
Concept explainers
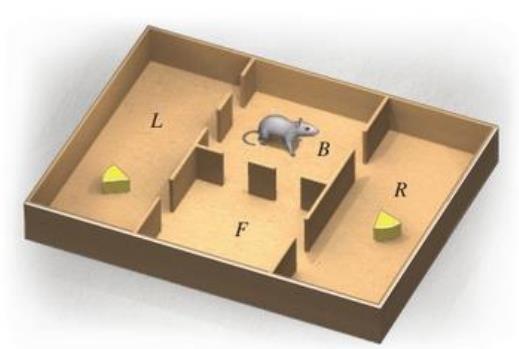
Psychology. A rat is placed in room
(A) What is the long-run probability that a rat placed in room
(B) What is the average number of exits that a rat placed in room
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Pearson eText for Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Introductory Statistics
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
- Sketch a possible graph of a function f, together with vertical asymptotes, that satisfies all of the following conditions. f(2)=0 f(4) is undefined lim f(x)=1 X-6 lim f(x) = -∞ x-0+ lim f(x) = ∞ lim f(x) = ∞ x-4 _8arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forwardDetermine the following limit. lim 35w² +8w+4 w→∞ √49w+w³ 3 Select the correct choice below, and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. ○ A. lim W→∞ 35w² +8w+4 49w+w3 (Simplify your answer.) B. The limit does not exist and is neither ∞ nor - ∞.arrow_forwardCalculate the limit lim X-a x-a 5 using the following factorization formula where n is a positive integer and x-➡a a is a real number. x-a = (x-a) (x1+x-2a+x lim x-a X - a x-a 5 = n- + xa an-2 + an−1)arrow_forwardThe function s(t) represents the position of an object at time t moving along a line. Suppose s(1) = 116 and s(5)=228. Find the average velocity of the object over the interval of time [1,5]. The average velocity over the interval [1,5] is Vav = (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardFor the position function s(t) = - 16t² + 105t, complete the following table with the appropriate average velocities. Then make a conjecture about the value of the instantaneous velocity at t = 1. Time Interval Average Velocity [1,2] Complete the following table. Time Interval Average Velocity [1, 1.5] [1, 1.1] [1, 1.01] [1, 1.001] [1,2] [1, 1.5] [1, 1.1] [1, 1.01] [1, 1.001] ப (Type exact answers. Type integers or decimals.) The value of the instantaneous velocity at t = 1 is (Round to the nearest integer as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the following limit or state that it does not exist. Assume b is a fixed real number. (x-b) 40 - 3x + 3b lim x-b x-b ... Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (x-b) 40 -3x+3b A. lim x-b x-b B. The limit does not exist. (Type an exact answer.)arrow_forwardx4 -289 Consider the function f(x) = 2 X-17 Complete parts a and b below. a. Analyze lim f(x) and lim f(x), and then identify the horizontal asymptotes. x+x X--∞ lim 4 X-289 2 X∞ X-17 X - 289 lim = 2 ... X∞ X - 17 Identify the horizontal asymptotes. Select the correct choice and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice. A. The function has a horizontal asymptote at y = B. The function has two horizontal asymptotes. The top asymptote is y = and the bottom asymptote is y = ☐ . C. The function has no horizontal asymptotes. b. Find the vertical asymptotes. For each vertical asymptote x = a, evaluate lim f(x) and lim f(x). Select the correct choice and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. earrow_forwardExplain why lim x²-2x-35 X-7 X-7 lim (x+5), and then evaluate lim X-7 x² -2x-35 x-7 x-7 Choose the correct answer below. A. x²-2x-35 The limits lim X-7 X-7 and lim (x+5) equal the same number when evaluated using X-7 direct substitution. B. Since each limit approaches 7, it follows that the limits are equal. C. The numerator of the expression X-2x-35 X-7 simplifies to x + 5 for all x, so the limits are equal. D. Since x²-2x-35 X-7 = x + 5 whenever x 7, it follows that the two expressions evaluate to the same number as x approaches 7. Now evaluate the limit. x²-2x-35 lim X-7 X-7 = (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardA function f is even if f(x) = f(x) for all x in the domain of f. If f is even, with lim f(x) = 4 and x-6+ lim f(x)=-3, find the following limits. X-6 a. lim f(x) b. +9-←x lim f(x) X-6 a. lim f(x)= +9-←x (Simplify your answer.) b. lim f(x)= X→-6 (Simplify your answer.) ...arrow_forwardEvaluate the following limit. lim X-X (10+19) Select the correct answer below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice. 10 A. lim 10+ = 2 ☐ (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.) X-∞ B. The limit does not exist.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL  College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
