
COST ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781264022021
Author: LANEN
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 61P
Utica Manufacturing (UM) was recently acquired by MegaMachines, Inc. (MM), and organized as a separate division within the company. Most manufacturing plants at MM use an ABC system, but UM has always used a traditional product costing system. Bob Miller, the plant controller at UM, has decided to experiment with ABC and has asked you to help develop a simple ABC system that would help him decide if it was useful. The controller’s staff has identified costs for the first month in the four
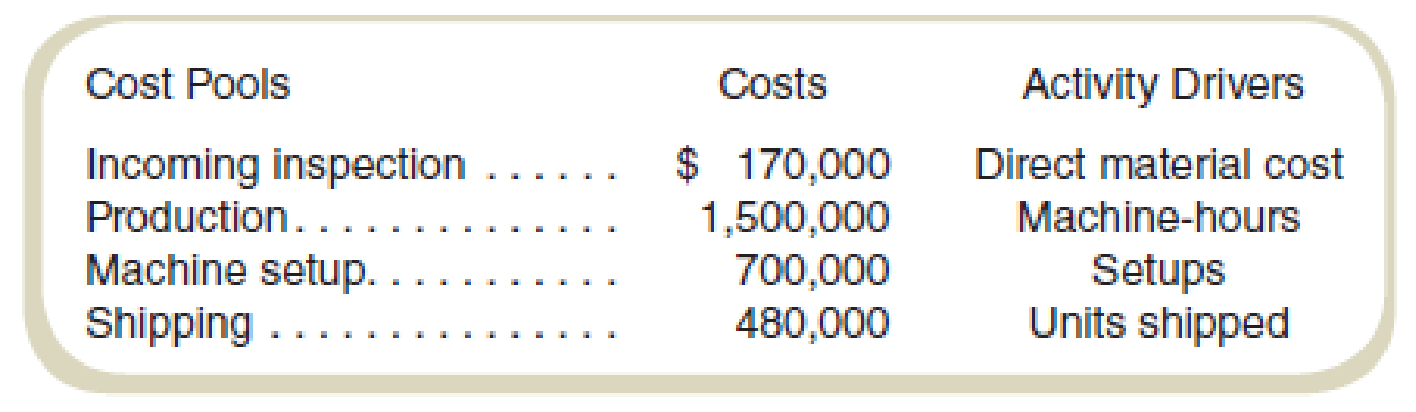
The company manufactures two basic products with model numbers 308 and 510. The following are data for production for the first month as part of MM:

Required
- a. The current cost accounting system charges overhead to products based on machine-hours. What unit product costs will be reported for the two products if the current cost system continues to be used?
- b. A consulting firm has recommended using an activity-based costing system, with the activities based on the cost pools identified by the cost accountant. What are the cost driver rates for the four cost pools identified by the cost accountant?
- c. What unit product costs will be reported for the two products if the ABC system suggested by the cost accountant’s classification of cost pools is used?
- d. If management should decide to implement an activity-based costing system, what benefits should it expect?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Burlington manufacturing complete solution general accounting question
Do fast answer of this general accounting question
Variance
Chapter 9 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT
Ch. 9 - Give examples of cost drivers commonly used to...Ch. 9 - What is the death spiral? How is it related to the...Ch. 9 - The product costs reported using either plantwide...Ch. 9 - Why do companies commonly use direct labor-hours...Ch. 9 - What are the costs of moving to an activity-based...Ch. 9 - What are the basic steps in computing costs using...Ch. 9 - Prob. 7RQCh. 9 - Prob. 8RQCh. 9 - What type of organization is most likely to...Ch. 9 - Prob. 10RQ
Ch. 9 - How does complexity lead to higher costs? Why is...Ch. 9 - Prob. 12RQCh. 9 - Prob. 13RQCh. 9 - Why are cost drivers based on direct labor widely...Ch. 9 - Prob. 15CADQCh. 9 - Activity-based costing could not be applied in a...Ch. 9 - Activity-based costing is the same as department...Ch. 9 - Prob. 18CADQCh. 9 - It is clear after reading this chapter that...Ch. 9 - Prob. 20CADQCh. 9 - Prob. 21CADQCh. 9 - Prob. 22CADQCh. 9 - Prob. 23CADQCh. 9 - Activity-based costing is just another inventory...Ch. 9 - Prob. 25CADQCh. 9 - Prob. 26CADQCh. 9 - Prob. 27CADQCh. 9 - One of the issues we identified with traditional...Ch. 9 - The cost accounting manager at your business says...Ch. 9 - Prob. 30CADQCh. 9 - Prob. 31ECh. 9 - Reported Costs and Decisions Kima Company...Ch. 9 - Plantwide versus Department Allocation Munoz...Ch. 9 - Plantwide versus Department Allocation Main Street...Ch. 9 - Unitwide versus Department...Ch. 9 - Prob. 36ECh. 9 - Prob. 37ECh. 9 - Upriver currently applies overhead on the basis of...Ch. 9 - Compute the unit costs for the two products, V-1...Ch. 9 - Prob. 40ECh. 9 - Prob. 41ECh. 9 - Activity-Based Costing in a Nonmanufacturing...Ch. 9 - Activity-Based versus Traditional Costing Maglie...Ch. 9 - Activity-Based Costing versus Traditional Costing...Ch. 9 - Activity-Based Costing in a Service Environment...Ch. 9 - Activity-Based versus Traditional Costing Isadores...Ch. 9 - Prob. 47ECh. 9 - Activity-Based Costing: Cost Flows through...Ch. 9 - Prob. 49ECh. 9 - Activity-Based Costing for an Administrative...Ch. 9 - Prob. 51ECh. 9 - Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing Kim...Ch. 9 - Time-Driven ABC for an Administrative Service The...Ch. 9 - Comparative Income Statements and Management...Ch. 9 - Comparative Income Statements and Management...Ch. 9 - Prob. 56PCh. 9 - Activity-Based Costing and Predetermined Overhead...Ch. 9 - Activity-Based Costing and Predetermined Overhead...Ch. 9 - Choosing an Activity-Based Costing System Pickle...Ch. 9 - Churchill Products is considering updating its...Ch. 9 - Utica Manufacturing (UM) was recently acquired by...Ch. 9 - Cain Components manufactures and distributes...Ch. 9 - Prob. 63PCh. 9 - Prob. 64PCh. 9 - Prob. 65PCh. 9 - Cawker Products has two manufacturing...Ch. 9 - MTI makes three types of lawn tractors: M3100,...Ch. 9 - Prob. 68PCh. 9 - Prob. 69PCh. 9 - Prob. 72IC
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Provide correct answer general Accounting questionarrow_forwardAnswer? ? General Accounting questionarrow_forwardABC Company has a beginning Work-in-Process inventory of 26,500 units (50% complete). During the period, 125,000 units were started and the ending work in Process inventory consisted of 21,500 units (80% complete). What are the equivalent units for conversion costs using the weighted average process costing?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Cost Accounting - Definition, Purpose, Types, How it Works?; Author: WallStreetMojo;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AwrwUf8vYEY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY