
Concept explainers
a.
To graph the given equation.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
Given function is
Graph :
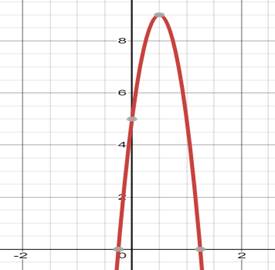
Interpretation :
The graph of a
This vertex point shall be:
Highest point (if
Or, lowest point (if
In this case, ‘a’ is lesser than 0 hence the graph will have a maximum and will open downwards.
A parabola always points to infinity, either negative or positive.
To graph a quadratic function, compute the axis of symmetry, vertex and y-intercept, post which, plot the same on a graph.
The axis of symmetry bisects the parabola into two equal parts. Hence each point on the parabola would have an equal point on the other side of the axis of symmetry. Plot these points on the graph with a smooth curve.
Formula to compute equation of the axis of symmetry
Axis of symmetry for the given function is
Formula for axis of symmetry.
Putting the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ .
Simplifying this
Vertex can be found out by putting the value of x computed in the axis of symmetry in the original function. This will give a value of y . These two coordinates of x and y would be the point where the vertex is.
Putting the value of
Simplifying the expression.
Thus the vertex is
y-intercept is computed by substituting the value of x in the equation by 0.
Simplifying
Hence the point of y-intercept is
Now, plot these points along with their reflecting symmetric points, starting from the vertex.
b.
To calculate the height from which the ball is thrown.
b.
Answer to Problem 21CYU
The height from with the ball is thrown is 5 feet .
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
The function provided is
Formula used :
The ball is thrown from a certain height. This can be calculated by finding the y-intercept of the equation.
For finding the y-intercept, substitute the value of x in the function with 0 and compute the value of y . Y -intercept is always given by the notion (0,y) .
Calculation :
y-intercept is computed by substituting the value of x in the equation by 0.
Simplifying
Hence the point of y-intercept is
Thus it can be said that the ball was initially at the height of 5 feet . This is the y coordinate of the point of the y-intercept.
c.
To calculate the maximum height that the ball reaches.
c.
Answer to Problem 21CYU
The maximum height that the ball reaches is 9 feet .
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
The function provided is
Formula used :
The maximum height can be calculated using the vertex formula. Here, find the y-coordinate of the point of the vertex. This value will be the maximum height attained by the ball.
Calculation :
Time at which the ball reaches maximum height.
Putting the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ .
Simplifying
Vertex can be found out by putting the value of x computed in the axis of symmetry in the original function. This will give a value of y , that will be the maximum height in feet.
Putting the value of
Simplifying the expression.
Thus, the maximum height is at 9 feet .
Chapter 9 Solutions
Algebra 1, Homework Practice Workbook (MERRILL ALGEBRA 1)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
- Round as specified A) 257 down to the nearest 10’s place B) 650 to the nearest even hundreds, place C) 593 to the nearest 10’s place D) 4157 to the nearest hundreds, place E) 7126 to the nearest thousand place arrow_forwardEstimate the following products in two different ways and explain each method  A) 52x39 B) 17x74 C) 88x11 D) 26x42arrow_forwardFind a range estimate for these problems A) 57x1924 B) 1349x45 C) 547x73951arrow_forward
- Draw the image of the following figure after a dilation centered at the origin with a scale factor of 14 退 14 12- 10 5- + Z 6 的 A X 10 12 14 16 18 G min 3 5arrow_forwardkofi makes a candle as a gift for his mom. The candle is a cube with a volume of 8/125 ft cubed. Kofi wants to paint each face of the candle exepct for the bottom. what is the area he will paint?arrow_forward10 6 9. 8 -7- 6. 5. 4- 3. 2 1- -1 0 -1 2 3 4 ·10 5 6 7 00 8 6 10arrow_forward
- Week 3: Mortgages and Amortiza X + rses/167748/assignments/5379530?module_item_id=23896312 11:59pm Points 10 Submitting an external tool Gider the following monthly amortization schedule: Payment # Payment Interest Debt Payment Balance 1 1,167.34 540.54 626.80 259,873.20 2 1,167.34 539.24 628.10 259,245.10 3 1,167.34 With the exception of column one, all amounts are in dollars. Calculate the annual interest rate on this loa Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a percent. Do NOT round until you calculate the final answer. * Previous a Earrow_forwardCafé Michigan's manager, Gary Stark, suspects that demand for mocha latte coffees depends on the price being charged. Based on historical observations, Gary has gathered the following data, which show the numbers of these coffees sold over six different price values: Price Number Sold $2.70 765 $3.50 515 $2.00 990 $4.30 240 $3.10 325 $4.00 475 Using simple linear regression and given that the price per cup is $1.85, the forecasted demand for mocha latte coffees will be cups (enter your response rounded to one decimal place).arrow_forwardGiven the correlation coefficient (r-value), determine the strength of the relationship. Defend your answersarrow_forward
- ??!!arrow_forwardrections: For problem rough 3, read each question carefully and be sure to show all work. 1. Determine if 9(4a²-4ab+b²) = (6a-3b)² is a polynomial identity. 2. Is (2x-y) (8x3+ y³) equivalent to 16x4-y4? 3. Find an expression that is equivalent to (a - b)³. Directions: For problems 4 and 5, algebraically prove that the following equations are polynomial identities. Show all of your work and explain each step. 4. (2x+5)² = 4x(x+5)+25 5. (4x+6y)(x-2y)=2(2x²-xy-6y²)arrow_forwardName: Mussels & bem A section of a river currently has a population of 20 zebra mussels. The population of zebra mussels increases 60 % each month. What will be the population of zebra mussels after 2 years? 9 10 # of months # of mussels 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 o Graph your data. Remember to title your graph. What scale should be used on the y-axis? What scale should be used on the x-axis? Exponential Growth Equation y = a(1+r)*arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





