
Concept explainers
Figure P1.27 shows an ammeter (AM) and voltmeter (VM) connected to measure the current and voltage, respectively, for circuit element A.When current actually enters the + terminal of the ammeter, the reading is positive, and when current leaves the + terminal, the reading is negative. If the actual voltage polarity is positive at the + terminal of the VM, the reading is positive; otherwise, it is negative. (Actually, for the connection shown, the ammeter reads the sum of the current in element A and the very small current taken by the voltmeter. For purposes of this problem, assume that the current taken by the voltmeter is negligible.) Find the power for element A and state whether energy is being delivered to element A or taken from it if
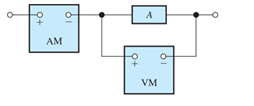
Figure P1.27
- the ammeter reading is +2 A and the voltmeter reading is +30 V;
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications (7th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
- I need help fixing this MATLAB code: as I try to get it working there were some problems:arrow_forwardI need help in construct a matlab code to find the voltage of VR1 to VR4, the currents, and the watts based on that circuit.arrow_forwardQ2: Using D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter. The counter counts in the sequence 1,3,5,7, 1,7,5,3,1,3,5,7,.... when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter count 0.arrow_forward
- From the collector characteristic curves and the dc load line given below, determine the following: (a) Maximum collector current for linear operation (b) Base current at the maximum collector current (c) VCE at maximum collector current. lc (mA) 600 ΜΑ 60- 500 με 50- 400 με 40- 300 μ Α 30- Q-point 200 ΜΑ 20- 10- 100 μ Α 0 VCE (V) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [6 Paarrow_forwardProcedure:- 1- Connect the cct. shown in fig.(2). a ADDS DS Fig.(2) 2-For resistive load, measure le output voltage by using oscilloscope ;then sketch this wave. 3- Measure the average values ::f VL and IL: 4- Repeat steps 2 & 3 but for RL load. Report:- 1- Calculate the D.C. output vcl age theoretically and compare it with the test value. 2- Calculate the harmonic cont :nts of the load voltage, and explain how filter components may be selected. 3- Compare between the three-phase half & full-wave uncontrolled bridge rectifier. 4- Draw the waveform for the c:t. shown in fig.(2) but after replaced Di and D3 by thyristors with a 30° and a2 = 90° 5- Draw the waveform for the cct. shown in fig.(2) but after replace the 6-diodes by 6- thyristor. 6- Discuss your results. Please solve No. 4 and 5arrow_forwardPlease I want solution by handwrittenarrow_forward
- 8 00 ! Required information Consider the circuit given below. 0/2 points awarded 3 ΚΩ www t=0 6kM Scored R 1.5i Vc 1 μF 10 V If R = 5.00 kQ, determine vao+). The value of va(0) is 1.4545 V.arrow_forwardI want to know what does it look in a breadboard circuit, because I want to created it but I not sure it is build properly, can you give me an illustuation base on this image, it do need to real, something like virutal examplearrow_forwardCharge neutrality Since doped semiconductor remains electroneutral, the concentration of negative charges equals the concentration of positive charges. n+ Na,ionized p+Nd,ionized np = n; 2 2 N-Na N N d d р + 2 2 n = Nd-Na 2 + Na - 2 Na +n₁ 2 71/2 1/2 2 2 +n Concentration of electrons and holes 1. Calculate concentrations of electrons and holes at room temperature in Si and Ge with donor concentration of 1.5x10¹7 cm³ and acceptor concentration of 8x1016 cm-3. 2. Will these concentrations change much with the temperature increase to 100°C?arrow_forward
- Answer the questions on the end of the image pleasearrow_forwardAnswer these two questions on the end of the image, please 1.Calculate intrinsic carrier concentration for Si, Ge and GaAs at temperatures -20°C, 20°C (room temperature) and 120°C 2.Compare the obtained data with n and p shown on previous slide 25arrow_forwardCan you help me achieve the requirements using Arduino? I have encountered some issues with these requirements. Q.2: Suppose you have two push buttons connected to ports (0 & 1) and four LED's connected to ports (6-9). Write a program to flash ON the odd LED's if we press the switch 0 for 4s, flash ON the even LED's if we press the switch 1 for 5s and flash ON all the LED's otherwise for 6s.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





