Ionic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium are two major concepts in chemistry. Ionic equilibrium deals with the equilibrium involved in an ionization process while chemical equilibrium deals with the equilibrium during a chemical change. Ionic equilibrium is established between the ions and unionized species in a system. Understanding the concept of ionic equilibrium is very important to answer the questions related to certain chemical reactions in chemistry.
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius acid act as a good electrolyte as it dissociates to its respective ions in the aqueous solutions. Keeping it similar to the general acid properties, Arrhenius acid also neutralizes bases and turns litmus paper into red.
Bronsted Lowry Base In Inorganic Chemistry
Bronsted-Lowry base in inorganic chemistry is any chemical substance that can accept a proton from the other chemical substance it is reacting with.
- You take 10.00 grams of pure acetic acid add top it up to 1.00 liter of solution.
- What is the pH of the solution at equilibrium? You will need to look up the pKa or Ka of acetic acid to figure this out (just google it).
- You add 20.00 grams of sodium acetate to the mixture and it causes a negligible increase in volume. What is the new pH once the solution reaches equilibrium?
- You add 1.00 mole of HClO4 (a strong acid) causing a negligible increase in volume again. What is the new pH?
- You add 1.00 mole of NaOH (strong base) causing a negligible increase in volume AGAIN (somehow?). What is the new pH?
Note: Since we only answer upto 3 sub parts we will answer the first 3.Please resubmit the question and specify the other sub parts.
Given data:
- pH of the solution at equilibrium need to calculate.
- If 20.00 grams of sodium acetate is added to the mixture and it causes a negligible increase in volume. Then new pH whenthe solution reaches equilibrium need to calculate.
- When 1.00 mole of HClO4 is added a negligible increase in volume again. New pH need to be write.
- 10.00 grams of pure acetic acid added to make 1.00 liter of solution.
- Amount of CH3COOH =10 gm
- Molecular weight of CH3COOH = 60.052 gm.
- Ka of acetic acid=1.8 x 10 -5
- Moles of CH3COOH =10.00/60.052 moles =0.167 moles.
- Molarity of CH3COOH =0.167 mole/1 litre =0.167 M
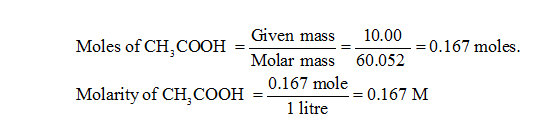
The dissociation of acetic acid is given by the equation:
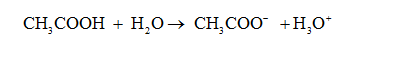
From ICE table
|
table |
CH3COOH |
CH3COO- |
H3O+ |
|
I |
0.167 M | 0 | 0 |
| C | -x | +x | +x |
| E | 0.167-x | +x | +x |
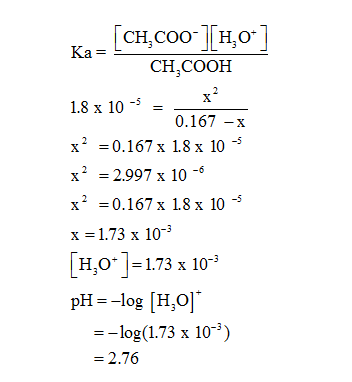
Thus the pH of the solution of equilibrium is 2.76.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images









