
Concept explainers
Name the following
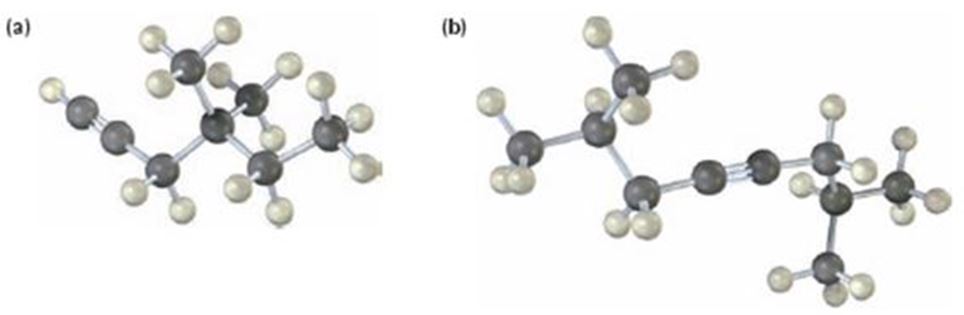
a)
Interpretation:
The alkyne shown is to be named and the products formed when it reacts with 1) H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst and 2) H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon triple bond is chosen. The chain is numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Compounds with more than one triple bond are called diynes, triynes and so forth. The substituents present, if any are written in the alphabetical order.
When reduced with Hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst the reduction of alkynes stops in the alkene stage. When treated with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4, alkynes undergo hydration following Markovnikov regiochemistry to give an enols which will tautomerize to yield aldehydes (terminal alkynes) or ketones (internal alkynes).
To give:
The name of the alkyne shown and to predict the products formed when it reacts with 1) H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst and 2) H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4.
Answer to Problem 14VC
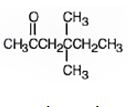
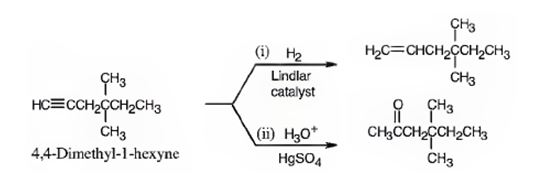
The name of the alkyne shown is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexyne.
The product formed when it reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexene.
The product formed when it reacts with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is 4,4-dimethyl-2-hexanone.
Explanation of Solution
The compound has a six carbon straight chain with two methyl groups on C4 with a triple bond between C1 & C2. Hence it’s name is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexyne.
When reduced with hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst, the triple bond becomes a double bond as each of the two carbons in the triple bond gets attached to a hydrogen and an alkene, 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexene,is thus produced.
When treated with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4, the addition of water takes place in the triple bond following Markovnikov regiochemistry. The OH group adds to more highly substituted carbon and H adds to the less highly substituted carbon in triple bond resulting in the formation of an enol which undergoes tautomerization to yield the ketone, 4,4-dimethyl-2-hexanone.
The name of the alkyne shown is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexyne.

The product formed when it reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexene.

The product formed when it reacts with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is 4,4-dimethyl-2-hexanone.

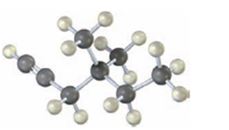
b)
Interpretation:
The alkyne shown is to be named and the products formed when it reacts with 1) H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst and 2) H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon triple bond is chosen. The chain is numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Compounds with more than one triple bond are called diynes, triynes and so forth. The substituents present, if any are written in the alphabetical order.
When reduced with Hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst the reduction of alkynes stops in the alkene stage. When treated with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4, alkynes undergo hydration following Markovnikov regiochemistry to give an enols which will tautomerize to yield aldehydes (terminal alkynes) or ketones (internal alkynes).
To give:
The name of the alkyne shown and to predict the products formed when it reacts with 1) H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst and 2) H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4.
Answer to Problem 14VC
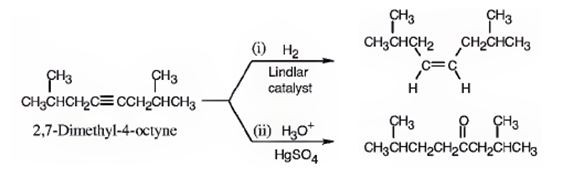
The name of the alkyne shown is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octyne.
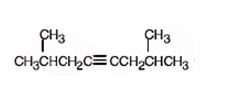
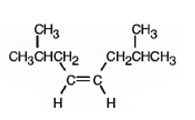
The product formed when it reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is cis-2,7-dimethyl-4-octene.
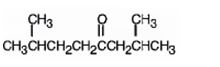
The product formed when it reacts with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octanone.
Explanation of Solution
The compound has an eight carbon straight chain with two methyl groups on C2 & C7 with a triple bond between C4 & C5. Hence it’s name is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octyne.
When reduced with hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst, the triple bond becomes a double bond as each of the two carbons in the triple bond gets attached to a hydrogen and an alkene, cis- 2,7-dimethyl-4-octene.is thus produced.
When treated with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4, the addition of water takes place in the triple bond. As the alkene is symmetrical the Markovnikov regiochemistry cannot be applied. The OH group adds to one carbon and H adds to the other carbon in triple bond resulting in the formation of an enol which undergoes tautomerization to yield the ketone, 2,7-dimethyl-4-octanone.
The name of the alkyne shown is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octyne.

The product formed when it reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is cis-2,7-dimethyl-4-octene.

The product formed when it reacts with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octanone.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- In the following molecule, indicate the hybridization and shape of the indicated atoms. CH3 CH3 H3C HO: CI:arrow_forwardWhich of the following are TRUE about linear syntheses? Question 7Select one: A. They are easier to execute B. They are the most efficient strategy for all syntheses C. They are generally shorter than convergent syntheses D. They are less versatile compared to convergent synthesesarrow_forwardWhich of the following characteristics is common among chiral pool substrates? Question 4Select one: A. They have good leaving groups B. They are all achiral C. All have a multiplicity of chiral centres D. They have poor leaving groupsarrow_forward
- Determine whether the following reaction is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction: H NO2 H+ NO 2 + Molecule A Molecule B Is this a nucleophilic substitution reaction? If this is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, answer the remaining questions in this table. What word or two-word phrase is used to describe the role Molecule A plays in this reaction? What word or two-word phrase is used to describe the role Molecule B plays in this reaction? Use a 6 + symbol to label the electrophilic carbon that is attacked during the substitution. Highlight the leaving group on the appropriate reactant. O Yes ○ No ☐ 0 dx 000 HE ?arrow_forwardDraw the major organic product of the Bronsted acid-base reaction. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore any counterions. :0: NaOH Harrow_forward5. Calculate the total amount of heat transferred as 50 g of wat Specific heat H₂O (g) 2.00 J/g°C -10 °C. Specific heat H₂O (1) Specific heat H₂O (s) 4.18 J/g°C 2.11 J/g°C Heat of vaporization 2260 J/g Heat of fusion 334 J/g Melting point 0°C 6. Calculate the total amount of heat transferred as 25 g of water is heated from 50 °C to 100 °C as a gas. Boiling point 100 °Carrow_forward
- Calculate the total amount of heat transferred as 50 g of Water -10°C. Calculate the total amount of heat transferred as 25 g of water is heated from 50°C to 100°C as a gas. \table[[Specific heat H₂O(g), 2.00°C Η 2 g 5. Calculate the total amount of heat transferred as 50 g of wat Specific heat H₂O (g) 2.00 J/g°C -10 °C. 4.18 J/g°C 2.11 J/g°C 2260 J/g 334 J/g Specific heat H₂O (1) Specific heat H₂O (s) Heat of vaporization Heat of fusion Melting point 6. Calculate the total amount of heat transferred as 25 g of water is heated from 50 °C to 100 °C as a gas. Boiling point 100 °C 0°Carrow_forwardWrite formulas for ionic compounds composed of the following ions. Use units as a guide to your solutions. 24. sodium and nitrate 25. calcium and chlorate 26. aluminum and carbonate 27. CHALLENGE Write the formula for an ionic compound formed by ions from a group 2 element and polyatomic ions composed of only carbon and oxygen.show work step by steparrow_forwardADDITIONAL PRACTICE PRACTICE Problems Write formulas for ionic compounds composed of the following ions. Use units as a guide to your solutions. 24. sodium and nitrate 25. calcium and chlorate 26. aluminum and carbonate 27. CHALLENGE Write the formula for an ionic compound formed by ions from a group 2 element and polyatomic ions composed of only carbon and oxygen. ounds 1998arrow_forward
- 7:35 < Dji Question 19 of 22 5G 50% Submit What is the pH of a buffer made from 0.350 mol of HBrO (Ka = 2.5 × 10-9) and 0.120 mol of KBRO in 2.0 L of solution? | 1 2 3 ☑ 4 5 6 C 7 8 ☐ 9 +/- Tap here for additional resources ||| 0 ×10 Гarrow_forwardaw the major substitution products you would expect for the reaction shown below. If substitution would not occur at a significant rate under these conditions, check the box underneath the drawing area instead. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products. Note for advanced students: you can assume that the reaction mixture is heated mildly, somewhat above room temperature, but strong heat or reflux is not used. B C Br HO O Substitution will not occur at a significant rate. Explanation Check + Х Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibarrow_forwardComplete the following reactions with the necessary reagents to complete the shown transformation. Example: 1. 2. ? 3. 018 Br OH Answer: H₂O, H2SO4, HgSO4arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

