
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The root for the given molecule is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
Answer to Problem B.1P
The root for the given molecule is cyclohexene.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
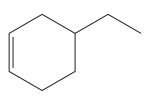
In this molecule, the largest ring containing the double bond has six carbon atoms. Hence, the root is cyclohexene, as shown below.
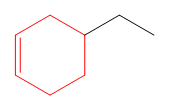
The root is determined from the longest carbon chain or the largest ring containing the double or triple bond between the carbon atoms.
(b)
Interpretation:
The root for the given molecule is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
Answer to Problem B.1P
The root for the given molecule is ethene.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
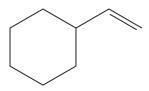
In this molecule, the double bond is a part of the chain attached to the ring. Although the ring has more carbon atoms than the side chain, the ring does not contain a
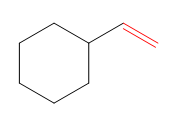
The root is determined from the longest carbon chain or the largest ring containing the double or triple bond between the carbon atoms.
(c)
Interpretation:
The root for the given molecule is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
Answer to Problem B.1P
The root for the given molecule is propyne.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
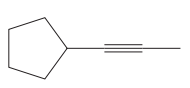
In this molecule, the triple bond is a part of the chain attached to the ring. Although the ring has more carbon atoms than the side chain, the ring does not contain a
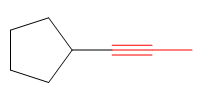
The root is determined from the longest carbon chain or the largest ring containing the double or triple bond between the carbon atoms.
(d)
Interpretation:
The root for the given molecule is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
Answer to Problem B.1P
The root for the given molecule is hexene.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
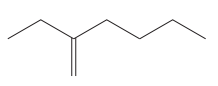
In this molecule, the longest carbon chain containing the double bond has six carbon atoms. Hence, the root is hexene, as shown below.
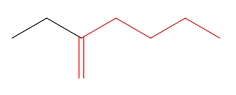
The root is determined from the longest carbon chain or the largest ring containing the double or triple bond between the carbon atoms.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter B Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms: Study Guide/solutions Manual (second)
- Gas Law Studies 1. Mass of zinc Determination of 0.899 2) Moles of zinc 0.01361 mol 3.) Moles of hydrogen 00? ← I was told to calculate this number from mole of zinc. 350m So does that mean it will be 0.01361 mol too? 4 Volume of water collected (mL) 5) VL of water collected (Liters) 0.350 L 6) Temp of water collected (°C) 7) Temp of water collected (°K) 8) Atmospheric pressure (mm) 9) Vapor pressure of water (mm) 10) Corrected pressure of hydrogen 20% 29°C 764.0mm Hg (mm) 17.5mm 11) Corrected pressure of hydrogen (atm) 12) Experimentally calculated value of 19 13. Literature value of R 14) % Error 15) Suggest reasons for the % error (#14)arrow_forwardNo wedge or dashes. Do proper structure. Provide steps and explanation.arrow_forward10 Question (1 point) Draw curved arrow notation to indicate the proton transfer between NaOH and CH3CO₂H. 2nd attempt :0- H See Periodic Table See Hint Draw the products of the proton transfer reaction. Don't add a + sign between the products.arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forward4. Experimental Procedure. a. How many (total) data plots are to be completed for this experiment? Account for each. b. What information is to be extracted from each data plot?arrow_forwardProvide the IUPAC name of the following molecule. Don't forget to include the proper stereochemistry where appropriate.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

