
To find: Describe the motion of the object. Be sure to give the mass and damping factor.
b. What is the initial displacement of the bob? That is, what is the displacement at ?
c. Graph the motion using a graphing utility.
d. What is the displacement of the bob at the start of the second oscillation?
e. What happens to the displacement of the bob as time increases without bound?
Answer to Problem 49AYU
a. It is damped motion with a bob of mass 35kg and a damping factor of
b. Initial displacement is meters leftward
c. Graph is plotted
d. Displacement of the bob at the second oscillation is meters leftwards.
e. Hence increases displacement tends to become 0 or the bob comes to rest.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The distance (in meters) of the bob of a pendulum of mass (in kilograms) from its rest position at time (in seconds) is given. The bob is released from the left of its rest position and represents a negative direction.
Formula used:
The displacement of an oscillating object from its at–rest position at time is given by ,
where is the damping factor or damping coefficient and is the mass of the oscillating object. Here is the displacement at , and is the period under simple harmonic motion (no damping).
Calculation:
a.
,
From the given equation
b the damping factor is and
mass of the bob is
It is damped motion with a bob of mass 15kg and a damping factor of
b. To find the initial displacement let us substitute in the given equation.
Initial displacement is meters leftward
c. The graph of
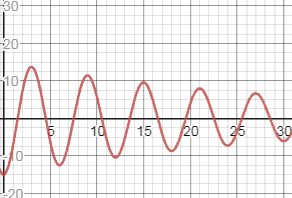
d. From the graph below we see that the displacement of the bob at the second oscillation is , that is meters leftwards.
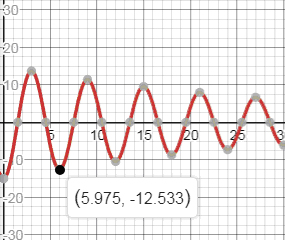
e. Displacement of the bob as t increases tends to 0. Hence increases displacement tends to become 0 or the bob comes to rest.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
- The graph of f' is below. Use it to determine where the local minima and maxima for f are. If there are multiple answers, separate with commas. 2 f'(x) N -5 -4 3-2-1 -1 -2 -3 -4 12 3 4 5 -x Local minima at x Local maxima at xarrow_forwardThe graph of f' is below. Use it to determine the intervals where f is increasing. -5-4-32 4- 3 2 1 -2 -3 +x 2 3 4 5arrow_forwardThe graph of f' is below. Use it to determine where the inflection points are and the intervals where f is concave up and concave down. If there are multiple inflection points, separate with a comma. 6 5 4 3 2 1 f'(x) +x -6-5-4-3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6+ Inflection point(s) at x = Concave up: Concave down:arrow_forward
- The graph of f' is below. Use it to determine where the local minima and maxima for f are. If there are multiple answers, separate with commas. f'(x) 4- -5-4-3-8-1 3 2 1 x 1 2 3 4 5 -1 -2 -3 -4 Local minima at a Local maxima at =arrow_forwardThe graph of f' is below. Use it to determine the intervals where f is increasing. f'(xx) 4- -5 -3 -2 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 Cit +x 7 2arrow_forwardPlease focus on problem ii.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





