
Introductory Statistics (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780321978271
Author: Robert Gould, Colleen N. Ryan
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 27SE
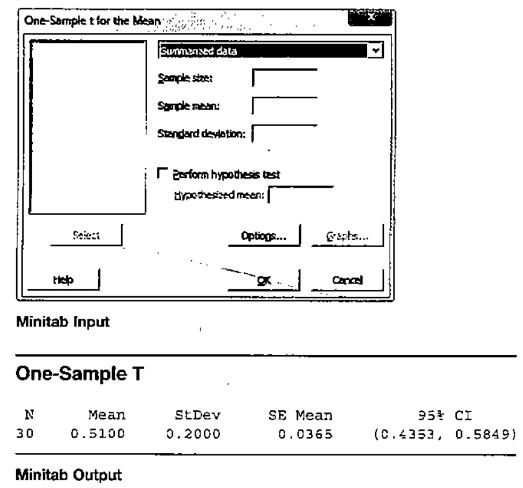
Hamburgers (Example 9) A hamburger chain sells large hamburgers. When we take a sample of 30 hamburgers and weigh them, we find that the
a. State how you would fill in the numbers below to do the calculation with Minitab.
b. Report the confidence interval in a carefully worded sentence.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In a study on speed control, it was found that the main reasons for regulations were to make traffic flow efficient and to minimize the risk of danger. An area that was focused on in the study was the distance required to completely stop a vehicle at various speeds. Use the following table to answer the questions.
MPH
Braking distance (yrds)
5
10
10
17
20
27
30
50
40
60
50
100
60
150
70
200
Business
3. Bayesian Inference – Updating Beliefs
A medical test for a rare disease has the following characteristics:
Sensitivity (true positive rate): 99%
Specificity (true negative rate): 98%
The disease occurs in 0.5% of the population.
A patient receives a positive test result.
Questions:
a) Define the relevant events and use Bayes’ Theorem to compute the probability that the patient actually has the disease.b) Explain why the result might seem counterintuitive, despite the high sensitivity and specificity.c) Discuss how prior probabilities influence posterior beliefs in Bayesian inference.d) Suppose a second, independent test with the same accuracy is conducted and is also positive. Update the probability that the patient has the disease.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Introductory Statistics (2nd Edition)
Ch. 9 - Ages A study of all the students at a small...Ch. 9 - Units A survey of 100 random full-time students at...Ch. 9 - Exam Scores The distribution of the scores on a...Ch. 9 - Exam Scores The distribution of the scores on a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 5SECh. 9 - Cellphone Calls Answers.com claims that the mean...Ch. 9 - Retirement Income Several times during the year,...Ch. 9 - Time Employed A human resources manager for a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9SECh. 9 - Prob. 10SE
Ch. 9 - Babies Weights (Example 2) Some sources report...Ch. 9 - Babies’ Weights, Again Some sources report that...Ch. 9 - Prob. 13SECh. 9 - Prob. 14SECh. 9 - CLT Shapes (Example 4) One of the histograms is a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 16SECh. 9 - Prob. 17SECh. 9 - Student Ages The mean age of all 2550 students at...Ch. 9 - Prob. 19SECh. 9 - Prob. 20SECh. 9 - Prob. 21SECh. 9 - Prob. 22SECh. 9 - Prob. 23SECh. 9 - Random Numbers If you take samples of 40 lines...Ch. 9 - t* (Example 8) A researcher collects one sample of...Ch. 9 - t* A researcher collects a sample of 25...Ch. 9 - Hamburgers (Example 9) A hamburger chain sells...Ch. 9 - Drinks A fast-food chain sells drinks that it...Ch. 9 - Men’s Pulse Rates (Example 10) A random sample of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 30SECh. 9 - Prob. 31SECh. 9 - Prob. 32SECh. 9 - Confidence Interval Changes State whether each of...Ch. 9 - Confidence Interval Changes State whether each of...Ch. 9 - Potatoes The weights of four randomly and...Ch. 9 - Tomatoes The weights of four randomly and...Ch. 9 - Human Body Temperatures (Example 12) A random...Ch. 9 - Reaction Distance Data on the disk and website...Ch. 9 - Potatoes Use the data from exercise 9.35. a. If...Ch. 9 - Tomatoes Use the data from exercise 9.36. a. Using...Ch. 9 - Cholesterol In the U.S. Department of Health has...Ch. 9 - BMI A body mass index (BMI) of more than 25 is...Ch. 9 - Male Height In the United States, the population...Ch. 9 - Vegetarians' Weights The mean weight of all...Ch. 9 - GPAs Thirty GPAs from a randomly selected sample...Ch. 9 - Prob. 46SECh. 9 - GPAs Using the data from Exercise 9.45 on GPAs,...Ch. 9 - Prob. 48SECh. 9 - Atkins Diet Difference Ten people went on an...Ch. 9 - Pulse Difference The following numbers are the...Ch. 9 - Student Ages Suppose that 200 statistics students...Ch. 9 - Presidents’ Ages at Inauguration A 95 confidence...Ch. 9 - Prob. 53SECh. 9 - Prob. 54SECh. 9 - Televisions: CI (Example 14) Minitab output is...Ch. 9 - Pulse and Gender: CI Using data from NHANES, we...Ch. 9 - Televisions (Example 15) The table shows the...Ch. 9 - Pulse Rates Using data from NHANES, we looked at...Ch. 9 - Triglycerides Triglycerides are a form of fat...Ch. 9 - Systolic Blood Pressures When you have your blood...Ch. 9 - Triglycerides, Again Report and interpret the 95...Ch. 9 - Blood Pressures, Again Report and interpret the 95...Ch. 9 - Clothes Spending A random sample of 14 college...Ch. 9 - College Athletes’ Weights A random sample of male...Ch. 9 - Prob. 65SECh. 9 - College Athletes’ Weights In exercise 9.64, you...Ch. 9 - Textbook Prices, UCSB vs. CSUN (Example 16) The...Ch. 9 - Textbook Prices. OC vs. CSUN The prices of a...Ch. 9 - Females’ Pulse Rates before and after a Fright...Ch. 9 - Males’ Pulse Rates before and after a Fright...Ch. 9 - Organic Food A student compared organic food...Ch. 9 - Smoking Mothers The birth weights of 35 babies...Ch. 9 - Ages of Brides and Grooms Data for the ages of...Ch. 9 - Surfers Surfers and statistics students Rex...Ch. 9 - Self-Reported Heights of Men (Example 18) A random...Ch. 9 - Eating Out Jacqueline Loya, a statistics student,...Ch. 9 - 9.77, 9.79, and 9.80 For these questions, the data...Ch. 9 - Prob. 78SECh. 9 - 9.77, 9.79, and 9.80 For these questions, the data...Ch. 9 - 9.77, 9.79, and 9.80 For these questions, the data...Ch. 9 - Choose a test for each situation: one-sample...Ch. 9 - Choose a t-test for each situation: one-sample...Ch. 9 - Cones: 3 Tests A McDonald’s fact sheet says its...Ch. 9 - Prob. 84CRECh. 9 - Brain Size Brain size for 20 random women and 20...Ch. 9 - Prob. 86CRECh. 9 - Heart Rate before and after Coffee Elena Lucin, a...Ch. 9 - Exam Grades The final exam grades for a sample of...Ch. 9 - Hours of Television Viewing The number of hours...Ch. 9 - Reaction Distances Reaction distances in...Ch. 9 - Shift Sleep Hours A survey was done comparing the...Ch. 9 - Prob. 92CRECh. 9 - Maximum Tax Rate A random sample of 10 Democrats...Ch. 9 - Prob. 94CRECh. 9 - Groceries The table shows the prices of identical...Ch. 9 - Parents The following table shows the heights (in...Ch. 9 - Why Is n1 in the Sample Standard Deviation? Why do...Ch. 9 - Prob. 98CRECh. 9 - Construct two sets of body temperatures (in...Ch. 9 - Construct heights for 3 or more sets of twins (6...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. Linear Regression - Model Assumptions and Interpretation A real estate analyst is studying how house prices (Y) are related to house size in square feet (X). A simple linear regression model is proposed: The analyst fits the model and obtains: • Ŷ50,000+150X YBoB₁X + € • R² = 0.76 • Residuals show a fan-shaped pattern when plotted against fitted values. Questions: a) Interpret the slope coefficient in context. b) Explain what the R² value tells us about the model's performance. c) Based on the residual pattern, what regression assumption is likely violated? What might be the consequence? d) Suggest at least two remedies to improve the model, based on the residual analysis.arrow_forward5. Probability Distributions – Continuous Random Variables A factory machine produces metal rods whose lengths (in cm) follow a continuous uniform distribution on the interval [98, 102]. Questions: a) Define the probability density function (PDF) of the rod length.b) Calculate the probability that a randomly selected rod is shorter than 99 cm.c) Determine the expected value and variance of rod lengths.d) If a sample of 25 rods is selected, what is the probability that their average length is between 99.5 cm and 100.5 cm? Justify your answer using the appropriate distribution.arrow_forward2. Hypothesis Testing - Two Sample Means A nutritionist is investigating the effect of two different diet programs, A and B, on weight loss. Two independent samples of adults were randomly assigned to each diet for 12 weeks. The weight losses (in kg) are normally distributed. Sample A: n = 35, 4.8, s = 1.2 Sample B: n=40, 4.3, 8 = 1.0 Questions: a) State the null and alternative hypotheses to test whether there is a significant difference in mean weight loss between the two diet programs. b) Perform a hypothesis test at the 5% significance level and interpret the result. c) Compute a 95% confidence interval for the difference in means and interpret it. d) Discuss assumptions of this test and explain how violations of these assumptions could impact the results.arrow_forward
- 1. Sampling Distribution and the Central Limit Theorem A company produces batteries with a mean lifetime of 300 hours and a standard deviation of 50 hours. The lifetimes are not normally distributed—they are right-skewed due to some batteries lasting unusually long. Suppose a quality control analyst selects a random sample of 64 batteries from a large production batch. Questions: a) Explain whether the distribution of sample means will be approximately normal. Justify your answer using the Central Limit Theorem. b) Compute the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample mean. c) What is the probability that the sample mean lifetime of the 64 batteries exceeds 310 hours? d) Discuss how the sample size affects the shape and variability of the sampling distribution.arrow_forwardA biologist is investigating the effect of potential plant hormones by treating 20 stem segments. At the end of the observation period he computes the following length averages: Compound X = 1.18 Compound Y = 1.17 Based on these mean values he concludes that there are no treatment differences. 1) Are you satisfied with his conclusion? Why or why not? 2) If he asked you for help in analyzing these data, what statistical method would you suggest that he use to come to a meaningful conclusion about his data and why? 3) Are there any other questions you would ask him regarding his experiment, data collection, and analysis methods?arrow_forwardBusinessarrow_forward
- What is the solution and answer to question?arrow_forwardTo: [Boss's Name] From: Nathaniel D Sain Date: 4/5/2025 Subject: Decision Analysis for Business Scenario Introduction to the Business Scenario Our delivery services business has been experiencing steady growth, leading to an increased demand for faster and more efficient deliveries. To meet this demand, we must decide on the best strategy to expand our fleet. The three possible alternatives under consideration are purchasing new delivery vehicles, leasing vehicles, or partnering with third-party drivers. The decision must account for various external factors, including fuel price fluctuations, demand stability, and competition growth, which we categorize as the states of nature. Each alternative presents unique advantages and challenges, and our goal is to select the most viable option using a structured decision-making approach. Alternatives and States of Nature The three alternatives for fleet expansion were chosen based on their cost implications, operational efficiency, and…arrow_forwardBusinessarrow_forward
- Why researchers are interested in describing measures of the center and measures of variation of a data set?arrow_forwardWHAT IS THE SOLUTION?arrow_forwardThe following ordered data list shows the data speeds for cell phones used by a telephone company at an airport: A. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency from the ungrouped data list. B. Group the data in an appropriate frequency table. C. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency using the table in point B. 0.8 1.4 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.6 4.5 4.5 4.6 6.2 6.5 7.7 7.9 9.9 10.2 10.3 10.9 11.1 11.1 11.6 11.8 12.0 13.1 13.5 13.7 14.1 14.2 14.7 15.0 15.1 15.5 15.8 16.0 17.5 18.2 20.2 21.1 21.5 22.2 22.4 23.1 24.5 25.7 28.5 34.6 38.5 43.0 55.6 71.3 77.8arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...
Algebra
ISBN:9781680331141
Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Statistics 4.1 Point Estimators; Author: Dr. Jack L. Jackson II;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2MrI0J8XCEE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Statistics 101: Point Estimators; Author: Brandon Foltz;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4v41z3HwLaM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Central limit theorem; Author: 365 Data Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b5xQmk9veZ4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Point Estimate Definition & Example; Author: Prof. Essa;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OTVwtvQmSn0;License: Standard Youtube License
Point Estimation; Author: Vamsidhar Ambatipudi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=flqhlM2bZWc;License: Standard Youtube License