
Concept explainers
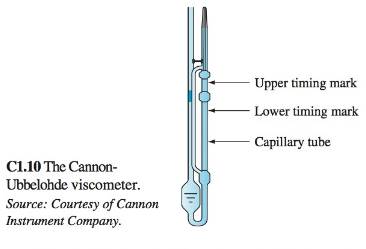
A popular gravity-driven instrument is the Cannon-Ubbelohde viscometer, shown in Fig. C1.10. The test liquid is drawn up above the bulb on the right side and allowed to drain by gravity through the capillary tube below the bulb. The time t for the meniscus to pass from upper to lower timing marks is recorded. The kinematic viscosity is computed by the simple formula: v = Ct where C is a calibration constant. For v in the range of 10U-50U mm2/s, the recommended constant is C = 0.50 mm2/s2, with an accuracy less than 0.5 percent.
(a) What liquids from Table A.3 arc in this viscosity range? (b) Is the calibration formula dimensionally consistent? (c) What system properties might the constant C depend upon? (d) What problem in this chapter hints at a formula for estimating the viscosity?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics
- 7) Please draw the front, top and side view for the following object. Please cross this line outarrow_forwardA 10-kg box is pulled along P,Na rough surface by a force P, as shown in thefigure. The pulling force linearly increaseswith time, while the particle is motionless att = 0s untilit reaches a maximum force of100 Nattimet = 4s. If the ground has staticand kinetic friction coefficients of u, = 0.6 andHU, = 0.4 respectively, determine the velocityof the A 1 0 - kg box is pulled along P , N a rough surface by a force P , as shown in the figure. The pulling force linearly increases with time, while the particle is motionless at t = 0 s untilit reaches a maximum force of 1 0 0 Nattimet = 4 s . If the ground has static and kinetic friction coefficients of u , = 0 . 6 and HU , = 0 . 4 respectively, determine the velocity of the particle att = 4 s .arrow_forwardCalculate the speed of the driven member with the following conditions: Diameter of the motor pulley: 4 in Diameter of the driven pulley: 12 in Speed of the motor pulley: 1800 rpmarrow_forward
- 4. In the figure, shaft A made of AISI 1010 hot-rolled steel, is welded to a fixed support and is subjected to loading by equal and opposite Forces F via shaft B. Stress concentration factors K₁ (1.7) and Kts (1.6) are induced by the 3mm fillet. Notch sensitivities are q₁=0.9 and qts=1. The length of shaft A from the fixed support to the connection at shaft B is 1m. The load F cycles from 0.5 to 2kN and a static load P is 100N. For shaft A, find the factor of safety (for infinite life) using the modified Goodman fatigue failure criterion. 3 mm fillet Shaft A 20 mm 25 mm Shaft B 25 mmarrow_forwardPlease sovle this for me and please don't use aiarrow_forwardPlease sovle this for me and please don't use aiarrow_forward
- 3. The cold-drawn AISI 1040 steel bar shown in the figure is subjected to a completely reversed axial load fluctuating between 28 kN in compression to 28 kN in tension. Estimate the fatigue factor of safety based on achieving infinite life (using Goodman line) and the yielding factor of safety. If infinite life is not predicted, estimate the number of cycles to failure. 25 mm + 6-mm D. 10 mmarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 1. The truss shown is supported by hinge at A and cable at E.Given: H = 4m, S = 1.5 m, α = 75⁰, θ = 33⁰.Allowable tensile stress in cable = 64 MPa.Allowable compressive stress in all members = 120 MPaAllowable tensile stress in all members = 180 MPa1.Calculate the maximum permissible P, in kN, if the diameter of the cable is 20 mm.2.If P = 40 kN, calculate the required area (mm2) of member BC.3. If members have solid square section, with dimension 15 mm, calculate the maximum permissible P (kN) based on the allowable strength of member HI.ANSWERS: (1) 45.6 kN; (2) 83.71 mm2; (3) 171.76 kNarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 2: A wire 4 meters long is stretched horizontally between points 4 meters apart. The wire is 25 mm2 in cross-section with a modulus of elasticity of 200 GPa. A load W placed at the center of the wire produces a sag Δ.1.Calculate the tension (N) in the wire if sag Δ = 30 mm.2.Calculate the magnitude of W, in N, if sag Δ = 54.3 mm.3. If W is 60 N, what is the sag (in mm)?ANSWERS: (1) 562 N, (2) 100 N, (3) 45.8 Narrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





