
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction:
The heat of the reaction
The formula to calculate
Or,
The bond energy of reactants is positive and the bond energy of products is negative.
The standard enthalpy of reaction is calculated by the summation of standard enthalpy of formation of the product minus the summation of standard enthalpy of formation of product at the standard conditions. The formula to calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction
Here, m and n are the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants and product in the balanced chemical equation.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.91P
Explanation of Solution
The given chemical equation for the gas-phase hydration of ethylene to ethanol is as follows:
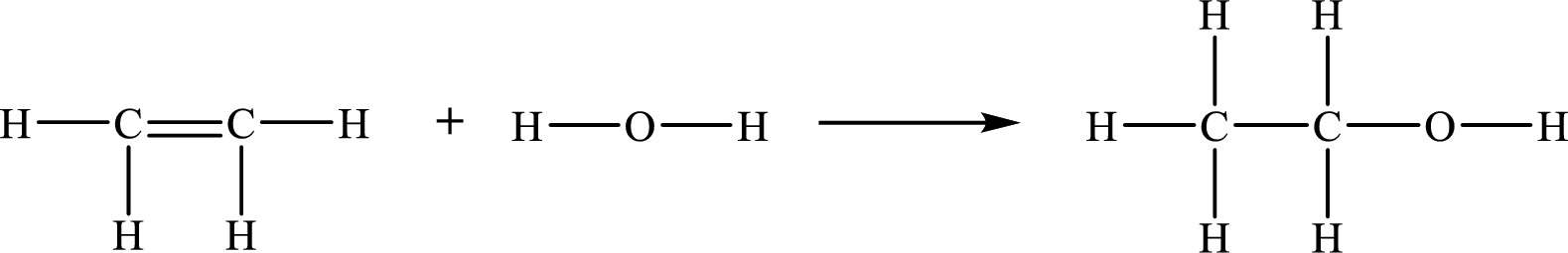
The number of broken bonds is
The number of bonds formed is
The formula to the enthalpy of the given reaction is as follows:
Substitute
The formula to calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction
Substitute
(b)
Interpretation:
Concept introduction:
The heat of the reaction
The formula to calculate
Or,
The bond energy of reactants is positive and the bond energy of products is negative.
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.91P
Explanation of Solution
The given chemical equation for the hydrolysis of ethylene glycol is as follows:
The number of broken bonds is
The number of bonds formed is
The formula to the enthalpy of the given reaction is as follows:
Substitute
(c)
Interpretation:
The reason for the relatively closer value for the hydration in part (a) but not that close for the hydrolysis in part (b) is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Bond energy is the amount of energy needed to break a bond between two gaseous atoms. Bond energy is measured in
The formula to calculate
Or,
The bond energy of reactants is positive and the bond energy of products is negative.
(c)
Answer to Problem 9.91P
In part (b), the same number of similar bonds are broken in the reactant side and formed in the product side so the value of the enthalpy change is zero. Bond energy is generally specific for a bond and remains the same in different molecules.
Explanation of Solution
Bond energy is generally specific for a bond and depends upon the strength of the bond. The bond energy value is the average value so remain same in different molecules.
In part (b), the same number of similar bonds are broken in the reactant side and formed in the product side so the value of the enthalpy change is zero.
For example, the value of bond energy of
The bond energy value is the average value so the bond energy of the same bond in different molecules remains same.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
CHEM 212:CHEMISTSRY V 2
- For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6], [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 4. Room temperature (20°C) measurement of molar magnetic susceptibility (Xm) for Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2×6H2O is 1.1888 x 102 cgs (Gaussian units). Calculate effective magnetic moment and provide a number of unpaired electrons for the iron ion. Use this number to rationalize the coordination geometry around iron center. (4 points)arrow_forward7. Describe the expected 31P and 19F (where applicable) NMR spectral patterns for the following compounds (indicate number of signals and their splitting patterns). a) tetraphenyldiphosphine Ph Ph P-P Ph Ph Ph Ph ' b) tetraphenyldiphosphine monoxide P-P-Ph Ph (2 points) (2 points c) tetrafluorophosphonium hexafluorophosphate [PF4]*[PF6]¯ (4 points)arrow_forward3. For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]4, [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ Which (if any) of these complexes would be expected to display Jahn-Teller distortion? (2 points)arrow_forward
- What is Instrumental Neutron Activation and what are the advantages and disadvantages in using its applications? (I'm doing an in class assignment and need better understanding of what the instrument can be used for) Please include references so that I can better understand the application of how the instrument works!arrow_forwardWhat is Isotope Analysis and what are the advantages and disadvantages in using its applications and instrumentalization? Please include references so that I can better understand how the instrument works!arrow_forward5. Count the electrons on the following complexes and state whether they follow the 18- electron rule: (3 points) Fe(CO)5 Ni(PMe3)4 PMe3 is trimethylphosphine Mn(CO)5Brarrow_forward
- For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]+, [CoCl4]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 2. Draw the corresponding d-orbital splitting for each of the complexes; predict the spin- state (low-spin/high spin) for each of the complexes (if applicable); explain your arguments. Calculate the crystal field stabilization energy for each complex (in Ao or At). (6 points)arrow_forwardFor questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]4, [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 1. Assign oxidation number to the metal, then indicate d-electron count. (3 points)arrow_forwardUsing iodometry I want to titrate a sodium thiosulfate solution and I use 15 mL. If I have 50 mL of a 0.90 M copper solution and KI, what will be the molarity of sodium thiosulfate?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





