
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260265453
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.4, Problem 8.130P
Prove that Eqs. (8.13) and (8.14) are valid for any shape of surface provided that the coefficient of friction is the same at all points of contact.
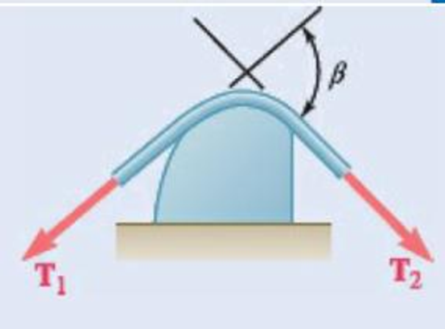
Fig. P8.130
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Procedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D \sum Fx=0 \sum Fy=0 \sum Fz=0 \sum Mx=0 \sum My=0 \Sigma Mz=0 2D \Sigma Fx=0 \Sigma Fy=0 \Sigma Mz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of the section
For each system below with transfer function G(s), plot the pole(s) on the s-plane.
and indicate whether the system is:
(a) "stable" (i.e., a bounded input will always result in a bounded output),
(b) "marginally stable," or
(c) "unstable"
Sketch a rough graph of the time response to a step input.
8
a) G(s) =
5-5
8
b) G(s) =
c) G(s) =
=
s+5
3s + 8
s² - 2s +2
3s +8
d) G(s):
=
s²+2s+2
3s+8
e) G(s):
=
s² +9
f) G(s):
8
00
==
S
Please answer the following question. Include all work and plase explain. Graphs are provided below. "Consider the Mg (Magnesium) - Ni (Nickel) phase diagram shown below. This phase diagram contains two eutectic reactions and two intermediate phases (Mg2Ni and MgNi2). At a temperature of 505oC, determine what the composition of an alloy would need to be to contain a mass fraction of 0.20 Mg and 0.80 Mg2Ni."
Chapter 8 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
Ch. 8.1 - Knowing that the coefficient of friction between...Ch. 8.1 - Two blocks A and B are connected by a cable as...Ch. 8.1 - A cord is attached to and partially wound around a...Ch. 8.1 - A 40-kg packing crate must be moved to the left...Ch. 8.1 - Determine whether the block shown is in...Ch. 8.1 - Determine whether the block shown is in...Ch. 8.1 - Determine whether the block shown is in...Ch. 8.1 - Determine whether the block shown is in...Ch. 8.1 - Knowing that = 45 in Prob. 8.1, determine the...Ch. 8.1 - The 20-lb block A hangs from a cable as shown....
Ch. 8.1 - The 10-kg block is attached to link AB and rests...Ch. 8.1 - Considering only values of less than 90,...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.9PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.10PCh. 8.1 - The 50-lb block A and the 25-lb block B are...Ch. 8.1 - The 50-lb block A and the 25-lb block B are...Ch. 8.1 - Three 4-kg packages A, B, and C are placed on a...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.14PCh. 8.1 - A uniform crate with a mass of 30 kg must be moved...Ch. 8.1 - A worker slowly moves a 50-kg crate to the left...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.17PCh. 8.1 - A 200-lb sliding door is mounted on a horizontal...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.19PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.20PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.21PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.22PCh. 8.1 - The 10-lb uniform rod AB is held in the position...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.24PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.25PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.26PCh. 8.1 - The press shown is used to emboss a small seal at...Ch. 8.1 - The machine base shown has a mass of 75 kg and is...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.29PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.30PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.31PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.32PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.33PCh. 8.1 - A driver starts the engine of an automobile that...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.35PCh. 8.1 - Two uniform rods each of weight W and length L are...Ch. 8.1 - A 1.2-m plank with a mass of 3 kg rests on two...Ch. 8.1 - Two identical uniform boards, each with a weight...Ch. 8.1 - A uniform 20-kg tube resting on a loading dock...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.40PCh. 8.1 - A 10-ft beam, weighing 1200 lb, is to be moved to...Ch. 8.1 - (a) Show that the beam of Prob. 8.41 cannot be...Ch. 8.1 - Two 8-kg blocks A and B resting on shelves are...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 8.44PCh. 8.1 - Prob. 8.45PCh. 8.1 - Two slender rods of negligible weight are...Ch. 8.1 - Two slender rods of negligible weight are...Ch. 8.2 - The machine part ABC is supported by a...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.49PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.50PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.51PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.52PCh. 8.2 - Solve Prob. 8.52 assuming that the end of the beam...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.54PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.55PCh. 8.2 - Block A supports a pipe column and rests as shown...Ch. 8.2 - A 200-lb block rests as shown on a wedge of...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.58PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.59PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.60PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.61PCh. 8.2 - An 8 wedge is to be forced under a machine base at...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.63PCh. 8.2 - A 15 wedge is forced under a 50-kg pipe as shown....Ch. 8.2 - A 15 wedge is forced under a 50-kg pipe as shown....Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.66PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.67PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.68PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.69PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.70PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.71PCh. 8.2 - The position of the automobile jack shown is...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.73PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.74PCh. 8.2 - In the vise shown, the screw is single-threaded in...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.76PCh. 8.3 - A lever of negligible weight is loosely fitted...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 8.78PCh. 8.3 - 8.79 and 8.80 The double pulley shown is attached...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 8.80PCh. 8.3 - 8.81 and 8.82 The double pulley shown is attached...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 8.82PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.83PCh. 8.3 - The block and tackle shown are used to lower a...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 8.85PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.86PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.87PCh. 8.3 - 8.87 and 8.88 A lever AB of negligible weight is...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 8.89PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.90PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.91PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.92PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.93PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.94PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.95PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.96PCh. 8.3 - Solve Prob. 8.93 assuming that the normal force...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 8.98PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.99PCh. 8.3 - A 900-kg machine base is rolled along a concrete...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 8.101PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.102PCh. 8.4 - A rope having a weight per unit length of 0.4...Ch. 8.4 - A hawser is wrapped two full turns around a...Ch. 8.4 - Two cylinders are connected by a rope that passes...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.106PCh. 8.4 - The coefficient of static friction between block B...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.108PCh. 8.4 - A band belt is used to control the speed of a...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.110PCh. 8.4 - The setup shown is used to measure the output of a...Ch. 8.4 - A flat belt is used to transmit a couple from drum...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.113PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.114PCh. 8.4 - The speed of the brake drum shown is controlled by...Ch. 8.4 - The speed of the brake drum shown is controlled by...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.117PCh. 8.4 - Bucket A and block C are connected by a cable that...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.119PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.120PCh. 8.4 - 8.121 and 8.123 A cable is placed around three...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.122PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.123PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.124PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.125PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.126PCh. 8.4 - The axle of the pulley is frozen and cannot rotate...Ch. 8.4 - The 10-lb bar AE is suspended by a cable that...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.129PCh. 8.4 - Prove that Eqs. (8.13) and (8.14) are valid for...Ch. 8.4 - Complete the derivation of Eq. (8.15), which...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.132PCh. 8.4 - Solve Prob. 8.113 assuming that the flat belt and...Ch. 8 - 8.134 and 8.135 The coefficients of friction are S...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.135RPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.136RPCh. 8 - A slender rod with a length of L is lodged between...Ch. 8 - The hydraulic cylinder shown exerts a force of 3...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.139RPCh. 8 - Bar AB is attached to collars that can slide on...Ch. 8 - Two 10 wedges of negligible weight are used to...Ch. 8 - A 10 wedge is used to split a section of a log....Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.143RPCh. 8 - A lever of negligible weight is loosely fitted...Ch. 8 - In the pivoted motor mount shown, the weight W of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The triangular plate, having a 90∘∘ angle at AA, supports the load PP = 370 lblb as shown in (Figure 1).arrow_forwardDesign a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, q= 210°, ß2 = −27° for left side and s = 1.24, y= 74°, ½ = − 40° for right side. φ 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° 2.138 P1 Figure 1 Xarrow_forwardDesign a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, q= 210°, B₂ = −27° for left side and s = 1.24, y= 74°, ½ = − 40° for right side. 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° P1 Figure 1 2.138 Xarrow_forward
- can you explain how in a coordinate frame transformation: v = {v_n}^T {n-hat} and then it was found that {n-hat} = [C]^T {b-hat} so v_n = {v_n}^T [C]^T {b-hat}, how does that equation go from that to this --> v_n = [C]^T v_barrow_forward6) If (k = 0,7 cm) find Imax for figure below. 225mm 100mm ثلاثاء. 100mm 150mm 75mm Ans: Tmax=45:27 N/cm F-400 Narrow_forwardThe man has a weight W and stands halfway along the beam. The beam is not smooth, but the planes at A and B are smooth (and plane A is horizontal). Determine the magnitude of the tension in the cord in terms of W and θ.arrow_forward
- A 15 cm-OD pipe is buried with its centerline 1.25 m below the surface of the ground [k of soil is 0.35 W/(m K)]. An oil having a density of 800 kg/m³ and a specific heat of 2.1 kJ/(kg K) flows in the pipe at 5.6 L/s. Assuming a ground surface temperature of 5°C and a pipe wall temperature of 95°C, estimate the length of pipe in which the oil temperature decreases by 5.5°C. + Tε = 5ºC Z= 1.25 m D= 15 cm 7p=95°Carrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) 4y+y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 0. 2) y+y=0, y(0) = A, y'(0) = B. 3) "+2y'-8y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=8. 4) y"-2y-3y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=7. 5) y"-ky' =0, y(0)=2, y'(0) =k. 6) y+ky'-2k2y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 2k. 7) y'+4y=0, y(0)=2.8 y+y-17sin(21) y(0)=-1. 9) y-y'-6y=0, y(0)=6. y'(0)=13. 10) y-y=0, 11) y"-4y+4y=0, y(0)=4, y'(0) = 0. y(0) = 2.1, y'(0)=3.9 12) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-3. 13) "+7y+12y=21e", y(0)=3.5, y'(0)=-10. 14) "+9y=10e", y(0)=0. y'(0) = 0. 15) y+3y+2.25y=91³ +64. y(0)=1, y'(0) = 31.5 16) "-6y+5y= 29 cos(21), y(0)=3.2, y'(0) = 6.2 17) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=1. 18) y+2y+17y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=12. 19) y-4y+5y=0, y(0)-1, y'(0) 2. 20) 9y-6y+y=0. y(0)=3, y'(0)=1. 21) -2y+10y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=3. 22) 4y-4y+37y=0, (0) 3. y(0) 1.5 23) 4y-8y+5y=0, (0)-0, y(0) 1. 24) y+y+1.25y=0, y(0) 1. y'(0) -0.5 25) y+y=2 cos(1). y(0) 2. y'(0) = 0. 26) -4y+3y=0, (0)-3, y'(0) = 7. 27) y+2y+y=e", y(0)-0. y'(0) = 0. 29) 28) y+2y-3y-10sinh(2),…arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting appreciate your time and effort!. Question:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY