
Concept explainers
9.29 and 9.30 Determine the reaction at the roller support and the deflection at point C.
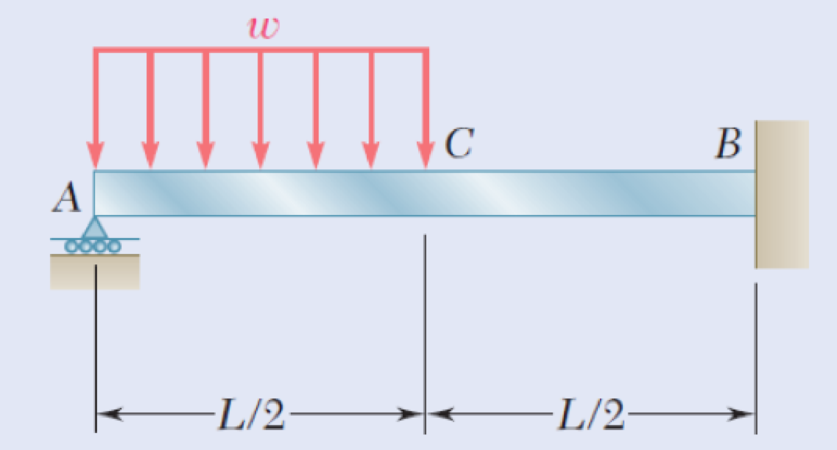
Fig. P9.29
Find the reaction at the roller support and the deflection at point C of the beam.
Answer to Problem 29P
The reaction at the roller support A is
The deflection at the point C is
Explanation of Solution
Consider a section at a distance x from left end A of the section AC.
Show the free-body diagram of the section AC as in Figure 1.
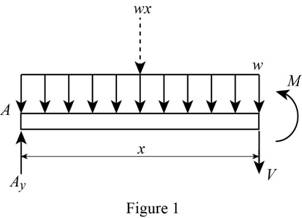
Determine the moment at the section by taking moment about the section.
Write the second order differential equation as follows;
Here, the moment at the corresponding section is
Substitute
Integrate the equation with respect to x;
Integrate the Equation (2) with respect to x.
Show the free-body diagram of the section BC as in Figure 2.
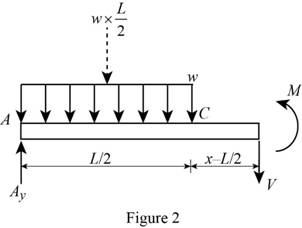
Determine the moment at the section by taking moment about the section.
Substitute
Integrate the equation with respect to x;
Integrate the Equation (4) with respect to x.
Boundary condition 1:
At the point A;
Substitute 0 for x and 0 for y in Equation (3).
Boundary condition 2:
At the point B;
Substitute L for x and 0 for
Boundary condition 3:
At the point C;
Equate Equation (2) and (4).
Substitute
Boundary condition 4:
At the point C;
Equate Equation (3) and (5).
Substitute
Boundary condition 5:
At the point B;
Substitute L for x, 0 for y,
Therefore, the reaction at the roller support A is
At the point C;
Substitute
Therefore, the deflection at the point C is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- Air modeled as an ideal gas enters an insulated compressor at a temperature of 300 K and 100 kPa, and leaves at 600 kPa. The mass flowrate of air entering the compressor is 50 kg/hr, and the power consumed by the compressor is 3 kW. (Rair = 0.287 kJ/kg-K, k = 1.4, cp = 1.0045 kJ/kg-K, cv = 0.718 kJ/kg-K) Determine the isentropic exit temperature (Te,s) of the air in [K]. Determine the actual exit temperature (Te) of the air in [K]. Determine the isentropic efficiency of the compressor. (Answer: ηc,s = 93.3%) Determine the rate of entropy generated through the compressor in [kW/K]. (Answer: Ṡgen = 0.000397 kW/K)arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardA metal plate of thickness 200 mm with thermal diffusivity 5.6 x10-6 m²/s and thermal conductivity 20 W/mK is initially at a uniform temperature of 325°C. Suddenly, the 2 sides of the plate are exposed to a coolant at 15°C for which the convection heat transfer coefficient is 100 W/m²K. Determine temperatures at the surface of the plate after 3 min using (a) Lumped system analysis (b) Analytical one term approximation (c) One dimensional Semi infinite solid Analyze and discuss the resultsarrow_forward
- Problem 3 This problem maps back to learning objectives 1-4 & 8. Consider the particle attached to a spring shown below. The particle has a mass m and the spring has a spring constant k. The mass-spring system makes an angle of 0 with respect to the vertical and the distance between point 0 and the particle can be defined as r. The spring is unstretched when r = l. Ꮎ g m a) How many degrees of freedom is this system and what are they? b) Derive the equation(s) of motion that govern the movement of this system.arrow_forwardChapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Scores ■Review Determine the maximum constant speed at which the pilot can travel, so that he experiences a maximum acceleration an = 8g = 78.5 m/s². Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. μΑ v = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B ? Determine the normal force he exerts on the seat of the airplane when the plane is traveling at this speed and is at its lowest point. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. о HÅ N = Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Units Next >arrow_forwardI want to know the Milankovich orbital element constraint equation. Is it e*cos(i) = cos(argp), where e is eccentricity, i is inclination, and argp is arguement of periapsisarrow_forward
- The following data were taken during a one-hour trial run on a single cylinder, single acting, four-stroke diesel engine of cylinder diameter of 175 mm and stroke 225 mm , the speed being constant at 1000 rpm : Indicated mep: 5.5 barsDiam. of rope brake: 1066 mmLoad on brake: 400 NReading of balance: 27 NFuel consumed: 5.7 kgCalorific value: 44.2 MJ/kg Calculate the indicated power, brake power, specific fuel consumption per indicated kWh and per brake kWh , mechanical efficiency, indicated thermal and brake thermal efficiency.arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Document Sharing P Pearson MyLab and Mastering User Settings Part A P Course Home b Success Confirmation of Question Submission | bartleby A particle moves along an Archimedean spiral r = (80) ft, where 0 is given in radians. (Figure 1) If ė = = 4 rad/s and € = 5 rad/s², determine the radial component of the particle's velocity at the instant Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure y r = Α ? Vr = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the transverse component of the particle's velocity. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. о MÅ ve = Value Submit Request Answer Part C Units ? 1 of 1 Determine the radial component of the particle's acceleration. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Ar = (80) ft о ΜΑ Value Units ? = π/2 rad.arrow_forwardCan you help me with a matlab code? I am trying to plot the keplerian orbital elements over time. I would usually find the orbit using cartesian system and then transform into keplerian orbital elements. Is there a way to directly integrate keplerian orbital elements?arrow_forward
- mylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardK mylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Scores Course Homearrow_forwardK mylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Scores Course Homearrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





