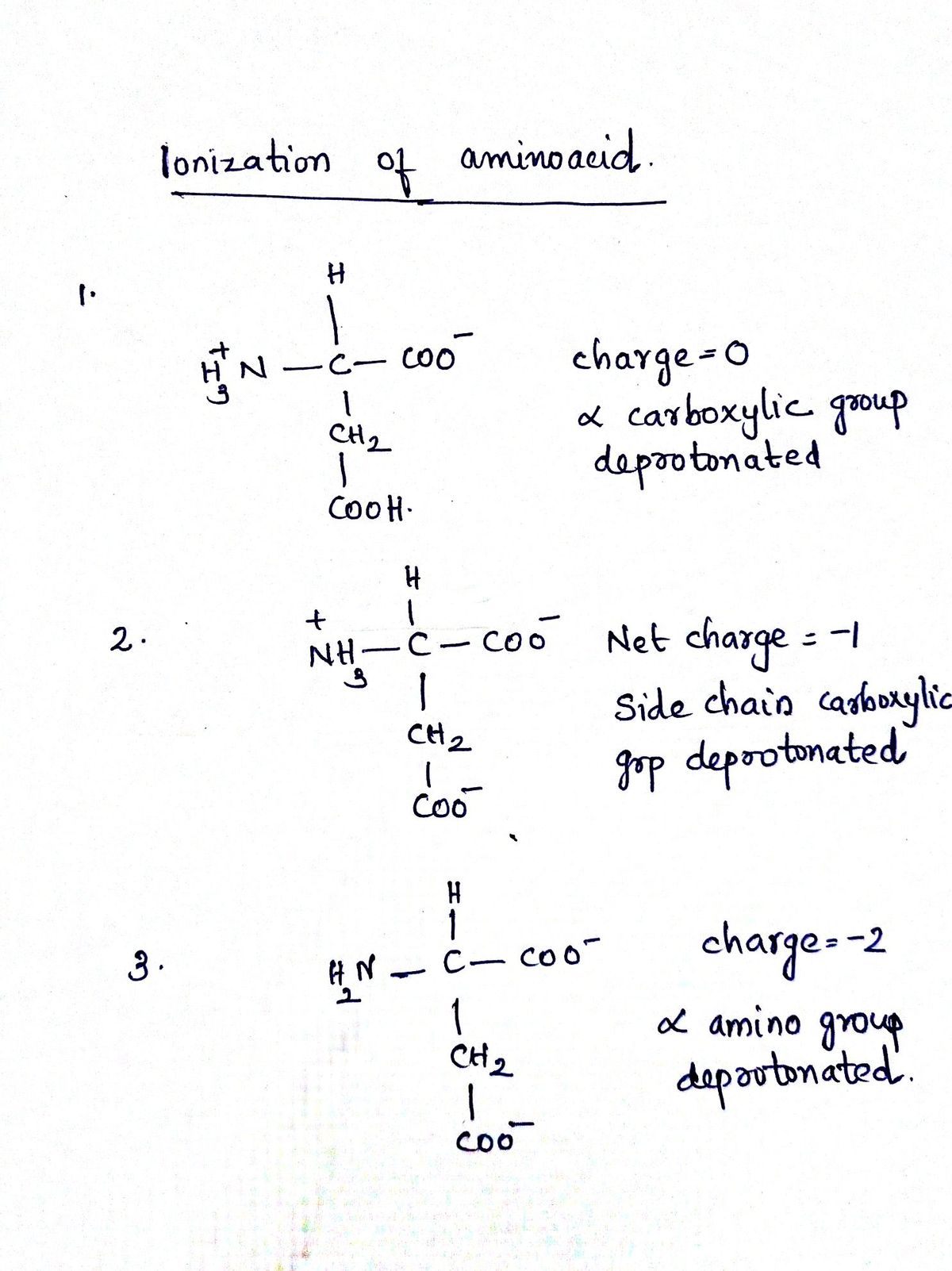
4. Ionic Forms of Aspartic Acid. Aspartic acid is a triprotic acid that can undergo three dissociation reactions (a) Given the structure of protonated aspartic acid below, draw the chemical structures of the other three forms that predominate in aqueous solution as the pH increases. Think about this in terms of a titration, adding OH. What acid base reactions occur? Note that the pKa of the carboxylic acid group (-COOH) nearest the -NH, is 2.1, The other -COOH has a pKa of 3.9, and the pKa of the amino group, - NH", is 9.7. НО. OH Ο ΘΝΗ, aspartic acid b) Draw the titration curve. What form of aspartic acid would be present at the highest concentration in solutions with the following pHs: 1.0, 4.5, 5.7, 2,0. Explain your answers in terms of the pKa values.
Please answer all parts to QUESTION 4 ONLY, posted with other questions as first attempt was rejected for lack of information. This is all that is provided. Please answer QUESTION 4 part A and B thoroughly and with explanations.

Aspartic acid is a triprotic acid, It can give 3 protons from 3 ionizable groups
- from the carboxylic group near to NH3+
- From the amino group
- From the side chain carboxyl group
with pKa values 2.1,9.7 and 3.9 respectively. Remember of pKa values are the pH at which half of the group deprotonate. For example pKa for side chain is 3.9 which indicates half of the side chain carboxylic acid deprotonates and becomes negatively charged. When the pH increases further then deronated form also increases. When the amino group loses protons loses the positive charge but carboxylic group has negative charge while deprotonate.
The 3 predominant ionic forms as pH increases
- lose protons from carboxylic acid near to aminogroup
- Both carboxylic acids lose protons
- all the group derotonate
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images









