
An aqueous slurry at 30°C containing 20.0 wt% solids is fed to an evaporator in which enough w ater is vaporized at 1 atm to produce a product slurry containing 35.0 wt% solids. Heat is supplied to the evaporator by feeding saturated steam at 2.6 bar absolute into a coil immersed in the liquid. The steam condenses in the coil, and the slurry boils at the normal boiling point of pure water. The heat capacity of the solids may be taken to be half that of liquid water.
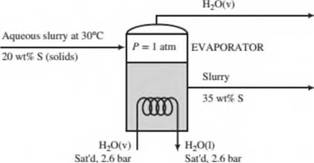
- Calculate the required steam feed rate (kg/h) for a slurry feed rate of 1.00 × 103 kg/h.
- Vapor recompression is often used in the operation of an evaporator. Suppose that the vapor (steam) generated in the evaporator described above is compressed to 2.6 bar and simultaneously heated to the saturation temperature at 2.6 bar, so that no condensation occurs. The compressed steam and additional saturated steam at 2.6 bar arc then fed to the evaporator coil, in which isobaric condensation occurs. How much additional steam is required?
- What more would you need to know to determine whether or not vapor recompression is economically advantageous in this process?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 8 Solutions
ELEMENTARY PRINCIPLES OF CHEM. PROCESS.
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Modern Database Management
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Ethylene glycol liquid is used as an antifreeze in many applications. If it is stored in a vessel at a pressure of at 150 psig flows through a ¾ inch-diameter hole to atmospheric pressure. Estimate the discharge rate if the ambient pressure is 1 atm. For ethylene glycol at 77°F, the specific gravity is 1.15 and the viscosity is 25 cP. The molecular weight is 62.07.arrow_forwardPlease help me with parts A through Darrow_forwardA semi-truck tire is inflated to 110 psig with nitrogen. What will be the initial gas discharge ratein lbm/s due to a 1/16-inch diameter hole? Assume at temperature of 80℉ and an ambientpressure of 1 atm.arrow_forward
- # 4 The reaction, AB, is to be carried out isothermally in a continuous flow reactor. The entering volumetric flow rate, vo is 10 L/h and is constant (v=vo). Calculate both the CSTR and PFR volumes necessary to reduce the entering concentration of species A from CAD to CA = 0.01 CAO when the entering molar flow rate of species A is 5 mol/h. (a) This reaction is a second order reaction. The reaction rate constant, k is given as 300 L/mol.h. (b) This reaction is a zeroth order reaction. The reaction rate constant, k is given as 0.05 mol/h.L.arrow_forward#3 Using the initial rates method and the given experimental data below to determine the rate law and the value of the rate constant for the reaction, as shown below. All trials are performed at the same temperature. 2NO + Cl2 → 2NCOCI Trial [NO] (mol/L) [Cl₂] (mol/L) Initial rates (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.00300 2 0.10 0.15 0.00450 3 0.15 0.10 0.00675arrow_forward#2 The reaction rate constant at temperature, T₁, is 15 mol/L-s while at the reaction rate constant changed to 7 mol/L-s when temperature changed to T2 at 398 K. What is T₁? Given the activation energy is 600 kJ/mol. Assume at this temperature interval, pre-exponential factor and activation energy are constant.arrow_forward
- #1 Chloral is consumed at a rate of 10 mol/L-s when reacting with chlorobenzene to form DDT and water in the reaction given below. Determine: i) the rate of disappearance of chlorobenzene. ii) the rate of formation of DDT. CCI CHO (Chloral) + 2C6H5Cl (Chlorobenzene) → (C6H4Cl)2CHCCI 3 (DDT) + H2Oarrow_forward#5 The irreversible liquid phase second order reaction, 2A → B, is carried out in a CSTR. The entering concentration of A, CAD is 2 mol/L, and the exit concentration of A, CA is 0.1 mol/L. The volumetric flow rate, vo, is at 3 L/s and is constant (v=vo). The reaction rate constant, k is 0.03 L/mol's. What is the corresponding reactor volume?arrow_forwardProblem 9.11 An 80 mm long line MN has its end M 15 mm in front of the V.P. The distance between the ends projector is 50 mm. The front view is parallel to and 20 mm above reference line. Draw the projections of the line and determine its inclination with the V.P. Also, locate the traces. Interpretation Front view of a line is parallel to xy, therefore, 1. The line is parallel to the H.P. 2. The top view of the line has true length. 3. The front view has projected length equal to the distance be- tween the projectors. Construction Refer to Fig. 9.11. 1. Draw a reference line xy. Mark point m' 20 mm above xy and point m 15 mm below xy. 2. Draw a 50 mm long line m'n' parallel to xy. 3. Draw an arc with centre m and radius 80 mm to meet projec- tor from point n' at point n. Join mn to represent the top view. Determine its inclination with xy as the inclination of line MN with the V.P. Here = 51°. 4. Traces Extend line mn to meet xy at point v. Project point v to meet m'n' produced at…arrow_forward
- oh 30 20 D и D P 60 60 80arrow_forward⑤ b Δε m ab C 40arrow_forwardProblem 10.16 An isosceles triangle of base 40 mm and altitude 54 mm has its base in the V.P. The surface of the plane is inclined at 50° to the V.P. and perpendicular to the H.P. Draw its projections. Construction Refer to Fig. 10.17. An isosceles triangle has its base in the V.P., so con- sider that initially the triangle ABC is placed in the V.P. with base AB perpendicular to the H.P. 1. First stage Draw a triangle a'b'c' keeping a'b' perpendicular to xy to represent the front view. Project the corners to xy and obtain ac as the top view. 2. Second stage Reproduce the top view of first stage keeping ab on xy and ac inclined at 50° to xy. Obtain new points a', b' and c' in the front view by joining the points of intersection of the vertical projectors from a, b and c of the second stage with the corresponding horizontal locus lines from a', b' and c' of the first stage. Join a'b'c' to represent the final front view. Here, the front view is an equilateral triangle of side 40 mm. X 54…arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





