
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781118539293
Author: J. David Irwin, R. Mark Nelms
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 42P
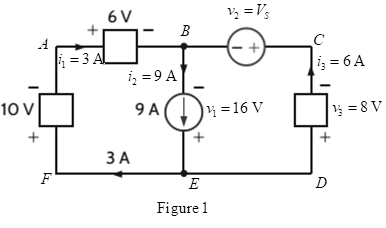
Is the source
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1. Is1 = 2ls2 = 4 × 10-16 A, B₁ = ẞ2 = 100, and R₁ = 5 kQ. Find the VB such that lx = 1 mA.
(30 points)
R1
ww
Q2
+
VB
Figure 1
2-2) Lathi & Ding prob. 2.6-1
2.6-1 Find the correlation coefficient p between of signal x(t) and each of the four pulses g1(1), 82(1),
83(1), and g4(f) shown in Fig. P2.6-1. To provide maximum margin against the noise along the
transmission path, which pair of pulses would you select for a binary communication?
Figure P.2.6-1
x(f)
(a)
8(1)
(b)
82(1)
(c)
1
1
sin 2πt
sin 4πt
-sin 2
0
0.707
83(1)
0
1
(d)
0
M
P
0.707
84(1)
(e)
0
0.5
-0.707
2. Determine the operation point and the small-signal model of Q₁ for each of the circuits
shown in Fig. 2. Assume Is = 8 × 10-16 A, B = 100 and VA = ∞.
a) 20 points
b) 20 points
0.8 V
RC
50 Ω
+
Vcc = 2.5 V
4A"
Figure 2-a
Rc1kQ
+
Vcc = 2.5 V
Figure 2-b
Chapter 1 Solutions
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
Ch. 1 - If the current in an electric conductor is 2.4 A,...Ch. 1 - Determine the time interval required for a 12�A...Ch. 1 - A lightning bolt carrying 30,000 A lasts for 50...Ch. 1 - If a 12-V battery delivers 100 J in 5 s, find (a)...Ch. 1 - The current in a conductor is 1.5 A. How many...Ch. 1 - If 60 C of charge pass through an electric...Ch. 1 - Determine the number of coulombs of charge...Ch. 1 - Five coulombs of charge pass through the element...Ch. 1 - The current that enters an element is shown in...Ch. 1 - The charge entering the positive terminal of an...
Ch. 1 - The charge entering the positive terminal of an...Ch. 1 - Prob. 12PCh. 1 - The power absorbed by the BOX in Fig. Pl. 13 is...Ch. 1 - The power absorbed by the BOX in Fig. Pl. 14 is...Ch. 1 - The energy absorbed by the BOX in Fig. P1.15 is...Ch. 1 - The charge that enters the BOX in Fig. P1.16 is...Ch. 1 - The energy absorbed by the BOX in Fig. Pl. 17 is...Ch. 1 - The charge entering the upper terminal of the BOX...Ch. 1 - The energy absorbed by the BOX in Fig. Pl. 19 is...Ch. 1 - Determine the amount of power absorbed or supplied...Ch. 1 - Calculate the power absorbed by element A in Fig....Ch. 1 - Calculate the power supplied by element A in Fig....Ch. 1 - Element A in the diagram in Fig. PI .23 absorbs 30...Ch. 1 - Element B in the diagram in Fig. P1.24 supplies 60...Ch. 1 - Element B in the diagram in Fig. PI .25 supplies...Ch. 1 - Element B in the diagram in Fig. Pl.26 supplies 72...Ch. 1 - (a) In Fig. Pl.27 (a), P1=36W. Is element 2...Ch. 1 - Two elements are connected in series, as shown in...Ch. 1 - Element 2 in Fig. Pl.29 absorbed 32W. Find the...Ch. 1 - Choose Is such that the power absorbed by element...Ch. 1 - Find the power that is absorbed or supplied by the...Ch. 1 - Find the power that is absorbed or supplied by the...Ch. 1 - Compute the power that is absorbed or supplied by...Ch. 1 - Find the power that is absorbed or supplied by...Ch. 1 - Find Ix in the network in Fig. P1.35.Ch. 1 - Prob. 36PCh. 1 - Find the power absorbed or supplied by element 1...Ch. 1 - Find the power absorbed or supplied by element 3...Ch. 1 - Find the power absorbed or supplied by element 1...Ch. 1 - Find Vx in the network in Fig. P1.40 using...Ch. 1 - Find Ix in the circuit in Fig. P1.41 using...Ch. 1 - Is the source Vs in the network in Fig. P1.42...Ch. 1 - Find I0 in the network in Fig. P1.43 using...Ch. 1 - Calculate the power absorbed by each element in...Ch. 1 - Calculate the power absorbed by each element in...Ch. 1 - In the circuit in Fig. P1.46, element 1 absorbs 40...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please explain in detail how to solve this question. Include steps with calculations and theory. thank youarrow_forwardFinding crystallographic direction Z pt. 2 head pt. 1: ៩ Example 2: pt. 1 x₁ = a, y₁ = b/2, z₁ = 0 pt. 2 x2=-a, y₂ = b, Z₂ = c -a-a b-b/2 c-0 a b c tail => -2, 1/2, 1 Multiplying by 2 to eliminate the fraction -4,1,2 => [412] where the overbar represents a negative index families of directionsarrow_forwardCrystallographic planes Crystallographic planes are denoted by Miller indices. 5b Algorithm for Miller indices 1. Read off intercepts of plane with axes in terms of a, b, c 2. Take reciprocals of intercepts 3. Reduce to smallest integer values 4. Enclose in parentheses, no commas. 353 1/3 1/5 1/3 535 (535) In the cubic system, a plane and a direction with the same indices are orthogonal. E.g. [100] direction is perpendicular to (100) plane. Correspondingly, [123] direction is perpendicular to (123) plane. [2,3,3] Plane intercepts axes at 3a, 2b, 2c 2 11 1 Reciprocal numbers are: 3'2'2 b. Indices of the plane (Miller): (2,3,3) 2 a Indices of the direction: [2,3,3] X (200) (100) (110) (111) (100) Indices of crystallographic plane can be found from cross product of indices of any two non-parallel directions in this plane.arrow_forward
- Crystallographic positions Crystallographic position is denoted by three numbers, which are coefficients of the position vector, e.g. ½½½ for the red atom. Here the 'new' atom is at a/2 + b/2 + c/2 Silicon crystal has so-called "diamond type lattice". Each Si atom has 4 nearest neighbors. Diamond lattice starts with a FCC lattice and then adds four additional INTERNAL atoms at locations r = a/4+b/4+c/4 away from each of the atoms. In other words, diamond lattice is formed by two FCC lattices sifted by the vector r.arrow_forwardfind the answers for this prelabarrow_forwardQ2: (30 Marks) Design a DC/DC converter that produce output waveforms that shown in figures below from a fixed DC source of 20 volts. Vo (Volt) 14.1 IL (Amp) 13.9 2.25 1.75 † (msec) Output voltage 0.18 0.2 t (msec) L 0.214 0.22 Output currentarrow_forward
- 6. Build the circuit shown in Figure 2 below in PSpice. Note that the power supply V1 is a VSIN power supply in the SOURCE library. Vcc is a VDC supply found in the SOURCE library. Model this circuit using the Time Domain (Transient) Analysis Type with a Run To Time of 2 ms. A. Paste your output graph showing the voltage at the base terminal, collector terminal and at the load. B. What is the voltage gain of the circuit? (Compare the voltage amplitude at the base terminal input (across Rb2) to that at the collector terminal. C. What happens to the output voltage at the collector terminal if the value of Rb1 is reduced by a factor of 10 (to 14.7 kn)? Simulate this situation and explain the result. D. What happens to the output voltage at the collector terminal if the value of Rb1 is increased by a factor of 3 (to 441 k)? Simulate this situation and explain the result. Rb1 RC 147k 1k C2 C1 Q1 Vcc 1u VOFF = 0 Q2N3904 10Vdc VAMPL = 0.1V1 1u FREQ = 2k R_load Rb2 Re AC = 0 250 40k 20 Figure…arrow_forwardThe input reactance of 1/2 dipole with radius of 1/30 is given as shown in figure below, Assuming the wire of dipole is conductor 5.6*107 S/m, determine at f=1 GHz the a-Loss resistance, b- Radiation efficiency c-Reflection efficiency when the antenna is connected to T.L shown in the figure. Rr Ro= 50 2 1/4 RL -j100 [In(l/a) - 1.5] tan(ẞl)arrow_forward6) For each independent source in this circuit calculate the amount of power being supplied or the amount of power being absorbed + 6V www +3V- www 20 ми ми 352 0.5A + 3Varrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Types of Energy for Kids - Renewable and Non-Renewable Energies; Author: Smile and Learn - English;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w16-Uems2Qo;License: Standard Youtube License