
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The pH of cabbage indicator when it turns red needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
An indicator is a substance which changes its color when placed in acidic and basic solutions.
Red cabbage is a natural indicator which turns its color in acids and bases.
In acids, it turns red and in bases it turns bluish green.
pH of acidic solutions is less than seven.
pH of basic solutions is greater than seven.
Answer to Problem 4STP
Option (A) 2 is the answer.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct option:
Cabbage solution turns red in acidic solutions.
Acids have pH less than seven.
Bases have pH greater than seven.
Neutral solutions have pH is equal to seven.
So, among the given options, option (A) is the correct answer.
Red cabbage indicator is represented as follows:
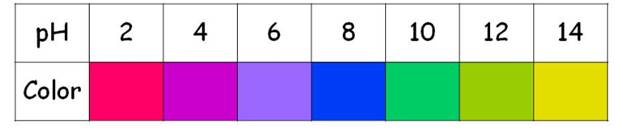
Reasons for incorrect options:
Acids have pH less than seven.
Bases have pH greater than seven.
Neutral solutions have pH is equal to seven.
Among the given options, option (B) has pH seven, which indicates a neutral solution.
(C) This option has pH 9 which indicates the solution is basic and the indicator color should be bluish green and not red. So, this is also a wrong option.
(D) This option has pH 9 which indicates the solution is basic and the indicator color should be bluish green and not red. So, this is also a wrong option.
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Chapter U6 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- Calculating the pH at equivalence of a titration A chemist titrates 210.0 mL of a 0.1003 M hydrobromic acid (HBr) solution with 0.7550M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = ] ☑ o0o 18 Ararrow_forwardDo you do chemistry assignmentsarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A This reaction is always spontaneous, but proceeds slower at temperatures above 120. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 117. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) This reaction is slower below 20. °C than C above. AS is |(pick one) ? 18 Ar 1arrow_forward
- Calculating the pH at equivalence of a titration Try Again Your answer is incorrect. 0/5 a A chemist titrates 70.0 mL of a 0.7089 M hydrocyanic acid (HCN) solution with 0.4574M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK of hydrocyanic acid is 9.21. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = 11.43] G 00. 18 Ar B•arrow_forwardBiological Macromolecules Naming and drawing the products of aldose oxidation and reduction aw a Fischer projection of the molecule that would produce L-ribonic acid if it were subjected to mildly oxidizing reaction conditions. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X AP ‡ 1/5 Naor Explanation Check McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibilarrow_forward● Biological Macromolecules Identifying the parts of a disaccharide Take a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH O H H H OH OH OH H H CH2OH H O OH H OH H H H H OH Is this a reducing sugar? Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. Explanation Check O yes X O no ○ yes O no Uarrow_forward
- The aim of the lab is to measure the sodium content from tomato sauce using the Mohr titration method. There are two groups being: Regular Tomato sauce & Salt Reduced tomato sauce QUESTION: State how you would prepare both Regular & Salt reduced tomato sauce samples for chemical analysis using the Mohr titration methodarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds faster at temperatures above -48. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) ✓ AS is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except below 114. °C but proceeds at a slower rate below 135. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is C This reaction is exothermic and proceeds faster at temperatures above -43. °C. (pick one) AS is (pick one) v Х 5 ? 18 Ararrow_forwardion. A student proposes the following Lewis structure for the perchlorate (CIO) io : :0: : Cl : - - : :0: ك Assign a formal charge to each atom in the student's Lewis structure. atom central O formal charge ☐ top O ☐ right O ☐ bottom O ☐ Cl ☐arrow_forward
- Decide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Yes. Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Cl- : 2: :Z: :Z: N—N : 0: C C1: O CO No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0". ☑arrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions ΔΗ is (pick one) A This reaction is faster above 103. °C than below. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous only above -9. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) C The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous. AS is (pick one) 18 Ararrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds slower at temperatures below 41. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 94. °C. AS is (pick one) This reaction is always spontaneous, but ΔΗ is (pick one) C proceeds slower at temperatures below −14. °C. AS is (pick one) Х 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ B 1 1arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





