
Concept explainers
By selecting three different types of measurement systems and identify which attributes of the system comprise the measurement stages.
Answer to Problem 1.1P
Following of measurement systems has been selected and attributed.
- Microphone/Amplifier/Speaker System.
- Room Heating Thermostat.
- Handheld Micrometer.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Measurement systems that we have studied.
The three distinct types of measurement systems are the speaker system, room heating thermostat, and handheld micrometer.
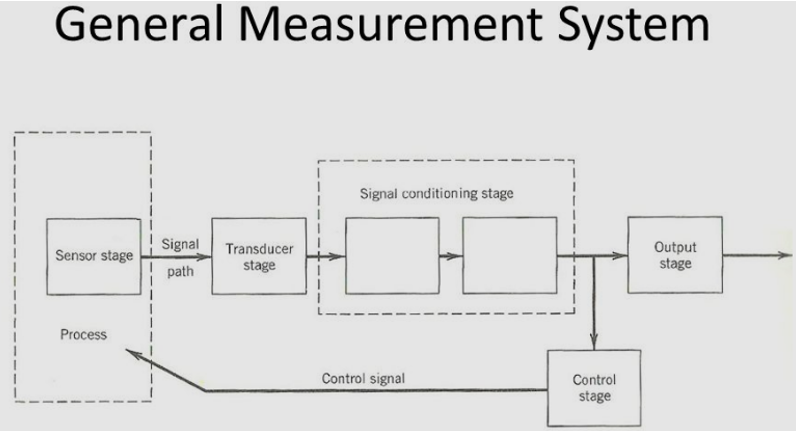
(i) Microphone/Amplifier/Speaker System:
Speaker systems are the principal components of the audio system. The principal components of a speaker system are the transducer, amplifier, and an output stage which consist about an output transducer. At the transducer stage, the input transducer collects sound waves and turns it to electrical energy.
At signal conditioning staging, the speaker system amplifies the electrical energy and at the output staging, the electrical energy is repeatedly converted into sound signals which are of high amplitude. That is when the intent of the speaker system is served. There are just transducer stage, signal conditioning stage and output staging.
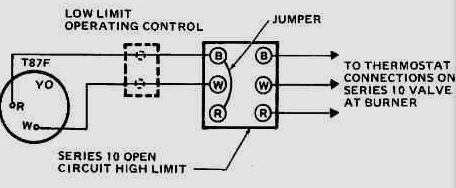
(ii) Room Heating Thermostat:
Thermostats are primarily used to measure the temperatures. A thermostat senses the temperature of the room and thereby switches the cooling apparatus which is implemented in the place.
Select room thermostats equipped in houses estimate the temperature of the air in the room, if it is cool it will turn on the central heating, and when it gets too hot it tells the central heating to set off. Room thermostats need an unrestricted flow of air to sense the heat, so they must not be blocked by screens or fittings or put near heat sources.
In the room heating thermostat at sensor stage, it sense the temperature of the room and imparts a sign to the transducer, the transducer is combined to the signal conditioning stage and sends an output signal that might be the actuating the buzzer or switching on the room heating device consequently.
A feedback signal is received before the output stage and transferred back to the sensor stage continuously to control the heat of the room if it is getting too hot it will turn off the heating equipment automatically.
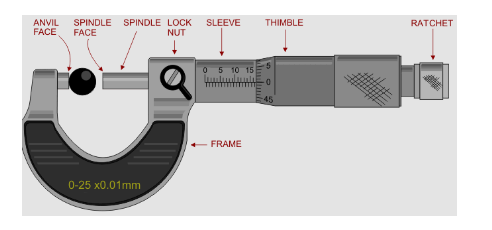
(iii) Handheld Micrometer:
The handheld micrometers are recognized for their precision but having a short measuring range these are superseded with laser micrometers.
Short lengths and depths of the channels can be found by using the handheld micrometer. These measurements are subjected to alternate, when the operator and operating conditions differs.
The micrometer should be taken with the hand and the object is to be embedded in the grips of the micrometer.
A torque must be employed against the machine taken in the jaws of the micrometer. The micrometer scale is displaced to some extent calibrated on the scale.
Conclusion:
Following measurement systems have been selected and attributed.
- Microphone/Amplifier/Speaker System.
- Room Heating Thermostat.
- Handheld Micrometer.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
- **Problem 8-45.** The man has a mass of 60 kg and the crate has a mass of 100 kg. If the coefficient of static friction between his shoes and the ground is \( \mu_s = 0.4 \) and between the crate and the ground is \( \mu_c = 0.3 \), determine if the man is able to move the crate using the rope-and-pulley system shown. **Diagram Explanation:** The diagram illustrates a scenario where a man is attempting to pull a crate using a rope-and-pulley system. The setup is as follows: - **Crate (C):** Positioned on the ground with a rope attached. - **Rope:** Connects the crate to a pulley system and extends to the man. - **Pulley on Tree:** The rope runs over a pulley mounted on a tree which redirects the rope. - **Angles:** - The rope between the crate and tree forms a \(30^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - The rope between the tree and the man makes a \(45^\circ\) angle with the horizontal. - **Man (A):** Pulling on the rope with the intention of moving the crate. This arrangement tests the…arrow_forwardplease solve this problems follow what the question are asking to do please show me step by steparrow_forwardplease first write the line action find the forces and them solve the problem step by steparrow_forward
- please solve this problem what the problem are asking to solve please explain step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problem and determine the stress for each point i like to be explained step by step with the correct answerarrow_forward
- please solve this problem for me the best way that you can explained to solve please show me the step how to solvearrow_forwardplese solbe this problem and give the correct answer solve step by step find the forces and line actionarrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problems first write the line of action and them find the forces {fx=0: fy=0: mz=0: and them draw the shear and bending moment diagram. please explain step by steparrow_forward
- please solve this problem step by step like human and give correct answer step by steparrow_forwardPROBLEM 11: Determine the force, P, that must be exerted on the handles of the bolt cutter. (A) 7.5 N (B) 30.0 N (C) 52.5 N (D) 300 N (E) 325 N .B X 3 cm E 40 cm cm F = 1000 N 10 cm 3 cm boltarrow_forwardUsing the moment-area theorems, determine a) the rotation at A, b) the deflection at L/2, c) the deflection at L/4. (Hint: Use symmetry for Part a (θA= - θB, or θC=0), Use the rotation at A for Parts b and c. Note that all deformations in the scope of our topics are small deformation and for small θ, sinθ=θ).arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





