
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The alcohol in the given pair that undergoes an elimination reaction more rapidly when heated with
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the alcohol in the presence of strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
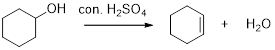
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
(b)
Interpretation:
The alcohol in the given pair that undergoes an elimination reaction more rapidly when heated with
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the alcohol in the presence of strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
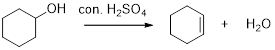
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
(c)
Interpretation:
The alcohol in the given pair that undergoes an elimination reaction more rapidly when heated with
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the alcohol in the presence of strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
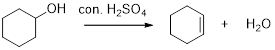
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
(d)
Interpretation:
The alcohol in the given pair that undergoes an elimination reaction more rapidly when heated with
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the alcohol in the presence of strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
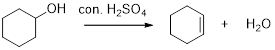
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- When talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?arrow_forwardUsing the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$arrow_forwardIndicate characteristics of oxodec acid.arrow_forward
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward

 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning




