
Concept explainers
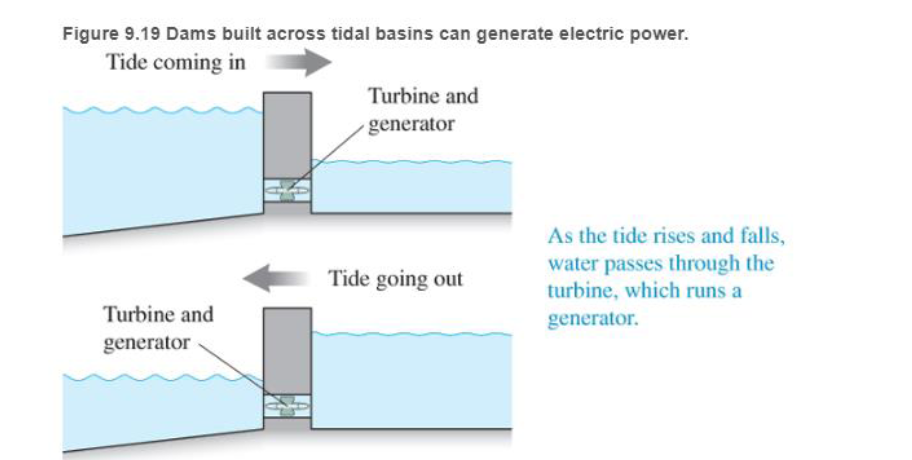
Tidal energy Tides are now used so gene-ate electric power in two ways. In the first, huge dams can be built. across the mouth of a river where it exits to the ocean. As the ocean tide moves in and out of this tidal bas in or estuary, the water flows through tunnels in the dam (see Figure 9.19). This flowing water turns turbines in the tunnels that run electric generators. Unfortunately, this technique works best with large increases in tides—a 5-m difference between high and low tide Such differences are found at only a small number of places Currently, France is the only country that successfully uses this power source A tidal basin plant in France, the Rance. Tidal Power Station. makes 240 megawatts of power—enough energy to power 240,000 homes. Damming tidal basins can have negative environmental effects because of reduced tidal flow and silt buildup. Another disadvantage is that they can only generate electricity when the tide is flowing in or out, for about 10 hours each day.
A second method for collecting energy from the tidal flow (as well as all water flow) is to place turbines directly in the water—like windmills in moving water instead of in moving air. These water turbines have the advantages that they are much cheaper to build, they do not have the environmental problems of a tidal basin, and there are many more suitable sites for such water flow energy farms. Also the energy density of flowing water is about 800 times the energy density of dry air flow. Verdant Power is developing turbine prototypes in the East River near New York City and in the Saint Lawrence Seaway in Canada, and they are looking at other sites in the Puget Sound and all over the world. The worldwide potential tor hydroelectric power is about
—enough to supply the world's energy needs.
If the Rance Tidal Power Station in France could produce power 24 hours a day, which answer below is closest to the daily amount of energy in joules that it could produce?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
College Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Lab Assignment #3 Vectors 2. Determine the magnitude and sense of the forces in cables A and B. 30° 30° 300KN 3. Determine the forces in members A and B of the following structure. 30° B 200kN Name: TA: 4. Determine the resultant of the three coplanar forces using vectors. F₁ =500N, F₂-800N, F, 900N, 0,-30°, 62-50° 30° 50° F₁ = 500N = 900N F₂ = 800Narrow_forwardLab Assignment #3 Vectors Name: TA: 1. With the equipment provided in the lab, determine the magnitude of vector A so the system is in static equilibrium. Perform the experiment as per the figure below and compare the calculated values with the numbers from the spring scale that corresponds to vector A. A Case 1: Vector B 40g Vector C 20g 0 = 30° Vector A = ? Case 2: Vector B 50g Vector C = 40g 0 = 53° Vector A ? Case 3: Vector B 50g Vector C 30g 0 = 37° Vector A = ?arrow_forwardThree point-like charges are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 20.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between q1 and q2 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (A). Let q1=-1.30 µC, q2=-4.20µC, and q3= +4.30 µC. __________________ N/Carrow_forward
- Find the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. 2.01 0.30 µF 2.5 µF 10 μF × HFarrow_forwardI do not understand the process to answer the second part of question b. Please help me understand how to get there!arrow_forwardRank the six combinations of electric charges on the basis of the electric force acting on 91. Define forces pointing to the right as positive and forces pointing to the left as negative. Rank in increasing order by placing the most negative on the left and the most positive on the right. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) [most negative 91 = +1nC 92 = +1nC 91 = -1nC 93 = +1nC 92- +1nC 93 = +1nC -1nC 92- -1nC 93- -1nC 91= +1nC 92 = +1nC 93=-1nC 91 +1nC 92=-1nC 93=-1nC 91 = +1nC 2 = −1nC 93 = +1nC The correct ranking cannot be determined. Reset Help most positivearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





