
a)
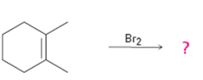
Interpretation:
The product formed with its stereochemistry, when 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene reacts with Br2 is to be given. The mechanism of its formation also is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The reaction of halogens to
To give:
The product expected, along with its stereochemistry, when Br2 is added to 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene.
b)
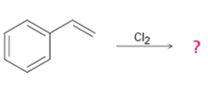
Interpretation:
The product obtained with its stereochemistry, in the reaction shown, is to be given. The mechanism of its formation also is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The reaction of halogens to alkenes occurs with anti stereochemistry, that is, the two halogen atoms come from opposite faces of the double bond, one from top face and other from bottom face. In the first step, the addition of halogen to the double bond in the alkenes results in the formation of a cyclic halonium ion with the simultaneous elimination of a halide ion. The large halonium ion shields one side of the molecule. Hence the attack of the halide ion occurs from the opposite, unshielded side to yield a trans product.
To give:
The product expected, along with its stereochemistry, when Cl2 is added to styrene (vinyl benzene).
c)
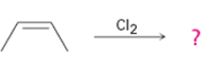
Interpretation:
The product obtained with its stereochemistry in the reaction shown is to be given. The mechanism of its formation also is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The reaction of halogens to alkenes occurs with anti stereochemistry, that is, the two halogen atoms come from opposite faces of the double bond- one from top face and other from bottom face. In the first step, the addition of halogen to the double bond in the alkenes results in the formation of a cyclic halonium ion with the simultaneous elimination of a halide ion. The large halonium ion shields one side of the molecule. Hence the attack of the halide ion occurs from the opposite, unshielded side to yield a trans-product.
To give:
The product expected, along with its stereochemistry, when Cl2 is added to 2-butene.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- H-Br Energy 1) Draw the step-by-step mechanism by which 3-methylbut-1-ene is converted into 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 2) Sketch a reaction coordinate diagram that shows how the internal energy (Y- axis) of the reacting species change from reactants to intermediate(s) to product. Brarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forwardWhat alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- 2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- 2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). H-Br CH2Cl2arrow_forward
