
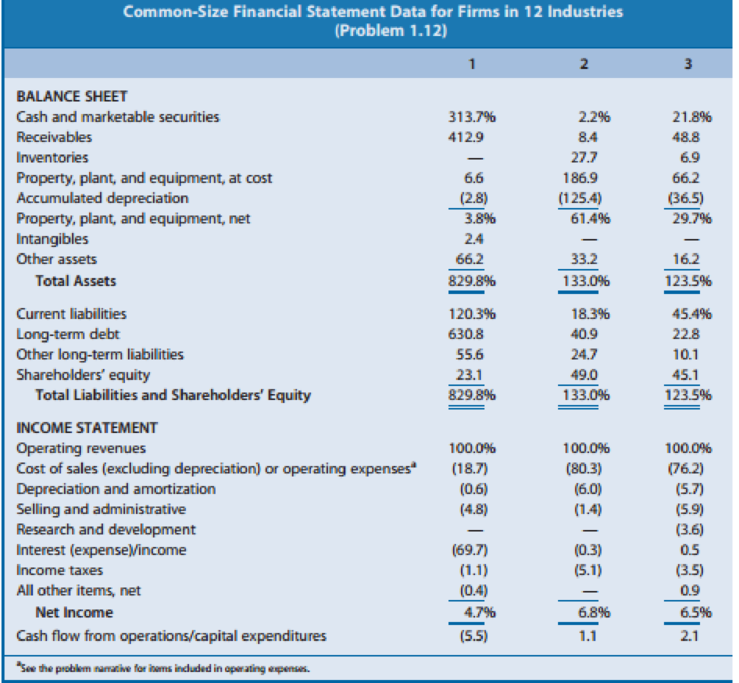
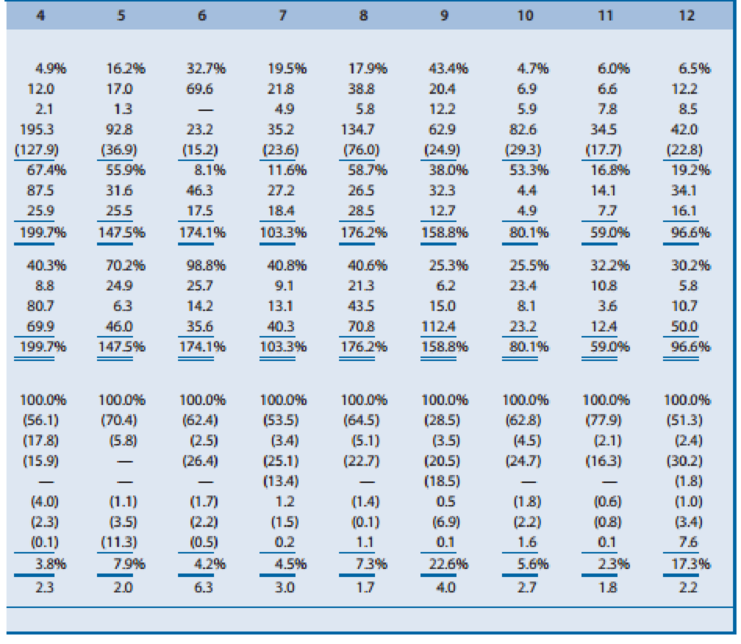
Effect of Industry Characteristics on Financial Statement Relations: A Global Perspective. Effective financial statement analysis requires an understanding of a firm’s economic characteristics. The relations between various financial statement items provide evidence of many of these economic characteristics. Exhibit 1.24 (pages 66–67) presents common-size condensed balance sheets and income statements for 12 firms in different industries. These common-size balance sheets and income statements express various items as a percentage of operating revenues. (That is, the statement divides all amounts by operating revenues for the year.) A dash for a particular financial statement item does not necessarily mean the amount is zero. It merely indicates that the amount is not sufficiently large for the firm to disclose it. A list of the 12 companies, the country of their headquarters, and a brief description of their activities follow.
- A. Accor (France): World’s largest hotel group, operating hotels under the names of Sofitel, Novotel, Motel 6, and others. Accor has grown in recent years by acquiring established hotel chains.
- B. Carrefour (France): Operates grocery supermarkets and hypermarkets in Europe, Latin America, and Asia.
- C. Deutsche Telekom (Germany): Europe’s largest provider of wired and wireless telecommunication services. The telecommunications industry has experienced increased deregulation in recent years.
- D. E.ON AG (Germany): One of the major public utility companies in Europe and the world’s largest privately owned energy service provider.
- E. Fortis (Netherlands): Offers insurance and banking services. Operating revenues include insurance premiums received, investment income, and interest revenue on loans. Operating expenses include amounts actually paid or amounts it expects to pay in the future on insurance coverage outstanding during the year.
- F. Interpublic Group (U.S.): Creates advertising copy for clients. Interpublic purchases advertising time and space from various media and sells it to clients. Operating revenues represent the commissions or fees earned for creating advertising copy and selling media time and space. Operating expenses include employee compensation.
- G. Marks & Spencer (U.K.): Operates department stores in England and other retail stores in Europe and the United States. Offers its own credit card for customers’ purchases.
- H. Nestlé (Switzerland): World’s largest food processor, offering prepared foods, coffees, milk-based products, and mineral waters.
- I. Roche Holding (Switzerland): Creates, manufactures, and distributes a wide variety of prescription drugs.
- J. Sumitomo Metal (Japan): Manufacturer and seller of steel sheets and plates and other construction materials.
- K. Sun Microsystems (U.S.): Designs, manufactures, and sells workstations and servers used to maintain integrated computer networks. Sun outsources the manufacture of many of its computer components.
- L. Toyota Motor (Japan): Manufactures automobiles and offers financing services to its customers.
REQUIRED
Use the ratios to match the companies in Exhibit 1.24 with the firms listed above.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 1 Solutions
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation
- You plan to retire in 4 years with $698,670. You plan to withdraw $X per year for 17 years. The expected return is 17.95 percent per year and the first regular withdrawal is expected in 5 years. What is X? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $arrow_forwardYou just borrowed $111,682. You plan to repay this loan by making X regular annual payments of $15,500 and a special payment of $44,900 in 10 years. The interest rate on the loan is 13.33 percent per year and your first regular payment will be made in 1 year. What is X? Input instructions: Round your answer to at least 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardYou just borrowed $174,984. You plan to repay this loan by making regular annual payments of X for 12 years and a special payment of $11,400 in 12 years. The interest rate on the loan is 9.37 percent per year and your first regular payment will be made today. What is X? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $arrow_forward
- You plan to retire in 7 years with $X. You plan to withdraw $54,100 per year for 15 years. The expected return is 13.19 percent per year and the first regular withdrawal is expected in 7 years. What is X? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. 59 $arrow_forwardYou plan to retire in 3 years with $911,880. You plan to withdraw $X per year for 18 years. The expected return is 18.56 percent per year and the first regular withdrawal is expected in 3 years. What is X? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. 99 $arrow_forwardYou have an investment worth $56,618 that is expected to make regular monthly payments of $1,579 for 25 months and a special payment of $X in 8 months. The expected return for the investment is 0.76 percent per month and the first regular payment will be made today What is X? Note: X is a positive number. Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $arrow_forward
- You plan to retire in 8 years with $X. You plan to withdraw $114,200 per year for 21 years. The expected return is 17.92 percent per year and the first regular withdrawal is expected in 9 years. What is X? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $ EAarrow_forwardYou have an investment worth $38,658 that is expected to make regular monthly payments of $1,130 for 16 months and a special payment of $X in 11 months. The expected return for the investment is 1.46 percent per month and the first regular payment will be made in 1 month. What is X? Note: X is a positive number. Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $arrow_forwardYou just borrowed $373,641. You plan to repay this loan by making regular annual payments of X for 18 years and a special payment of $56,400 in 18 years. The interest rate on the loan is 12.90 percent per year and your first regular payment will be made in 1 year. What is X? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. EA $arrow_forward
- How much do you need in your account today if you expect to make quarterly withdrawals of $6,300 for 7 years and also make a special withdrawal of $25,700 in 7 years. The expected return for the account is 4.56 percent per quarter and the first regular withdrawal will be made today. Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $ 69arrow_forwardYou just bought a new car for $X. To pay for it, you took out a loan that requires regular monthly payments of $2,200 for 10 months and a special payment of $24,100 in 6 months. The interest rate on the loan is 1.07 percent per month and the first regular payment will be made today. What is X? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. 59 $arrow_forward3 years ago, you invested $9,200. In 3 years, you expect to have $14,167. If you expect to earn the same annual return after 3 years from today as the annual return implied from the past and expected values given in the problem, then in how many years from today do you expect to have $28,798? Input instructions: Round your answer to at least 2 decimal places. 1.62 yearsarrow_forward
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College




