
(a)
Interpretation:
To draw the mixture of enantiomers A and B obtained from cis and Trans isomers of 1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with KOC (CH3)3.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
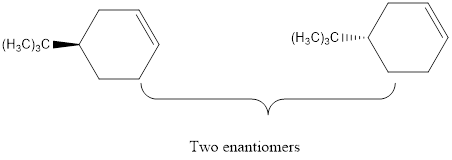
Explanation of Solution
The elimination of the Br from the reactant using base to form the respective

(b)
Interpretation:
To determine the isomer that reacts faster with KOC(CH3)3.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the alkyl halide and the base appear in the rate equation. The most straightforward explanation for the second-order kinetics is a concerted reaction: all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. In other words simultaneously all bonds are broken and formed.
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
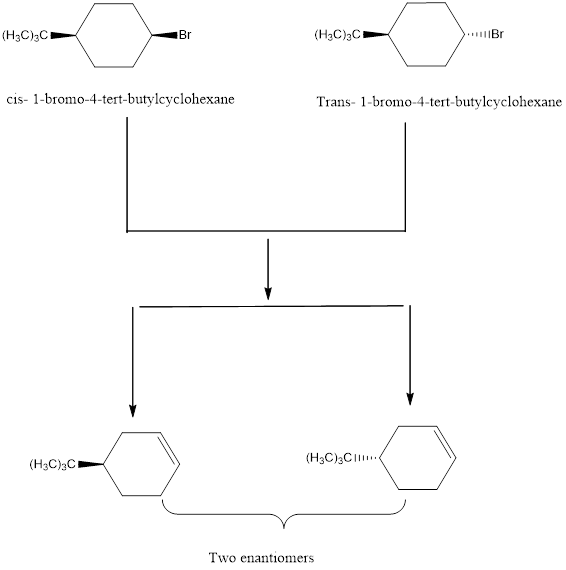
The bulky tert-butyl group in the cyclohexane ring is in the equatorial position.

In the cis-isomer, the Br is in the axial position. So cis-isomer is faster than the trans-isomer.
Explanation of Solution

The bulky tert-butyl group in the cyclohexane ring is in the equatorial position. The cis isomer has the Br in the axial position while in the trans isomer the Br is in the equatorial position. For the dehydrogenation to occur, the halogen must be in the axial position to afford trans diaxial elimination of H and X. Thus the cis isomer react faster than trans where the Br lies in the equatorial position.
Thus cis-isomer is faster than the trans-isomer due to axial position of Br in the structure.
(c)
Interpretation:
To draw the structures for C and D from cis and trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the alkyl halide and the base appear in the rate equation. The most straightforward explanation for the second-order kinetics is a concerted reaction: all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. In other words simultaneously all bonds are broken and formed.
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
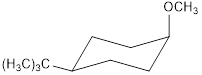
cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3 forms the product
![]()
trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3 forms the product
Explanation of Solution
The major products C and D formed when cis and trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane reacts with NaOCH3 is shown. The respective reaction takes place by SN2 reaction mechanism that is by backside attack of the nucleophile.
.
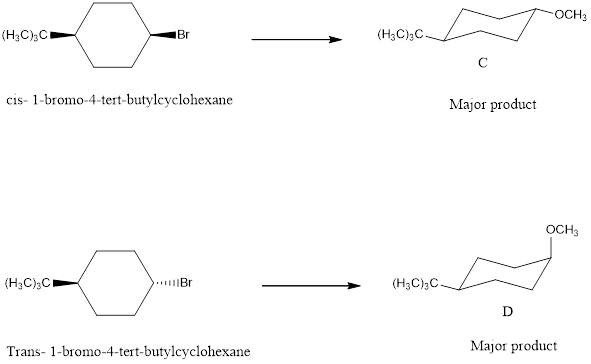
cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3 forms the product.
![]()
trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3 forms the product.

(d)
Interpretation:
To determine the isomer that reacts faster with NaOCH3.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the alkyl halide and the base appear in the rate equation. The most straightforward explanation for the second-order kinetics is a concerted reaction: all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. In other words simultaneously all bonds are broken and formed.
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
The cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane reacts faster when compared to trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane.
cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3.
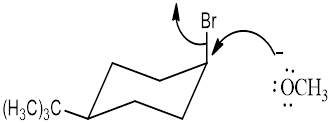
trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3
Explanation of Solution
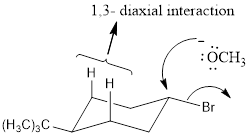
NaOCH3, is a strong nucleophile. The reaction follows the SN2 in which the backside attack occurs. With the cis isomer the nucleophile can attack by the equatorial position to avoid the 1, 3-diaxial interaction. Moreover only the cis isomer has the Br and Β carbon in the anti periplanar that is in trans diaxial arrangement when compared to trans isomer. Thus the cis isomer reacts faster than trans isomer.
cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3
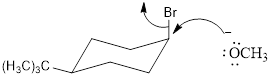
trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3

Thus the cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane reacts faster when compared to trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane
(e)
Interpretation:
To explain why there is different products formed when the alkyl halides uses two different alkoxides.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the alkyl halide and the base appear in the rate equation. The most straightforward explanation for the second-order kinetics is a concerted reaction: all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. In other words simultaneously all bonds are broken and formed.
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
The bulky base –OC(CH3)3 favours the elimination by an E2 reaction mechanism, to get a mixture of enantiomers A and B. The strong nucleophile –OCH3 favours nucleophile substitution by an SN2 mechanism. Inversion of configuration results from backside attack of the nucleophile. Thus different product are formed.
Explanation of Solution
-OCH3, is a strong nucleophile. The reaction follows the SN2 in which the backside attack occurs. With the cis isomer the nucleophile can attack by the equatorial position to avoid the 1, 3-diaxial interaction. Moreover only the cis isomer has the Br and Β carbon in the anti periplanar that is in trans diaxial arrangement when compared to trans isomer. Thus the cis isomer reacts faster than trans isomer. The bulky base –OC(CH3)3 favours the elimination by an E2 reaction mechanism, to get a mixture of enantiomers A and B.
Thus different product are formed when the alkyl halides uses two different alkoxides are used.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- If I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when chlorobenzene acid reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by reacting benzenesulfonic acid with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting ethylbenzene with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when tert-butylbenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when acetophenone reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile with a sulfonitric mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained in the reaction of p-Toluidine with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-methylbenzonitrile with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 2-nitrophenol with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





