
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: In the presence of per acid an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
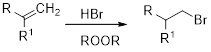
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: In the presence of per acid an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
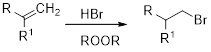
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: In the presence of per acid an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
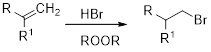
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: In the presence of per acid an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
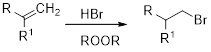
(e)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: In the presence of per acid an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
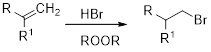
(f)
Interpretation:
The major product obtained in the given reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Markovnikov’s rule: An unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule: In the presence of per acid an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with hydrogen halide in which halide ions goes to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond which provides alkyl halides.
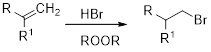
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, WITH SOL. MAN/ STUDY
- Hi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forwardDraw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.025 M HCl is titrated with 0.035 M KOH. What volume of KOH is needed?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





