which components...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a combined gassteam power plant that has...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 89PCh. 10.9 - What is the difference between the binary vapor...Ch. 10.9 - Why is mercury a suitable working fluid for the...Ch. 10.9 - Why is steam not an ideal working fluid for vapor...Ch. 10.9 - By writing an energy balance on the heat exchanger...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 94RPCh. 10.9 - Steam enters the turbine of a steam power plant...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant operating on the...Ch. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal Rankine...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on a...Ch. 10.9 - Repeat Prob. 1098 assuming both the pump and the...Ch. 10.9 - Consider an ideal reheatregenerative Rankine cycle...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 101RPCh. 10.9 - A textile plant requires 4 kg/s of saturated steam...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a cogeneration power plant that is...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 104RPCh. 10.9 - Prob. 105RPCh. 10.9 - Reconsider Prob. 10105E. It has been suggested...Ch. 10.9 - Reconsider Prob. 10106E. During winter, the system...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 108RPCh. 10.9 - Prob. 109RPCh. 10.9 - A steam power plant operates on an ideal...Ch. 10.9 - A Rankine steam cycle modified for reheat, a...Ch. 10.9 - Show that the thermal efficiency of a combined...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 118RPCh. 10.9 - A solar collector system delivers heat to a power...Ch. 10.9 - Starting with Eq. 1020, show that the exergy...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a simple ideal Rankine cycle with fixed...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a simple ideal Rankine cycle. If the...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a simple ideal Rankine cycle with fixed...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a simple ideal Rankine cycle with fixed...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steady-flow Carnot cycle with water as...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 126FEPCh. 10.9 - Prob. 127FEPCh. 10.9 - A simple ideal Rankine cycle operates between the...Ch. 10.9 - Pressurized feedwater in a steam power plant is to...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a steam power plant that operates on the...Ch. 10.9 - Consider a combined gas-steam power plant. Water...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words.
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- P₂ 7+1 * P₁ ART 2 P (P₁ - P₂- Zgp) 21 / Prove that :- m² a cda A₂ == * Cde actual mip Solutionarrow_forwardQ1/ Show that (actual 02/ A simple iet == Cda Cdf х Af 2/Y - Y+1/Y 2P(P1-P2-zxgxpr)arrow_forward5. Determine the transfer function of G(s) = 01(s)/T₁(s) and 02(s)/T₁ for the mechanical system shown in Figure Q5. (Hints: assume zero initial condition) T₁(t) 01(t) 102(1) Ол N1 D1 D2 No. 1790220000 N2 Figure Q5 K2arrow_forward
- A spring package with two springs and an external force, 200N. The short spring has a loin of 35 mm. Constantly looking for spring for short spring so that total compression is 35 mm (d). Known values: Long spring: Short spring:C=3.98 N/mm Lo=65mmLo=87.4mmF=c·fTotal compression is same for both spring. 200 = (3.98(c1) × 35) + (c₂ × 35) 200 = 139.3 + 35c₂ 200 - 139.3 = 35c₂ 60.7 = 35c₂ c₂ = 60.7/35 Short spring (c₂) = 1.73 N/mm According to my study book, the correct answer is 4.82N/mm What is wrong with the calculating?arrow_forwardWhat is the reason for this composition?arrow_forwardHomework: ANOVA Table for followed design B AB Dr -1 -1 1 (15.18,12) 1 -1 -1 (45.48.51) -1 1 -1 (25,28,19) 1 1 (75.75,81)arrow_forward
- 20. [Ans. 9; 71.8 mm] A semi-elliptical laminated spring is made of 50 mm wide and 3 mm thick plates. The length between the supports is 650 mm and the width of the band is 60 mm. The spring has two full length leaves and five graduated leaves. If the spring carries a central load of 1600 N, find: 1. Maximum stress in full length and graduated leaves for an initial condition of no stress in the leaves. 2. The maximum stress if the initial stress is provided to cause equal stress when loaded. [Ans. 590 MPa ; 390 MPa ; 450 MPa ; 54 mm] 3. The deflection in parts (1) and (2).arrow_forwardQ6/ A helical square section spring is set inside another, the outer spring having a free length of 35 mm greater than the inner spring. The dimensions of each spring are as follows: Mean diameter (mm) Side of square section (mm) Active turns Outer Inner Spring Spring 120 70 8 7 20 15 Determine the (1) Maximum deflection of the two springs and (2) Equivalent spring rate of the two springs after sufficient load has been applied to deflect the outer spring 60 mm. Use G = 83 GN/m².arrow_forwardQ2/ The bumper springs of a railway carriage are to be made of rectangular section wire. The ratio of the longer side of the wire to its shorter side is 1.5, and the ratio of mean diameter of spring to the longer side of wire is nearly equal to 6. Three such springs are required to bring to rest a carriage weighing 25 kN moving with a velocity of 75 m/min with a maximum deflection of 200 mm. Determine the sides of the rectangular section of the wire and the mean diameter of coils when the shorter side is parallel to the axis of the spring. The allowable shear stress is not to exceed 300 MPa and G = 84 kN/mm². Q6/ A belicalarrow_forward
- 11. A load of 2 kN is dropped axially on a close coiled helical spring, from a height of 250 mm. The spring has 20 effective turns, and it is made of 25 mm diameter wire. The spring index is 8. Find the maximum shear stress induced in the spring and the amount of compression produced. The modulus of rigidity for the material of the spring wire is 84 kN/mm². [Ans. 287 MPa; 290 mm]arrow_forwardWhat is the reason for this composition?arrow_forwardHomework: ANOVA Table for followed design B AB Dr -1 -1 1 (15.18,12) 1 -1 -1 (45.48.51) -1 1 -1 (25,28,19) 1 1 (75.75,81)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Power Plant Explained | Working Principles; Author: RealPars;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HGVDu1z5YQ8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY