
Concept explainers
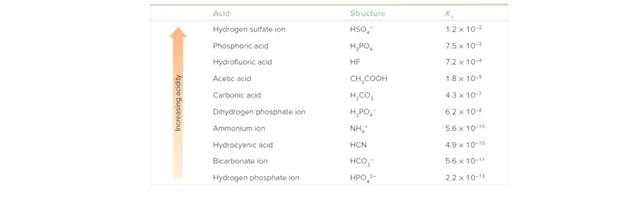
Label the acid in the reactants and the conjugate acid in the products in each reaction. Use the data in Tables 9.2 and 9.3 to determine whether the reactants or products are favored at equilibrium. Explain your reasoning.
a.
b.
c.
Table 9.2 Relative Strength of Acids and Their Conjugate Bases
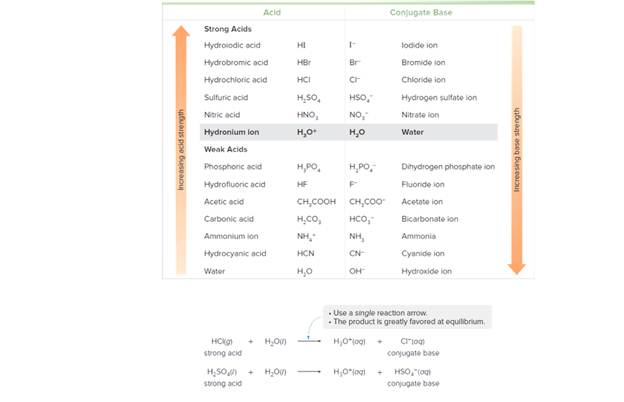 Table 9.3 Acid Dissociation Constants
Table 9.3 Acid Dissociation Constants
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Complete each of these reactions by filling in the blanks. Predict whether each reaction is product-favored or reactant-favored, and explain your reasoning. (a) _________ (aq) + Br(aq) NH3(aq) + HBr(aq) (b) CH3COOH(aq) + CN(aq) ________ (aq) + HCN(aq) (c) ________ (aq)+H2O () NH3(aq) + OH(aq)arrow_forwardMost naturally occurring acids are weak acids. Lactic acid is one example. CH3CH(OH)CO2H(s)+H2O(l)H3O+(aq)+CH3CH(OH)CO2(aq) If you place some lactic acid in water, it will ionize to a small extent, and an equilibrium will be established. Suggest some experiments to prow that this is a weak acid and that the establishment of equilibrium is a reversible process.arrow_forwardPredict which of these acid-base reactions are product-favored and which are reactant-favored. In each case write a balanced equation for any reaction that might occur, even if the reaction is reactant-favored. Consult Table 14.2 if necessary. H2O(ℓ) + HNO3(aq) H3PO4(aq) + H2O(ℓ) CN−(aq) + HCl(aq)arrow_forward
- Predict which of these acid-base reactions are product-favored and which are reactant-favored. In each case write a balanced equation for any reaction that might occur, even if the reaction is reactant-favored. Consult Table 14.2 if necessary. (a) NH4+(aq)+HPO42(aq) (b) CH3COOH(aq) + OH(aq) (c) HSO4(aq)+H2PO4(aq) (d) CH3COOH(aq) + F(aq)arrow_forward1. The odor of spoiled butter is due in part to butanoic acid (HC4H7O2) which results from the breakdown of the fat in butter. A 0.100M solution of butanoic acid is 1.23% ionized. a. Write the chemical equation for the ionization of this acid in water. b. Write the Ka expression for this acid. c. What is the equilibrium concentration of each product and the reactant?arrow_forwardCan someone solve part B and then explain why its the right answer. I'm confused on how to solve b.arrow_forward
- Consider the K, values for the following acids: Cyanic acid, HOCN, 3.5x 10+ Formic acid, HCHO, 17*10* Lactic acid, HC,H,O,, 13 x 10 Propionic acid, HC,H,O,, 1.3 × 10-5 Benzoic acid, HC-H502, 6.3 × 10 Given initially equimolar solutions of each weak acid, which solution will have the lowest pH once equilibrium is established? OHCHO2 HOCN HC3H5O3 HC3H5O2 HCH5O2arrow_forwardThe pH of a solution containing a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 x 10-5 is: A. 3 and its pOH is 6B. 3 and its pOH is 7C. 5 and its pOH is 8D. 5 and its pOH is 9arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate K for the following acid/base reaction? H25 (aq) +F (aq) ++ HF (aq) +HS (aq) ACID BASE HCI C H2SO4 HNO3 H30 (aq) HSO H3PO4 HSO NO3 H2O so, H,PO, F HF CH3COOH H,CO3 H,S H,PO, NH, CH;COO HCO, HS HPO, NH, CO PO OH HCO HPO. 1,0 OH H, CH CH, OA unable to determine OB. K.<1 Base strength increasing Acid strength increasingarrow_forward
- Heroin, a derivative of morphine, is a powerful analgesic and a powerful narcotic agent. Calculate K, for heroin if the pH of a 1.7 x 10-3 M solution was found to be 9.60. O 9.5 x 10-7 2.3 x 10-2 O 9.3 x 10-7 O 1.5 x 10-7arrow_forwardFor each of the following reactions, identify the acid and the base. Also indicate which acid- base definition (Lewis, Brønsted-Lowry) applies. In some cases, more than one definition may apply. a. AlBr3 + Br → AIBr, b. HCIO4 + CH;CN→ CH;CNH† + CIO4¯ c. Ni2+ + 6 NH3 d. NH3 + CIF→H¿N•CIF →[Ni(NH3)6]** -arrow_forwardWhich direction does the equilibrium below favor and what is the deciding factor? H+ cat. H20 HO, HOarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





