
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The volume of the atoms in bcc and fcc unit cell in comparison to the volume of the unit cell itself has to be calculated. From these data, the fraction of space occupied by atoms in bcc and fcc unit cell has to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Bcc unit cell:
Eight atoms occupy the corner position of a cube each contributing
Relationship between unit cell edge length and radius of a unit cell of a bcc arrangement:
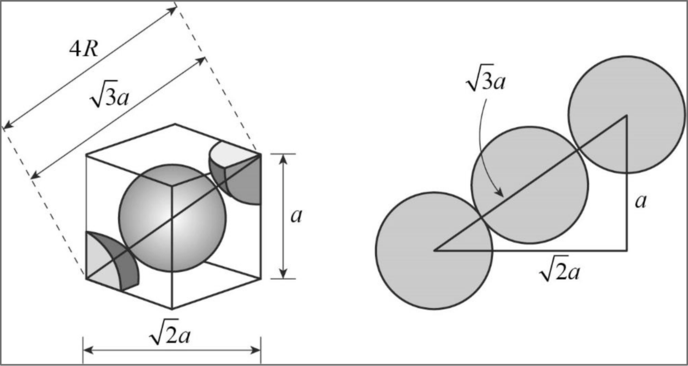
Figure 1
Applying Pythagoras theorem, from the diagram we can clearly concluded that
Body diagonal
Fcc unit cell:
Eight atoms occupy the corner position of a cube each contributing
Relationship between unit cell edge length and radius of a unit cell of a fcc arrangement:
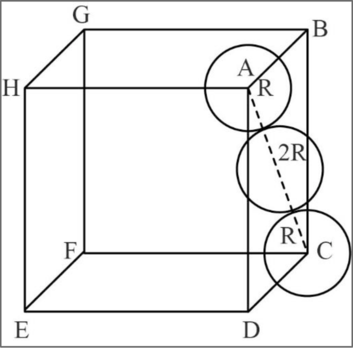
Figure 2
In fcc, the corner spheres are in touch with the face centered sphere as shown in the above figure. Hence, the face diagonal
Consider right angled triangle ACD.
Volume of a cubic unit cell:
Volume of cubic unit cell
Volume of a sphere:
Volume of a sphere
Packing fraction:
Packing fraction is the fraction of space occupied by total number of atoms per unit cell.
Mathematically, it can be represented as given below.
Fraction of space occupied by atoms in a unit cell
Where,
Answer to Problem 115QRT
The fraction of space occupied by atoms in bcc and fcc unit cell is
Explanation of Solution
The atoms can be assumed to be spherical in shape with radius
There are two atoms present per one bcc unit cell. The relationship between unit cell edge length and radius of a unit cell of a bcc arrangement is given below.
Now, the total volume of two atoms present in a bcc unit cell can be calculated as given below.
There are four atoms present per one fcc unit cell. The relationship between unit cell edge length and radius of a unit cell of a fcc arrangement is given below.
Now, the total volume of two atoms present in a bcc unit cell can be calculated as given below.
Volume of cubic unit cell ,
Now, the fraction of space occupied by atoms can be calculated as given below.
For bcc unit cell:
Fraction of space occupied by atoms
For fcc unit cell:
Fraction of space occupied by atoms
Therefore, the fraction of space occupied by atoms in bcc and fcc unit cell is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
OWLV2 FOR MOORE/STANITSKI'S CHEMISTRY:
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





