
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780078028229
Author: Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.7, Problem 9PP
Determine v and i for t > 0 in the circuit of Fig. 8.28. (See comments about current sources in Practice Prob. 7.5.)
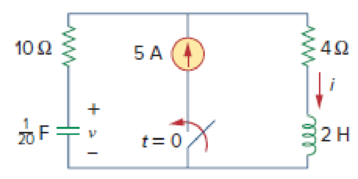
Figure 8.28
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
help on this question about three-phase half-wave rectifier? Also it envolves a little bit of signals and systems.
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Chapter 8 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Ch. 8.2 - The switch in Fig. 8.4 was open for a long time...Ch. 8.2 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.7, find: (a) iL(0+),...Ch. 8.3 - If R = 10 , L = 5 H, and C = 2 mF in Fig. 8.8,...Ch. 8.3 - The circuit in Fig. 8.12 has reached steady state...Ch. 8.4 - In Fig. 8.13, let R = 2 , L = 0.4 H, C = 25 mF,...Ch. 8.4 - Refer to the circuit in Fig. 8.17. Find v(t) for t...Ch. 8.5 - Having been in position a for a long time, the...Ch. 8.6 - Find i(t) and v(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 8.7 - Determine v and i for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 8.7 - For t 0, obtain v0(t) in the circuit of Fig....
Ch. 8.8 - In the op amp circuit shown in Fig. 8.34, vs =...Ch. 8.9 - Find i(t) using PSpice for 0 t 4 s if the pulse...Ch. 8.9 - Refer to the circuit in Fig. 8.21 (see Practice...Ch. 8.10 - Draw the dual circuit of the one in Fig. 8.46.Ch. 8.10 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.50, obtain the dual...Ch. 8.11 - In Fig. 8.52, find the capacitor voltage vC for t ...Ch. 8.11 - The output of a D/A converter is shown in Fig....Ch. 8 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.58, the capacitor...Ch. 8 - For Review Questions 8.1 and 8.2. 8.2For the...Ch. 8 - When a step input is applied to a second-order...Ch. 8 - If the roots of the characteristic equation of an...Ch. 8 - In a series RLC circuit, setting R = 0 will...Ch. 8 - Prob. 6RQCh. 8 - Refer to the series RLC circuit in Fig. 8.59. What...Ch. 8 - Consider the parallel RLC circuit in Fig. 8.60....Ch. 8 - Match the circuits in Fig. 8.61 with the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 10RQCh. 8 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.62, find: (a)i(0+) and...Ch. 8 - Using Fig. 8.63, design a problem to help other...Ch. 8 - Refer to the circuit shown in Fig. 8.64....Ch. 8 - In the circuit of Fig. 8.65, find: (a) v(0+) and...Ch. 8 - Refer to the circuit in Fig. 8.66. Determine: (a)...Ch. 8 - In the circuit of Fig. 8.67, find: (a) vR(0+) and...Ch. 8 - A series RLC circuit has R = 20 k, L = 0.2 mH, and...Ch. 8 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 8 - The current in an RLC circuit is described by...Ch. 8 - The differential equation that describes the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 11PCh. 8 - If R = 50 , L = 1.5 H, what value of C will make...Ch. 8 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.68, calculate the value...Ch. 8 - The switch in Fig. 8.69 moves from position A to...Ch. 8 - The responses of a series RLC circuit are...Ch. 8 - Find i(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig. 8.70....Ch. 8 - In the circuit of Fig. 8.71, the switch...Ch. 8 - Find the voltage across the capacitor as a...Ch. 8 - Obtain v(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig. 8.73....Ch. 8 - The switch in the circuit of Fig. 8.74 has been...Ch. 8 - Calculate v(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 8 - Assuming R = 2 k, design a parallel RLC circuit...Ch. 8 - For the network in Fig. 8.76, what value of C is...Ch. 8 - The switch in Fig. 8.77 moves from position A to...Ch. 8 - Using Fig. 8.78, design a problem to help other...Ch. 8 - The step response of an RLC circuit is given by...Ch. 8 - Prob. 27PCh. 8 - A series RLC circuit is described by...Ch. 8 - Solve the following differential equations subject...Ch. 8 - Prob. 30PCh. 8 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 8.79. Find vL(0+) and...Ch. 8 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.80, find v(t) for t 0.Ch. 8 - Find v(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig. 8.81.Ch. 8 - Calculate i(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 8 - Using Fig. 8.83, design a problem to help other...Ch. 8 - Obtain v(t) and i(t) for t 0 in the circuit of...Ch. 8 - For the network in Fig. 8.85, solve for i(t) for t...Ch. 8 - Refer to the circuit in Fig. 8.86. Calculate i(t)...Ch. 8 - Determine v(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 8 - The switch in the circuit of Fig. 8.88 is moved...Ch. 8 - For the network in Fig. 8.89, find i(t) for t 0....Ch. 8 - Given the network in Fig. 8.90, find v(t) for t ...Ch. 8 - The switch in Fig. 8.91 is opened at t = 0 after...Ch. 8 - A series RLC circuit has the following parameters:...Ch. 8 - In the circuit of Fig. 8.92, find v(t) and i(t)...Ch. 8 - Prob. 46PCh. 8 - Find the output voltage vo(t) in the circuit of...Ch. 8 - Given the circuit in Fig. 8.95, find i(t) and v(t)...Ch. 8 - Determine i(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 8 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.97, find i(t) for t 0....Ch. 8 - Find v(t) for t 0 in the circuit of Fig. 8.98....Ch. 8 - The step response of a parallel RLC circuit is...Ch. 8 - After being open for a day, the switch in the...Ch. 8 - Using Fig. 8.100, design a problem to help other...Ch. 8 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.101, find v(t) for t 0....Ch. 8 - In the circuit of Fig. 8.102, find i(t) for t 0....Ch. 8 - Given the circuit shown in Fig. 8.103, determine...Ch. 8 - In the circuit of Fig. 8.104, the switch has been...Ch. 8 - The switch in Fig. 8.105 has been in position 1...Ch. 8 - Obtain i1 and i2 for t 0 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 8 - For the circuit in Prob. 8.5, find i and v for t ...Ch. 8 - Find the response vR(t) for t 0 in the circuit of...Ch. 8 - For the op amp circuit in Fig. 8.108, find the...Ch. 8 - Using Fig. 8.109, design a problem to help other...Ch. 8 - Determine the differential equation for the op amp...Ch. 8 - Obtain the differential equations for vo(t) in the...Ch. 8 - In the op amp circuit of Fig. 8.112, determine...Ch. 8 - For the step function vs = u(t), use PSpice or...Ch. 8 - Given the source-free circuit in Fig. 8.114, use...Ch. 8 - For the circuit in Fig. 8.115, use PSpice or...Ch. 8 - Obtain v(t) for 0 t 4 s in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 8 - The switch in Fig. 8.117 has been in position 1...Ch. 8 - Design a problem, to be solved using PSpice or...Ch. 8 - Draw the dual of the circuit shown in Fig. 8.118.Ch. 8 - Obtain the dual of the circuit in Fig. 8.119.Ch. 8 - Find the dual of the circuii in Fig. 8.120.Ch. 8 - Draw the dual of the circuit in Fig. 8.121.Ch. 8 - An automobile airbag igniter is modeled by the...Ch. 8 - A load is modeled as a 100-mH inductor in parallel...Ch. 8 - A mechanical system is modeled by a series RLC...Ch. 8 - An oscillogram can be adequately modeled by a...Ch. 8 - The circuit in Fig. 8.123 is the electrical analog...Ch. 8 - Figure 8.124 shows a typical tunnel-diode...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
A byte is made up of eight a. CPUs b. addresses c. variables d. bits
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Correlation of experimental data for the average heat transfer coefficient for turbulent flow through tubes is given by NUD =hD/k=0.023 (Rep) 0.8 (Pr) 1/3 The Reynolds number, Re₁ = πD/v, is based on the tube diameter D, the average flow velocity ū and the kinematic viscosity v. Consider the flow of air and of water through tubes of identical size. Assume that the average velocity is the same for both fluids. If the average temperature for both fluids is 80°C, determine the ratio of the heat transfer coefficient of water to that of air.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- help on questions about singals and systems?arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardI have this code in matlab: clc; n=0:8; %20 harmonic indices jn=besselj(n,5);% 5 is the modulation index jnn=abs(jn); jn1 = 20.*log10(jnn*0.5); fc=1e+6; %carrier frequency fm=10e+3; %message frequency frq1 = (fc+n.*fm)*1e-06; frq2 = (fc-n.*fm)*1e-06; frequencies = [frq2,frq1]; %Lower and upper side magnitudes = [jn1,jn1]; %Magnitude of Jn corresponding to the frequencies % Plot figure; stem(frequencies, magnitudes, 'filled'); % Stem plot for spectrum visualization title('Magnitude Spectrum of FM Signal'); xlabel('Frequency (MHz)'); ylabel('Magnitude'); grid on; I am getting the lines opposite (the line should be traced from bottom to top not from top to bottom) as shown in the picture. How can I fix this?arrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward.I need in the way of spaces and not in shortened ways A 3-phase, 50 Hz, 132 kV overhead line transpose system of bundle conductors .a radius of conductor is 0.5 cm Calculate the total inductance of the line.) bi 4m C1 al 4m m birarrow_forward1B) Suppose the flip-flops are 74F74 devices and the AND gates are 74F08 devices. Let maxtpd,D=9ns, maxtsu,D=3ns, and maxtpd,AND=6ns. What is the maximum clock frequency at which the circuit can operate reliably? 2) Compare serial transmission and parallel transmission and discuss their advantages and disadvantages. 3) Explain briefly how the slave can protect itself from being overwhelmed by the master in I2 4) A hypothetical logic family has the following specifications. VOH=4.6V VIH=4.0V VOL=0.5V VIL=1.0V IOH=-1mA IIH=50μA IOL=8mA IIL=-0.6mA (4a) What are the noise margins? (4b) What is the fan-out capability? That is, suppose all gates are chosen from the same logic family, how many gates can an output gate reliably drive? 5) Explain briefly why USB device address and…arrow_forward
- can you drow set Vi=0, set Vo=0 B. For the FET amplifier circuit of Fig.(2), determine the topolgy, and the gain without and with feedback with the following circuit values: rao, and g 4mS Is Voo 60 K www 100 K 0.25 K IK Fig.(2) 20 K ww Voarrow_forwardcan you draw acircuit For the feedback circuit shown below VDD Set Vico set Vo=0 Is 100 K 26 K 2 K Q1 76 K IF 60 K 40 K Voarrow_forwardThe previous solutions are incorrect and unclear. If possible, please solve the question on the images .clearly. Thank you A 3-phase, 50 Hz, 132 kV overhead line transpose system of bundle conductors .a radius of conductor is 0.5 cm. Calculate the total inductance of the line. bi 4m m im birarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
ENA 9.2(1)(En)(Alex) Sinusoids & Phasors - Explanation with Example 9.1 ,9.2 & PP 9.2; Author: Electrical Engineering Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vX_LLNl-ZpU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Electrical Engineering: Ch 10 Alternating Voltages & Phasors (8 of 82) What is a Phasor?; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2I1tF3ixNg0;License: Standard Youtube License