
Concept explainers
Ed the robot is standing at point A and will walk to point D along the route shown on the map in Figure 10.32. 0n the map. each segment between two dots represents 10 of Ed‘s paces.
A. Trace or redraw the map in Figure 10.329. At the points where Ed will turn, indicate his angle of turning. Use a protector to measure these angles, an mark themon the map
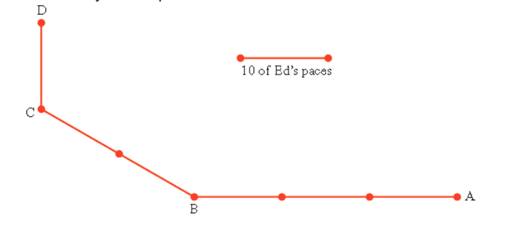
Figure 10.32 ED’s route
B. Ed is a robot, so you must tell Ed exactly how to walk to point D. At points where Ed must turn, tell him how many degrees to turn, and which way.
C. Determine Ed’s total amount of turning along his route by adding the angles you measured in part (a).
D. Now determine Ed's total amount of turning along his route without measuring the individual angles and adding them. Hint: Consider the directions that Ed faces as he travels along his route

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK MATHEMATICS FOR ELEMENTARY TEACHERS
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Precalculus
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
- 4x-3 2. Determine the interval over which the function is continuous. x+4arrow_forward1. Find the average rate of change for the following functions over the given intervals. a) f(x)=4x-2x²+3x between x=-1 and x=4 b) y lnx between x=1 and x=4arrow_forward1. Find all values x=a where the function is discontinuous, determine if the discontinuity is removable or non- removable. For each value of x, give the limit of the function as x approaches a. Be sure to note when the limit doesn't exist and explain how you know. a) f(x)= 2-x x²(x+5) b) f(x)= x²-9x x²+3x c) p(x)=-3x²+2x²+5x-8arrow_forward
- Task Description: Read the following case study and answer the questions that follow. Ella is a 9-year-old third-grade student in an inclusive classroom. She has been diagnosed with Emotional and Behavioural Disorder (EBD). She has been struggling academically and socially due to challenges related to self-regulation, impulsivity, and emotional outbursts. Ella's behaviour includes frequent tantrums, defiance toward authority figures, and difficulty forming positive relationships with peers. Despite her challenges, Ella shows an interest in art and creative activities and demonstrates strong verbal skills when calm. Describe 2 strategies that could be implemented that could help Ella regulate her emotions in class (4 marks) Explain 2 strategies that could improve Ella’s social skills (4 marks) Identify 2 accommodations that could be implemented to support Ella academic progress and provide a rationale for your recommendation.(6 marks) Provide a detailed explanation of 2 ways…arrow_forward1. Iodine-131 is tone of the most commonly used radioactive isotopes of iodine. It is used to treat hyper- thyroidism and some kinds of thyroid cancer. (a) Iodine-131 has a half-life of about 8 days. Find an expression for I(t), the mass of Iodine-131 remaining after t days, in terms of t and Io, the initial mass of Iodine-131 present at time t = 0. (b) If a dose of 0.9 mg of Iodine-131 is administered, how much is still present after 24 hours? (c) How much Iodine-131 is present after one week? Does your answer make sense?arrow_forwardQuestion 2: When John started his first job, his first end-of-year salary was $82,500. In the following years, he received salary raises as shown in the following table. Fill the Table: Fill the following table showing his end-of-year salary for each year. I have already provided the end-of-year salaries for the first three years. Calculate the end-of-year salaries for the remaining years using Excel. (If you Excel answer for the top 3 cells is not the same as the one in the following table, your formula / approach is incorrect) (2 points) Geometric Mean of Salary Raises: Calculate the geometric mean of the salary raises using the percentage figures provided in the second column named “% Raise”. (The geometric mean for this calculation should be nearly identical to the arithmetic mean. If your answer deviates significantly from the mean, it's likely incorrect. 2 points) Starting salary % Raise Raise Salary after raise 75000 10% 7500 82500 82500 4% 3300…arrow_forward
- d₁ ≥ ≥ dn ≥ 0 with di even. di≤k(k − 1) + + min{k, di} vi=k+1 T2.5: Let d1, d2,...,d be integers such that n - 1 Prove the equivalence of the Erdos-Gallai conditions: for each k = 1, 2, ………, n and the Edge-Count Criterion: Σier di + Σjeл(n − 1 − d;) ≥ |I||J| for all I, JC [n] with In J = 0.arrow_forwardT2.4: Let d₁arrow_forwardSolve the following boundary value problem using method of separation of variables: 1 ə ди r dr 70% (107) + 1 д²и = 0, 12802 -πarrow_forwardT2.3: Prove that there exists a connected graph with degrees d₁ ≥ d₂ >> dn if and only if d1, d2,..., dn is graphic, d ≥ 1 and di≥2n2. That is, some graph having degree sequence with these conditions is connected. Hint - Do not attempt to directly prove this using Erdos-Gallai conditions. Instead work with a realization and show that 2-switches can be used to make a connected graph with the same degree sequence. Facts that can be useful: a component (i.e., connected) with n₁ vertices and at least n₁ edges has a cycle. Note also that a 2-switch using edges from different components of a forest will not necessarily reduce the number of components. Make sure that you justify that your proof has a 2-switch that does decrease the number of components.arrow_forwardT2.2 Prove that a sequence s d₁, d₂,..., dn with n ≥ 3 of integers with 1≤d; ≤ n − 1 is the degree sequence of a connected unicyclic graph (i.e., with exactly one cycle) of order n if and only if at most n-3 terms of s are 1 and Σ di = 2n. (i) Prove it by induction along the lines of the inductive proof for trees. There will be a special case to handle when no d₂ = 1. (ii) Prove it by making use of the caterpillar construction. You may use the fact that adding an edge between 2 non-adjacent vertices of a tree creates a unicylic graph.arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you

 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
