
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for a carbonyl group.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be drawn by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity of atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 10.29P
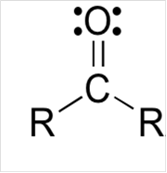
Lewis structure for a carbonyl group:
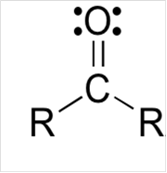
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for a carbonyl group, following are the steps:
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for a carboxyl group.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be prepared by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity o atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 10.29P
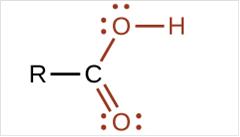
To draw Lewis structure for a carboxyl group:
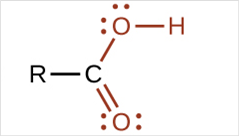
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for a carboxyl group, following are the steps:
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for a hydroxyl group.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be prepared by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity o atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 10.29P
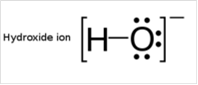
To draw Lewis structure for a hydroxyl group:
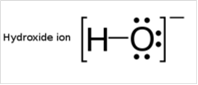
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for a hydroxyl group, following are the steps:
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for a primary
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be prepared by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity o atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 10.29P
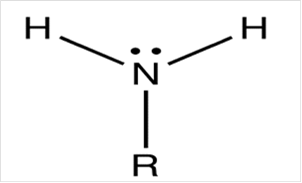
To draw Lewis structure for a primary amino group:
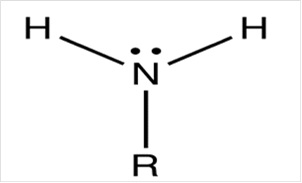
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for a carbonyl group, following are the steps:
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure formula with all valence electrons should be drawn for an ester group.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures can be prepared by following some point for any compound as mentioned below:
- Find out number of valence electrons present in the molecule
- The connectivity o atoms need to be understood like which atoms are linked with each other and connect them with covalnet bonds
- The arrangements of electrons in proper manner to achieve complete outer shell
Answer to Problem 10.29P
To draw Lewis structure for an ester group:
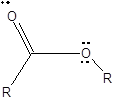
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom of prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
Single covalent bond occurs by sharing one pair of electrons and can be represented by single line in between atoms.
Double and triple bonds are formed when two and three pairs of electrons are shared in between atoms respectively and can be represented by two or three lines in between the atoms.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
To draw Lewis structure for an ester group, following are the steps:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





