
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134484143
Author: Allan R. Hambley
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.21P
Compute the power for each element shown in Figure P1.21. For each element, state whether energy is being absorbed by the element or supplied by it.
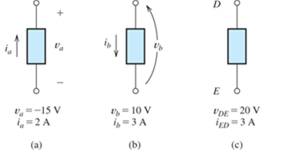
Figure P1.21
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve on paper not using chatgpt
Assume that a building manager instructed you to install a water heater. The specs on the water heater nameplate reveals the following 240V, 2PH, 60HZ, 5.7KW. The manager insisted for the installation to be done with 10 AWG copper THWN-2 conductor, the length of run is 1200 FT away from the service panel. Calculate the voltage after the installation.
Please confirm that my solution is correct, especially the block diagram. Please DRAW (not type) what the block diagram would look like if it's incorrect.
thank you
Chapter 1 Solutions
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications (7th Edition)
Ch. 1 - Broadly speaking, what are the two main objectives...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.2PCh. 1 - List eight subdivisions of electrical engineering.Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.4PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.5PCh. 1 - In the fluid-flow analogy for electrical circuits,...Ch. 1 - The charge of an electron is 1.601019C . A current...Ch. 1 - The ends of a length of wire are labeled a and b....Ch. 1 - The circuit element shown in Figure P1.9 has v=12V...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.10P
Ch. 1 - The net charge through a cross section of a...Ch. 1 - The current through a particular circuit element...Ch. 1 - The current through a given circuit element is...Ch. 1 - The net charge through a cross section of a...Ch. 1 - A copper wire has a diameter of 2.05 mm and...Ch. 1 - A certain lead acid storage battery has a mass of...Ch. 1 - A circuit element having terminals a and b has...Ch. 1 - An electron moves through a voltage of 9 V from...Ch. 1 - A typical “deep-cycle” battery (used for electric...Ch. 1 - Define the term passive reference configuration....Ch. 1 - Compute the power for each element shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - The terminals of an electrical device are labeled...Ch. 1 - The terminals of a certain battery are labeled a...Ch. 1 - The element shown in Figure P1.24 I has v(t)=10V...Ch. 1 - The current and voltage of an electrical device...Ch. 1 - Suppose that the cost of electrical energy is...Ch. 1 - Figure P1.27 shows an ammeter (AM) and voltmeter...Ch. 1 - Repeat Problem P1.27 with the meters connected as...Ch. 1 - A certain type of D-cell battery that costs $0.50...Ch. 1 - The electronics aboard a certain sailboat consume...Ch. 1 - What s a node in an electrical circuit? Identify...Ch. 1 - State Kirchhoff’s current law.Ch. 1 - Two electrical elements are connected in series....Ch. 1 - Suppose that in the fluid-flow analogy for an...Ch. 1 - Identify elements that are in series in the...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.36. Which...Ch. 1 - Use KCL to find the values of ia, ic , and id for...Ch. 1 - Find the values of the other currents in Figure...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.39PCh. 1 - State Kirchhoff’s voltage law.Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.36. Which...Ch. 1 - Use KVL to solve for the voltages va , vb, and vc...Ch. 1 - Solve for the other voltages shown in Figure P1.43...Ch. 1 - Use KVL and KCL to solve for the labeled currents...Ch. 1 - Identify elements that are in parallel in Figure...Ch. 1 - Points a, b, c, and d appear in a certain circuit....Ch. 1 - In your own words, define an ideal conductor; an...Ch. 1 - Name four types of dependent sources and give the...Ch. 1 - State Ohm’s law, including references.Ch. 1 - Draw a circuit that contains a 5 resistance, a...Ch. 1 - Repeat Problem P1.50, placing all three elements...Ch. 1 - The resistance of a certain copper wire is 0.5. ....Ch. 1 - Draw a circuit that contains a 5 resistor, a 10-V...Ch. 1 - Draw a circuit that contains a 5 resistor, a 10-V...Ch. 1 - A power of 100 W is delivered to a certain...Ch. 1 - The voltage across a 10 resistor is given by...Ch. 1 - The voltage across a 10 resistor is given by...Ch. 1 - A certain wire has a resistance of 0.5 . Find the...Ch. 1 - Plot i versus v to scale for each of the parts of...Ch. 1 - Which of the following are self-contradictory...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.61. Find...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.62. Find...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.63. Find...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.64. Use...Ch. 1 - Determine the value of Ix in the circuit shown in...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.66. Figure...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.67PCh. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.68. Figure...Ch. 1 - Solve for the currents shown in Figure P1.69....Ch. 1 - The circuit shown in Figure P1.70 contains a...Ch. 1 - Determine the value of vx and iy in the circuit...Ch. 1 - A 10-V independent voltage source is in series...Ch. 1 - A 10-V independent voltage source is in parallel...Ch. 1 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P1.74. Figure...Ch. 1 - The circuit shown in Figure P1.75 contains a...Ch. 1 - For the circuit shown in Figure P1.76, solve for...Ch. 1 - For the circuit shown in Figure P1.77, solve for...Ch. 1 - Match each entry in Table T1.1(a) with the best...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.2PTCh. 1 - The circuit of Figure T1.3 has I1=3A , I2=1A ,...Ch. 1 - The circuit shown in Figure T1.4 has Vs=12V ,...Ch. 1 - We are given Vs=15V , R=10 , and =0.3S for the...Ch. 1 - We are given i4=2A for the circuit of Figure T1.6....
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- use this code on the bottom to answer the question in the photo clc; clearvars; % Read the file [y, Fs] = audioread('106miles.wav'); N = length(y); Nfft = 2^nextpow2(N); dt = 1/Fs; t = (0:dt:(N-1)*dt)'; % Ensure t is a column vector y = y - mean(y); % Remove DC component (if not already zero-mean) % Carrier signal (25 kHz) fc = 25000; % Carrier frequency in Hz carrier = cos(2 * pi * fc * t); % DSB-SC Modulation modulated_signal = y .* carrier; % Plot Time Domain Signal figure; subplot(2,1,1); plot(t, y); title('Original Signal (Time Domain)'); xlabel('Time (s)'); ylabel('Amplitude'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(t, modulated_signal); title('DSB-SC Modulated Signal (Time Domain)'); xlabel('Time (s)'); ylabel('Amplitude'); % Frequency Domain (FFT) Y = fft(y, Nfft) / Nfft; Modulated_Y = fft(modulated_signal, Nfft) / Nfft; f = Fs * (0:(Nfft/2)) / Nfft; % Frequency vector % Plot Frequency Domain Signal figure; subplot(2,1,1); plot(f, abs(Y(1:Nfft/2+1))); title('Original Signal…arrow_forward5-9 A 230 V shunt motor has a nominal arma- ture current of 60 A. If the armature resist- ance is 0.152, calculate the following: a. The counter-emf [V] b. The power supplied to the armature [W] c. The mechanical power developed by the motor, [kW] and [hp] 5-10 a. In Problem 5-9 calculate the initial start- ing current if the motor is directly con- nected across the 230 V line. b. Calculate the value of the starting resistor needed to limit the initial current to 115 A.arrow_forwardhow to solve this?arrow_forward
- For the circuit in Fig. P8.52, choose the load impedance ZLso that the power dissipated in it is a maximum. How much powerwill that be?arrow_forwardhow to solve the attached question? please explain or give reference where required in the solution.arrow_forwardHANDWRITTEN SOLUTION REQUIRED NOT USING CHATGPTarrow_forward
- Please only do part E and F. Please show your work and be as detailed as possible. Please explain the relationship between K the gain and stability of the system. Also, show how to plot the poles and why they are on either the real or imaginary axis. What is it about the example that indicated that? thank youarrow_forwardPlease draw the block diagram for this problem and explain how. thank youarrow_forwardPlease show your work and be as detailed as possible. I would like to really understand the connection between the type of loop, the dampness, and the gain, K. Thank youarrow_forward
- In the zone refining of silicon, an RF-heater is used to remove trace amounts of impuritiesfrom the silicon. If the silicon has the impurity of 10^14 Co (k = 8*10^-6) what is the purityof the crystal after one pass of the zone refiner? After two passes? Plot concentration as afunction of crystal length from 0 to 8ft (total length of the crystal). The width of the moltenzone is 5”.arrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forwardSolve on paper not using AI or chatgptarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Conductivity and Semiconductors; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5zz6LlDVRl0;License: Standard Youtube License