
Concept explainers
To write and graph:
Anequationdescribing the possible numbers of basic and deluxe washes that could have been done. Give three possible combinations of deluxe and basic car washes.
Answer to Problem 48E
The three possible combination of washes would be 15 basic washes and 70 deluxe washes, or 30 basic washes and 60 deluxe washes, or 60 basic washes and 40 deluxe washes.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A car wash charges $8 for a basic wash and $12 for a deluxe wash that includes wax. On a certain day, sales at the car wash total $960.
Calculation:
Let x represent number of basic car washes and y represent number of deluxe car washes.
We have been given that a car wash charges $8 for a basic wash, so amount earned from x basic car washes would be
We have been given that a car wash charges $12 for a deluxe wash, so amount earned from ydeluxe car washes would be
Since total amount earned i$960, so we will set amount earned from x basic car washes and y deluxe car washes equal to $960 as:
We will use intercepts to graph our equation.
Therefore, the x -intercept of our given equation is
To find y- intercept, we will substitute
Therefore, the y -intercept of our given equation is
Upon graphing our given equation, we will get our required graph as shown below:
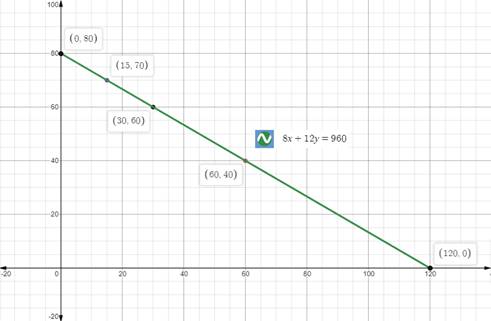
Upon looking at our graph, we can see that points (15,70), (30,60), and (60,40) lie on the line. Therefore, the three possible combination of washes would be 15 basic washes and 70 deluxe washes, or 30 basic washes and 60 deluxe washes, or 60 basic washes and 40 deluxe washes.
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK PRE-ALGEBRA
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
- The only problems I need help with ae the last 8 ones, Thanksarrow_forwardGraph without using the calculator y-1 = | x+4 |arrow_forward9:43 AS く Akbar © Printed in the United States 15) Scale: 1 cmal unit on both axes .ill 64% The graph above shows a straight line QT intersecting the y-axis at T. i State the co-ordinates of T. ii Calculate the gradient of QT 16) iii Determine the equation of QT. A (-1, 9) ||| i L Г (5 marks)arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forwardSolve the system of equation for y using Cramer's rule. Hint: The determinant of the coefficient matrix is -23. - 5x + y − z = −7 2x-y-2z = 6 3x+2z-7arrow_forwarderic pez Xte in z= Therefore, we have (x, y, z)=(3.0000, 83.6.1 Exercise Gauss-Seidel iteration with Start with (x, y, z) = (0, 0, 0). Use the convergent Jacobi i Tol=10 to solve the following systems: 1. 5x-y+z = 10 2x-8y-z=11 -x+y+4z=3 iteration (x Assi 2 Assi 3. 4. x-5y-z=-8 4x-y- z=13 2x - y-6z=-2 4x y + z = 7 4x-8y + z = -21 -2x+ y +5z = 15 4x + y - z=13 2x - y-6z=-2 x-5y- z=-8 realme Shot on realme C30 2025.01.31 22:35 farrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





