
Concept explainers
through 5.7 Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses shown, using the method of joints.
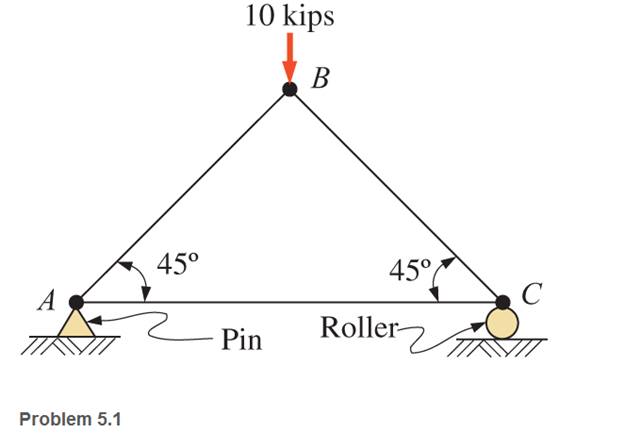
The forces in the member from method of joints.
Answer to Problem 5.1P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Two reactions at the pin support is Ax and Ay.
At roller support one reaction is Cy.
Force on the member
Free body diagram of the truss.
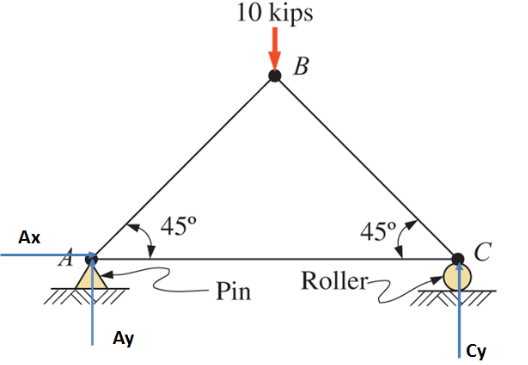
Taking moment about A
From equilibrium equations
Considering joint A
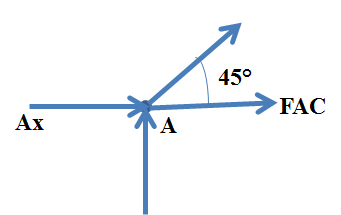
From the equilibrium equation
Considering joint C
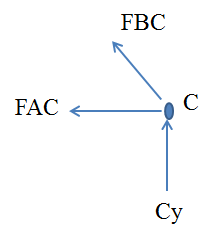
Conclusion:
Forces in the member
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- A double thread worm gear has a pitch of 1 1/8 and a pitch diameter of 3 in. It has a coefficient of friction of 0.20 and normal angle (pressure angle) of 14.5o. The worm is supplied by 12 hp at 1200 rpm motor. Find the tangential force on the gear. The worm is left hand threads.arrow_forwardA 2 mm thick, 5L vessel made of nickel is used ot store hydrogen gas at 358 K and 300 kPa. If the total inner surface area of the vessel is 1600 cm^2, determine the rate of gas loss from the nickel vessel via mas diffusion. Also, determine the fraction of the hydrogen lost by mass diffusion after one year of storage.arrow_forward< 7:19 The 1st homework 6. Multiple Choice a)唧筒机构 5G31 Which of followings can be th e kinematic diagram of this mechanism? A B Darrow_forward
- 2:54 The 1st homework . 5G 27 b)回转柱塞泵机构 Which of followings can be the kinematic diagram of this mechanis m? A B D Carrow_forwardIm struggling to find the moment about point D. Please explain how to set up and solvearrow_forwardI keep trying this problem but cant seem to get the sheer right can you help me figure this out please?arrow_forward
- The pillar crane is subjected to the crate having a mass of 1000 kgkg. The boom is held in position shown in (Figure 1).Determine the force in the tie rod ABAB.Determine the horizontal and vertical reactions at the pin support CC.arrow_forwardProblem 7.1 Part A In (Figure 1), F₁ = 550 lb, F2 = 250 lb, and F3 = 340 lb. Figure F F B Part B Determine the shear force at point C. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Vc=522 ? lb Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 15 attempts remaining Part C Determine the moment at point C. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 1 of 1 Mc = 1867 F E D lb.ft Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 24 attempts remaining ▸ Part D 6 ft- 4 ft- 4 ft- 6 ft 12 ftarrow_forwardSketch h, for Problem 13.64 13 13.65 In Sketch i the tension on the slack side of the left pulley is 20% of that on the tight side. The shaft rotates at 1000 rpm. Select a pair of deep-groove roller bearings to sup- port the shaft for 99% reliability and a life of 20,000 hr. Assume Eq. (13.83) can be used to account for lubricant cleanliness. All length dimensions are in millimeters. b Z 02 0 y 200 500. 187 100 30° B TONE 500 diam 800 N 650 diam 100 N Sketch i, for Problem 13.65 வarrow_forward
- Problem 2: Consider the rectangular wood beam below. Use E=1.0. 1. Determine the slope at A. 2. Determine the largest deflection between A and B. Use the elastic curve equation. Show all work. (20%) 3 kN/m A 2.4 m - 50 mm AT 150 mm 0000 - B C 1.2 m→arrow_forwardPlease give a clear solution.arrow_forwardUSE MATLAB ONLY Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),... axis([-1 6 -4 4]), ... title('Velocity Triangle'), ... xlabel('x'),ylarrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
