
Chemistry: Atoms First
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780073511184
Author: Julia Burdge, Jason Overby Professor
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.6, Problem 9PPC
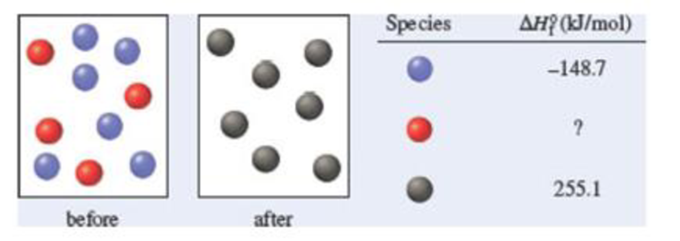
The diagrams represent a system before and after a
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
how many moles of H2O2 are required to react with 11g of N2H4 according to the following reaction? (atomic weights: N=14.01, H=1.008, O= 16.00) 7H2O2 + N2H4 -> 2HNO3 + 8H20
calculate the number of moles of H2 produced from 0.78 moles of Ga and 1.92 moles HCL? 2Ga+6HCL->2GaCl3+3H2
an adult human breathes 0.50L of air at 1 atm with each breath. If a 50L air tank at 200 atm is available, how man y breaths will the tank provide
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First
Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.1.1SRCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.1.2SRCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.1.3SRCh. 10.2 - Calculate the overall change in internal energy,...Ch. 10.2 - Calculate the change in total internal energy for...Ch. 10.2 - Calculate the magnitude of q for a system that...Ch. 10.2 - The diagram on the left shows a system before a...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.2.1SRCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.2.2SRCh. 10.3 - Determine the work done (in joules) when a sample...
Ch. 10.3 - Calculate the work done by or on the system during...Ch. 10.3 - (a) Against what external pressure must a gas...Ch. 10.3 - The diagram on the left shows a sample of gas...Ch. 10.3 - Given the thermochemical equation for...Ch. 10.3 - Calculate the solar energy required to produce...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 3PPBCh. 10.3 - The diagrams represent systems before and after...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.3.1SRCh. 10.3 - Prob. 10.3.2SRCh. 10.4 - Prob. 10.4WECh. 10.4 - Prob. 4PPACh. 10.4 - Prob. 4PPBCh. 10.4 - A metal pellet with a mass of 100.0 g. originally...Ch. 10.4 - What would the final temperature be if the pellet...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 5PPBCh. 10.4 - Prob. 5PPCCh. 10.4 - A Famous Amos bite-sized chocolate chip cookie...Ch. 10.4 - A serving of Grape-Nuts cereal (5.80 g) is burned...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 6PPBCh. 10.4 - Suppose an experiment to determine the energy...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 10.4.1SRCh. 10.4 - Prob. 10.4.2SRCh. 10.4 - Prob. 10.4.3SRCh. 10.4 - Prob. 10.4.4SRCh. 10.5 - Given the following thermochemical equations....Ch. 10.5 - Use the thermochemical equations provided in...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 10.5.1SRCh. 10.5 - Prob. 10.5.2SRCh. 10.6 - Prob. 10.8WECh. 10.6 - Using data from Appendix 2, calculate Hrn for...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 8PPBCh. 10.6 - The diagrams represent a system before and after a...Ch. 10.6 - Given the following information, calculate the...Ch. 10.6 - Use the following data to calculate Hf for...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 9PPBCh. 10.6 - The diagrams represent a system before and after a...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.6.1SRCh. 10.6 - Prob. 10.6.2SRCh. 10.6 - Prob. 10.6.3SRCh. 10.7 - Use bond enthalpies from Table 10.4 to estimate...Ch. 10.7 - Use bond enthalpies from fable 10.4 to estimate...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10PPBCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10PPCCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.7.1SRCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.7.2SRCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.7.3SRCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.7.4SRCh. 10.8 - Prob. 10.11WECh. 10.8 - Prob. 11PPACh. 10.8 - The lattice energy of MgO is 3890 kJ/mol, and the...Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 11PPCCh. 10.8 - Prob. 10.8.1SRCh. 10.8 - Prob. 10.8.2SRCh. 10 - Define these terms: system, surroundings, thermal...Ch. 10 - What is heat? How does heat differ from thermal...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.3QPCh. 10 - Define these terms: thermochemistry, exothermic...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.5QPCh. 10 - Describe two exothermic processes and two...Ch. 10 - Decomposition reactions are usually endothermic,...Ch. 10 - On what law is the first law of thermodynamics...Ch. 10 - Explain what is meant by a state function. Give...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.10QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.11QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.12QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.13QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.14QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.15QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.16QPCh. 10 - Define these terms: enthalpy and enthalpy of...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.18QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.19QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.20QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.21QPCh. 10 - A gas expands and does PV work on the surroundings...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.23QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.24QPCh. 10 - Consider the reaction at a certain temperature. If...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.26QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.27QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.28QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.1VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.2VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.3VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.4VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.5VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.6VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.7VCCh. 10 - Referring to the process depicted in Figure 10.10,...Ch. 10 - What is the difference between specific heat and...Ch. 10 - Define calorimetry and describe two commonly used...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.31QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.32QPCh. 10 - A sheet of gold weighing 10.0 g and at a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.34QPCh. 10 - A quantity of 2.00 102 mL of 0.862 M HC1 is mixed...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.36QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.37QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.38QPCh. 10 - A 25.95-g sample of methanol at 35.6C is added to...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.40QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.41QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.42QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.43QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.44QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.45QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.46QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.47QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.48QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.49QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.50QPCh. 10 - What is meant by the standard-state condition?Ch. 10 - How are the standard enthalpies of an element and...Ch. 10 - What is meant by the standard enthalpy of a...Ch. 10 - Write the equation for calculating the enthalpy of...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.55QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.56QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.57QPCh. 10 - Calculate the heats of combustion for the...Ch. 10 - Calculate the heats of combustion for the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.60QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.61QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.62QPCh. 10 - From the standard enthalpies of formation,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.64QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.65QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.66QPCh. 10 - Which is the more negative quantity at 25C: Hf for...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.68QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.69QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.70QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.71QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.72QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.73QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.74QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.75QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.76QPCh. 10 - For the reaction 2C2H6(g)+7O2(g)4CO2(g)+6H2O(g)...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.78QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.79QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.9VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.10VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.11VCCh. 10 - Prob. 10.12VCCh. 10 - Explain how the lattice energy of an ionic...Ch. 10 - Specify which compound in each of the following...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.82QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.83QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.84QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.85QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.86QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.87QPCh. 10 - Hydrazine (N2H4) decomposes according to the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.89QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.90QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.91QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.92QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.93QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.94QPCh. 10 - You are given the following data....Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.96QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.97QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.98QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.99QPCh. 10 - Compare the heat produced by the complete...Ch. 10 - The so-called hydrogen economy is based on...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.102QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.103QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.104QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.105QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.106QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.107QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.108QPCh. 10 - A certain gas initially at 0.050 L undergoes...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.110QPCh. 10 - The first step in the industrial recovery of zinc...Ch. 10 - Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the...Ch. 10 - Portable hot packs are available for skiers and...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.114QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.115QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.116QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.117QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.118QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.119QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.120QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.121QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.122QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.123QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.124QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.125QPCh. 10 - Vinyl chloride (C2H3Cl) differs from ethylene...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.127QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.128QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.129QPCh. 10 - Determine the standard enthalpy of formation of...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.131QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.132QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.133QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.134QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.135QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.136QPCh. 10 - Both glucose and fructose arc simple sugars with...Ch. 10 - About 6.0 1013 kg of CO2 is fixed (converted to...Ch. 10 - Experiments show that it takes 1656 kJ/mol to...Ch. 10 - From a thermochemical point of view, explain why a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.141QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.142QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.143QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.144QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.145QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.146QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.147QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.148QPCh. 10 - A drivers manual states that the stopping distance...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.150QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.151QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.152QPCh. 10 - When 1.034 g of naphthalene (C10H8), is burned in...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.154QPCh. 10 - A gas company in Massachusetts charges 27 cents...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.156QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.157QPCh. 10 - According to information obtained from...Ch. 10 - Using data from Appendix 2, calculate the standard...Ch. 10 - Using data from Appendix 2, calculate the standard...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.3KSPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.4KSP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO2 (g) = N2O4(g) AGº = -5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.53 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) at 279. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to '2' rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 00 rise ☐ x10 fall yes no ☐ atm G Ar 1arrow_forwardWhy do we analyse salt?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H H CH3OH, H+ H Select to Add Arrows H° 0:0 'H + Q HH ■ Select to Add Arrows CH3OH, H* H. H CH3OH, H+ HH ■ Select to Add Arrows i Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forward
- What are examples of analytical methods that can be used to analyse salt in tomato sauce?arrow_forwardA common alkene starting material is shown below. Predict the major product for each reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the relative stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts H Šali OH H OH Select to Edit Select to Draw 1. BH3-THF 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O =U= 2. H2O2, NaOH 2. NaBH4, NaOH + Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forwardWhat is the MOHR titration & AOAC method? What is it and how does it work? How can it be used to quantify salt in a sample?arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this reaction. Cl₂ hv ? Draw only the major product or products in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If there will be no products because there will be no significant reaction, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Note for advanced students: you can ignore any products of repeated addition. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 10 m 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility DII A F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 EO F11arrow_forwardGiven a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of η as a function of current density- at low fields is linear.- at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law.Calculate the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for both cases (the maximum relative difference will be 5%, compared to the behavior for higher fields).arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AGº = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm Х ด ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Calorimetry Concept, Examples and Thermochemistry | How to Pass Chemistry; Author: Melissa Maribel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nSh29lUGj00;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY