Suppose you have an observable N with three eigenvalues 4, 8, and -1, with orthonormal eigenvectors |1), 2), and 3), respectively. A quantum particle in state |) = |1) – V 2) + 13). Use this information to answer the following questions. What is AN?
Suppose you have an observable N with three eigenvalues 4, 8, and -1, with orthonormal eigenvectors |1), 2), and 3), respectively. A quantum particle in state |) = |1) – V 2) + 13). Use this information to answer the following questions. What is AN?
Related questions
Question
![Suppose you have an observable Ω with three eigenvalues 4, 8, and -1, with orthonormal eigenvectors \( |1\rangle \), \( |2\rangle \), and \( |3\rangle \), respectively. A quantum particle in state
\[
|\psi\rangle = \frac{i}{3} |1\rangle - \frac{i\sqrt{3}}{3} |2\rangle + \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} |3\rangle
\]
Use this information to answer the following questions.
What is \(\Delta \Omega\)?
- \( \frac{\sqrt{51}}{2} \)
- \( \frac{2\sqrt{347}}{9} \)
- \( \frac{3\sqrt{37}}{8} \)
- \( \frac{17\sqrt{349}}{2} \)](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fbbeeb476-a64f-4459-b8af-acf5dbdffec4%2F6a307b88-de1c-4405-8eb3-4204172fc843%2Fahe8n3_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose you have an observable Ω with three eigenvalues 4, 8, and -1, with orthonormal eigenvectors \( |1\rangle \), \( |2\rangle \), and \( |3\rangle \), respectively. A quantum particle in state
\[
|\psi\rangle = \frac{i}{3} |1\rangle - \frac{i\sqrt{3}}{3} |2\rangle + \frac{\sqrt{5}}{3} |3\rangle
\]
Use this information to answer the following questions.
What is \(\Delta \Omega\)?
- \( \frac{\sqrt{51}}{2} \)
- \( \frac{2\sqrt{347}}{9} \)
- \( \frac{3\sqrt{37}}{8} \)
- \( \frac{17\sqrt{349}}{2} \)
Expert Solution
Step 1
The given wave function and its complex conjugate are given as below,
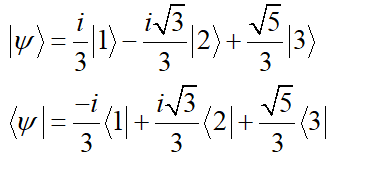
Also given,
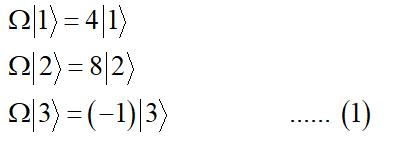
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 6 images
