Suppose a 1D quantum system is represented by the wavefunction in position space: (x|½(t)) = p(x, t) = Ae-3¤+5it where it only exists 0 < x <• ! Normalize the wavefunction, i.e., what is A?
Suppose a 1D quantum system is represented by the wavefunction in position space: (x|½(t)) = p(x, t) = Ae-3¤+5it where it only exists 0 < x <• ! Normalize the wavefunction, i.e., what is A?
Related questions
Question
![Suppose a 1D quantum system is represented by the wavefunction in position space:
\[
\langle x|\psi(t)\rangle = \psi(x, t) = Ae^{-3x+5it}
\]
where it only exists \(0 \leq x < \infty\).
Normalize the wavefunction, i.e., what is \(A\)?](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fbbeeb476-a64f-4459-b8af-acf5dbdffec4%2Fe61a603b-e26e-42e8-b1f6-cbf062afec2c%2Fw9b3sih_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a 1D quantum system is represented by the wavefunction in position space:
\[
\langle x|\psi(t)\rangle = \psi(x, t) = Ae^{-3x+5it}
\]
where it only exists \(0 \leq x < \infty\).
Normalize the wavefunction, i.e., what is \(A\)?
Expert Solution
Step 1
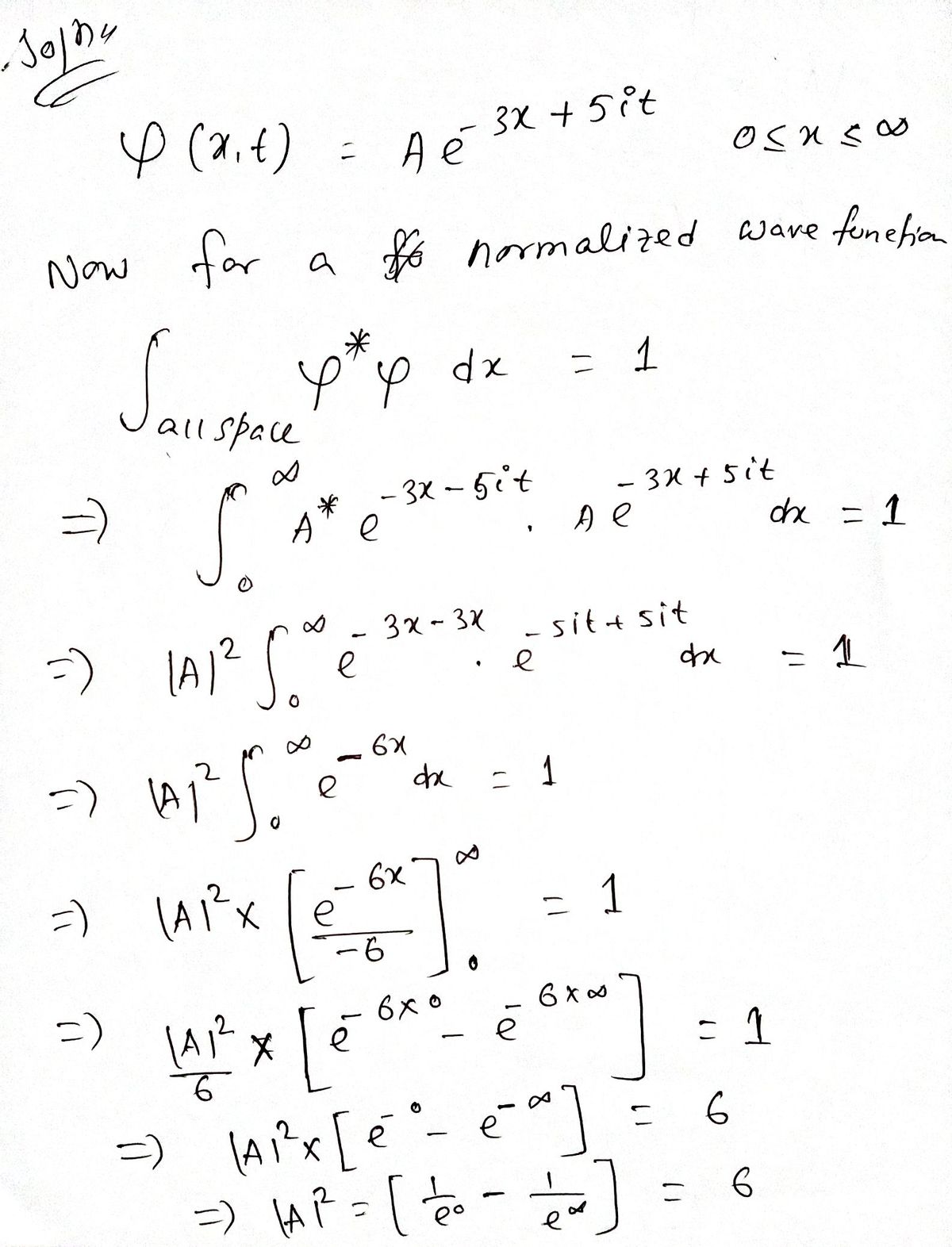
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
