
Concept explainers
Use the method of superposition to solve the following problems and assume that the flexural rigidity El of each beam is constant.
9.90 Before the load P was applied, a gap, δ0 = 0.5 mm, existed between the cantilever beam AC and the support at B. Knowing that E = 200 GPa, determine the magnitude of P for which the deflection at C is 1 mm.
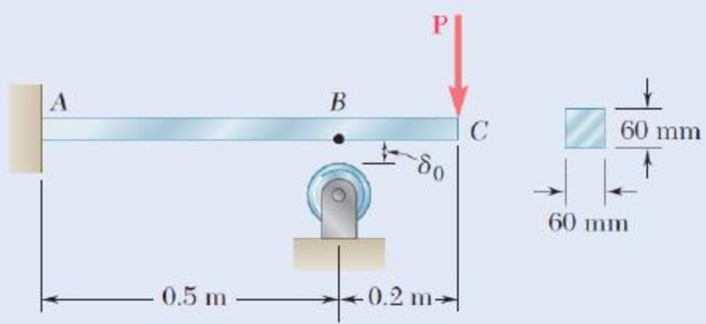
Fig. P9.90
Find the magnitude of load P for the given condition using superposition method.
Answer to Problem 90P
The magnitude of load P in the beam is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap at the point B is
The modulus of elasticity of the material is
The size of the square cross section is
The deflection at point C is
Calculation:
Find the moment of inertia of the square cross section (I) using the relation.
Here, the size of the square cross section is a.
Substitute 60 mm for a.
Consider the portion AB of the beam.
The load P at point C will be converted into a load and moment at point B.
Show the free-body diagram of the superimposed beam AB as in Figure 1.
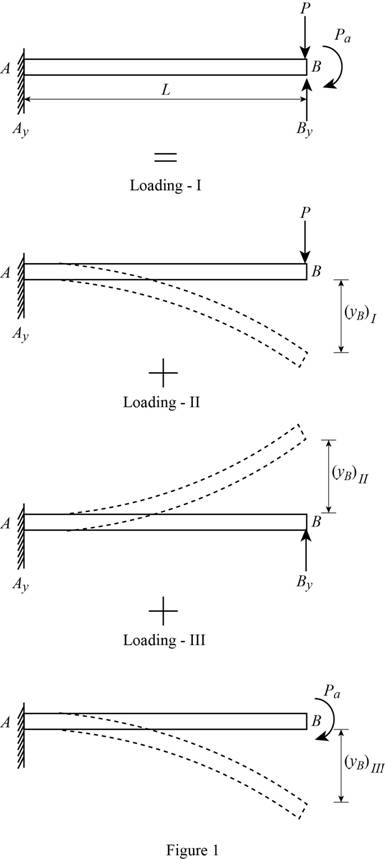
Loading I:
The downward load P is acting at point B of the beam.
Refer to Case 1 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the deflection equation for concentrated load acting in a cantilever beam as follows;
Find the deflection at point B due to load P at point B as follows;
Loading II:
The upward reaction
Refer to Case 1 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the deflection equation for concentrated load acting in a cantilever beam as follows;
Find the deflection at point B due to reaction at point B as follows;
Loading III:
The clockwise moment is acting at point B of the beam.
Refer to Case 3 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the deflection equation for moment in a cantilever beam as follows;
Find the deflection at point B due to the moment at point B as follows;
Find the resultant deflection at point B as follows.
Substitute
Substitute 0.5 mm for
Consider the beam ABC.
Show the free-body diagram of the superimposed beam ABC as in Figure 2.
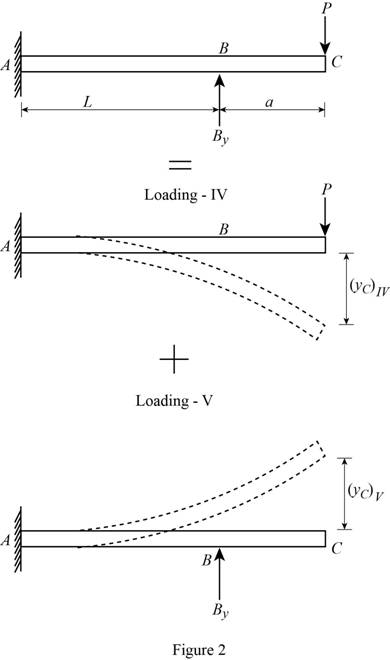
Loading IV:
The downward load P is acting at point C of the beam.
Refer to Case 1 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the deflection equation for concentrated load acting in a cantilever beam as follows;
Find the deflection at point C due to load P at point C as follows;
Loading V:
The upward reaction
Refer to Case 1 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the slope and deflection equation for concentrated load acting in a cantilever beam as follows;
Find the deflection at point B due to reaction at point B as follows;
Find the slope at point B due to reaction at point B as follows;
The portion BC remains straight.
Find the deflection at point C due to reaction at point B as follows;
Substitute
Find the resultant deflection at point C as follows.
Substitute
Substitute 1 mm for
Solve the Equation (1) and (2).
Therefore, the magnitude of load P in the beam is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- c. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40) handplot only, and solve for eacharrow_forwardA ship of 9000 tonne displacement floats in fresh water of 1.000 t/m3 at a draught 50 mm below the sea water line. The waterplane area is 1650 m2. Calculate the mass of cargo which must be added so that when entering seawater of 1.025 t/m3 it floats at the seawater line.arrow_forwardA ship of 15000 tonne displacement floats at a draught of 7 metres in water of 1.000t/cub. Metre.It is required to load the maximum amount of oil to give the ship a draught of 7.0 metre in seawater ofdensity 1.025 t/cub.metre. If the waterplane area is 2150 square metre, calculate the massof oil requiredarrow_forward
- A ship of 8000 tonne displacement floats in seawater of 1.025 t/m3 and has a TPC of 14. The vessel moves into fresh water of 1.000 t/m3 and loads 300 tonne of oil fuel. Calculate the change in mean draught.arrow_forwardAuto Controls DONT COPY ANSWERS - will report Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forwardI submitted the below question and received the answer i copied into this question as well. Im unsure if it is correct, so looking for a checkover. i am stuck on the part tan-1 (0.05) = 0.04996 radians. Just unsure where the value for the radians came from. Just need to know how they got that answer and how it is correct before moving on to the next part. If any of the below information is wrong, please feel free to give me a new answer or an entire new explanation. An Inclining experiment done on a ship thats 6500 t, a mass of 30t was moved 6.0 m transvesly causing a 30 cm deflection in a 6m pendulum, calculate the transverse meta centre height. Here is the step-by-step explanation: Given: Displacement of the ship (W) = 6500 tonnes = 6500×1000=6,500,000kg Mass moved transversely (w) = 30 tonnes=30×1000=30,000kg The transverse shift of mass (d) = 6.0 meters Pendulum length (L) = 6.0 meters Pendulum deflection (x) = 30 cm = 0.30 meters Step 1: Formula for Metacentric Height…arrow_forward
- A distillation column with a total condenser and a partial reboiler is separating ethanol andwater at 1.0 atm. Feed is 0.32 mol fraction ethanol and it enters as a saturated liquid at 100mol/s on the optimum plate. The distillate product is a saturated liquid with 80 mol% ethanol.The condenser removes 5615 kW. The bottoms product is 0.05 mol fraction ethanol. AssumeCMO is valid.(a) Find the number of equilibrium stages for this separation. [6 + PR](b) Find how much larger the actual reflux ratio, R, used is than Rmin, i.e. R/Rmin. [3]Note: the heats of vaporization of ethanol and water are λe = 38.58 and λw = 40.645 arrow_forwardA ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water. i would like to get the above question sloved in detail. ive attached the picture of the answer from the reeds book. just not sure of all the steps theyve used and the formula in which they started with.arrow_forwardPlunger Gauses:) - True or False "A Plunger gage can read small fluctuations in pressure such as a change in pressure of 2 psi"arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





