
Engineering Electromagnetics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781260029963
Author: Hayt
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.17P
Determine the average power absorbed by each resistor in Figure 10.30.
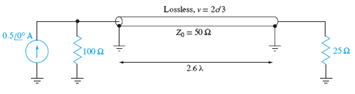
Figure 10.30 See Problem 10.17.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Do NOT WANT AI. need diagram fully labeled please
Calculate the current magnitude in the coils e1, e2 of theMagnetic circuit, if:ɸa = 3.00 x 10^-3 Wb, φb = 0.80 x 10^-3 Wb, ɸc = 2.20 x 10^-3 Wb
L ab = 0.10 m,A ab = 5.0 cm^2L afeb = L acdb = 0.40 mA afeb = A acdb = 20 cm^2
MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICSH (At/m) 240 350 530 1300 5000 9000B (T) 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 1.5 1.6
A toroid magnetic circuit is composed of three sections A, B and C, thesection C has an air gap, section A has an 850 round coil thatconsumes a current of 1.2 A. the physical and magnetic properties of each sectionare:
Section A: Length = 80 mm, Cross section = 120 mm^2, μr = 400
Section B: Length = 60 mm, Cross section = 40 mm^2, μr = 250
Section C: Length = 50 mm, Cross section = 200 mm^2, μr = 600
Gap: Length = 1 mm, Cross section = 40 mm^2, μr = 1
Calculate:The magnetic field density in each of the sections
Chapter 10 Solutions
Engineering Electromagnetics
Ch. 10 - The parameters of a certain transmission line...Ch. 10 - A sinusoidal wave on a transmission line is...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10 - A sinusoidal voltage V0, frequency , and phase...Ch. 10 - Two voltage waves of equal amplitude V0 and radian...Ch. 10 - A 50 load is attached to a 50-m section of the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.7PCh. 10 - An absolute measure of power is the dBm scale, in...Ch. 10 - A 100-m transmission line is used to propagate a...Ch. 10 - Two lossless transmission lines having different...
Ch. 10 - Two voltage waves of equal amplitude V0, which...Ch. 10 - In a circuit in which a sinusoidal voltage source...Ch. 10 - The skin effect mechanism in transmission lines is...Ch. 10 - A lossless transmission line having characteristic...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.29 See Problem 10.15. For the...Ch. 10 - A 100 lossless transmission line is connected to a...Ch. 10 - Determine the average power absorbed by each...Ch. 10 - The line shown in Figure 10.31 is lossless. Find s...Ch. 10 - A lossless transmission line is 50 cm in length...Ch. 10 - (a) Determine s on the transmission line of Figure...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.21PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.22PCh. 10 - The normalized load on a lossless transmission...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.24PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.25PCh. 10 - A 75 lossless line is of length 1.2 . It is...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.27PCh. 10 - The wavelength on a certain lossless line is 10...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.29PCh. 10 - A two-wire line constructed of lossless wire of...Ch. 10 - In order to compare the relative sharpness of the...Ch. 10 - In Figure 10.17, let ZL=250 and Z0=50. Find the...Ch. 10 - In Figure 10.17, let ZL=100+j150 and Z0=100. Find...Ch. 10 - The lossless line shown in Figure 10.35 is...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.35PCh. 10 - The two-wire lines shown in Figure 10.36 are all...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.37PCh. 10 - Repeat Problem 10.37, with, Z0=50 and RL=Rg=25....Ch. 10 - In the transmission line of Figure 10.20, Z0=50,...Ch. 10 - In the charged line of Figure 10.25, the...Ch. 10 - In the transmission line of Figure 10.37, the...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.38 See Problem 10.42. A simple frozen...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.39 See Problem 10.43. In Figure 10.39,...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3) Compute the input impedance of Fig. 3. (10 points) Rin R1 R₂ Figure 3 T Vccarrow_forwardShow the workarrow_forward2) A bypass capacitor CE in parallel with RE is added to the above circuit. a) Draw the equivalent small-signal circuit. (10 points) b) Find the input resistance Rib looking into the base. (10 points) c) Find the output resistance looking into the collector, while the source is shorted, i.e. Vs 0 V and Rs = 0 2. (10 points) Vo Vs d) Find the voltage gain A₁ = ✓ using the above equivalent small signal circuit. (10 points)arrow_forward
- Handwritten solution required do not use chatgptarrow_forwardA conductor 300 mm long carries a current of 13A and is at right-angles to a magnetic fieldbetween two circular pole faces, each of diameter 80 mm. If the total flux between the polefaces is 0.75 mWb, calculate the force exerted on the conductor. [ANS = 0.582 N]arrow_forwarda) find Rthb) Find Vth in the circuit c)Draw the Thevenin Equivalent of the circuit to tge left of the a and b terminalsarrow_forward
- An electric car runs on batteries, but needs to make constant stops to re-charge. If a trailer is attached to the car that carries a generator, and the generator is turned by a belt attached to the wheels of the trailer, will the car be able to drive forever without stopping?arrow_forwardA singl core cable of voltage 30 kv. The diameter of Conductor is 3 cm. The diameter of cable is 25 cm. This cable has Two layer of insulator having arelative permittivity 5-3 respectively of The ratio of maximum electric stress of maximum electric stress 8 First layer to the of second layer is 10 Find & 1- The thickness of each layers. 3- The voltage of each layers. §. Layers The saving in radius of cable if another ungrading cable has the Same maximum electric stress, Total village, Conductor diameter of grading cable.arrow_forward66 KV sing care Cable has a drameter of conductor of 3 cm. The radius of cable is 10 cm. This Cable house Two relative permmitivity of insulation 6 and 4 respectively. If The ratio of maximum electric stress of first layer to the maximum eledric streep & second layer is s 1- find the village & each layers. 2- Min- electric stress J Cable 3- Compare the voltage of ungrading Cable has the same distance and relectric stresses.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Why Use Bode Plots? | Understanding Bode Plots, Part 1; Author: MATLAB;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F6-EaZobHNk;License: Standard Youtube License