
Concept explainers
For which reaction mechanisms,
a. The mechanism involves carbocation intermediates.
b. The mechanism has two steps.
c. The reaction rate increases with better leaving groups.
d. The reaction rate increases when the solvent is changed from
e. The reaction rate depends on the concentration of the alkyl halide only.
f. The mechanism is concerted.
g. The reaction of
h. Racemization of a stereogenic center occurs.
i. Tertiary
j. The reaction follows a second-order rate equation.
(a)
Interpretation: The validation of the given statement is to be stated according to the mechanism involved in the reaction.
Concept introduction: The two-step unimolecular elimination reaction that favors the removal of a HX substituent and the formation of a carbocation intermediate takes place in its first step. In the second step of the reaction, the carbocation forms a double bond. This type of reaction is termed E1 elimination reaction.
The two-step unimolecular reaction which favors the removal of a HX substituent and the formation of a carbocation intermediate takes place in its first step. Then, in the second step, the carbocation undergoes substitution. This type of reaction is termed as
Answer to Problem 8.54P
The given statement is true for
Explanation of Solution
The two-steps reactions are
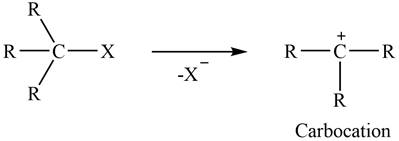
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation: The reaction in which the mechanism has two steps is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The two-step unimolecular elimination reaction that favors the removal of a HX substituent and the formation of a carbocation intermediate takes place in its first step. In the second step of the reaction, the carbocation forms a double bond. This type of reaction is termed
The two-step unimolecular reaction which favors the removal of a HX substituent and the formation of a carbocation intermediate takes place in its first step. Then, in the second step, the carbocation undergoes substitution. This type of reaction is termed as
Answer to Problem 8.54P
Explanation of Solution
The two-steps reactions are
(c)
Interpretation: The reactions for which the reaction rate increases with better leaving groups is to be stated.
Concept introduction: A good leaving groups is preferred by all substitution and elimination reactions as they increase the rate of the reaction by lowering the transition state energy.
Answer to Problem 8.54P
The rate of
Explanation of Solution
The more the bigger the atom the better it will be as a leaving group and more efficiently it will leave the group to which they are attached and hence increasing the reaction rate. They do so by lowering the transition state energy.
The rate of
(d)
Interpretation: The reactions for which the reaction rate increases when the solvent is changed from
Concept introduction: The choice of the solvent being used determines the mechanism being followed.
Answer to Problem 8.54P
The rate of
Explanation of Solution
The rate of
(e)
Interpretation: The reactions for which the reaction rate depends on the concentration of the alkyl halide only is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The rate law for
The rate law depends only on the concentration of alkyl halide.
Answer to Problem 8.54P
For
Explanation of Solution
The two step reactions are
The rate of both the reactions depends only on the concentration of alkyl halide and is independent of the base concentration.
For
(f)
Interpretation: The reaction for which the mechanism is concerted is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The one-step bimolecular elimination reaction that favors the removal of a proton from carbon adjacent to the leaving group by a base that results in the formation of a carbocation. Then, the formation of a double bond takes place simultaneously. This type of reaction is termed
The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 8.54P
Explanation of Solution
In a concerted mechanism, all the bond breaking and bond making takes place simultaneously in a single step. In
(g)
Interpretation: The mechanism followed by the reaction of
Concept introduction: Substitution and elimination depends on the base being employed.
Answer to Problem 8.54P
Explanation of Solution
In the given question the alkyl halide is primary and the base is a strong base as well as a strong nucleophile. So, substitution as well as elimination is possible. Since,
(h)
Interpretation: The reaction for which racemization of a stereogenic center occurs is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Racemization is possible where a planar carbocation is the intermediate.
Answer to Problem 8.54P
For SN1 reaction, racemization of a stereogenic center occurs.
Explanation of Solution
Racemization can take place where a planar carbocation intermediate is formed and the incoming nucleophile approaches it from both the sides. In a SN1 reaction, a planar carbocation is formed as the intermediate and attack of the nucleophile is possible from both the sides leading to a mixture of enantiomers being formed.
For
(i)
Interpretation: The reactions for which tertiary
Concept introduction: A tertiary carbocation is more stable then secondary followed by a primary carbocation.
Answer to Problem 8.54P
For
Explanation of Solution
In SN1 and E1 reaction, the first step is the formation of carbocation and follows the order
For
(j)
Interpretation: The reaction which follows a second-order rate equation is to be stated.
Concept introduction: Second order reaction is one in which the reaction rate depends on the concentration of both the reacting species.
Answer to Problem 8.54P
Explanation of Solution
In
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
- Identifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. 2.2 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 1.4M HF solution. acids: П bases: Х other: ☐ ப acids: 0.51 mol of KOH is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is bases: 1.3M in both HF and NaF. other: ☐ 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g) AG⁰ = 5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 1.68 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N204) at 148. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no 0.42 atm ☑ 5 0/5 ? مله Ararrow_forwardHomework 13 (Ch17) Question 4 of 4 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 2 of 2 ✓ 1 ✓ 2 = 3 4 Time Remaining: 4:25:54 Using the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy of the following chemical reaction: 2CH3OH (g)+302 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 4H₂O (g) Round your answer to zero decimal places. ☐ kJ x10 ☐ Subm Check 2020 Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cearrow_forward
- Identifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria Your answer is incorrect. • Row 2: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 3: Your answer is incorrect. • Row 6: Your answer is incorrect. 0/5 The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. acids: HF 0.1 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 0.7M HF solution. bases: 0.13 mol of HCl is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.0M in both HF and KF. Exponent other: F acids: HF bases: F other: K 1 0,0,... ? 000 18 Ararrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NOCI (g) 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) AGº =41. kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.50 atm of nitrosyl chloride (NOCI) and 6.38 atm of chlorine (C12) at 212. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: ? rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of NOCI tend to rise or fall? x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO? In other words, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO? Similarly, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding NO? yes no If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 0.035 atm ✓ G 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardHighlight each glycosidic bond in the molecule below. Then answer the questions in the table under the drawing area. HO- HO- -0 OH OH HO NG HO- HO- OH OH OH OH NG OHarrow_forward
- € + Suppose the molecule in the drawing area below were reacted with H₂ over a platinum catalyst. Edit the molecule to show what would happen to it. That is, turn it into the product of the reaction. Also, write the name of the product molecule under the drawing area. Name: ☐ H C=0 X H- OH HO- H HO- -H CH₂OH ×arrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection of the disaccharide made by joining D-glucose and D-mannose with a ẞ(1-4) glycosidic bond. If the disaccharide has more than one anomer, you can draw any of them. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardEpoxides can be opened in aqueous acid or aqueous base to produce diols (molecules with two OH groups). In this question, you'll explore the mechanism of epoxide opening in aqueous acid. 2nd attempt Be sure to show all four bonds at stereocenters using hash and wedge lines. 0 0 Draw curved arrows to show how the epoxide reacts with hydronium ion. 100 +1: 1st attempt Feedback Be sure to show all four bonds at stereocenters using hash and wedge lines. See Periodic Table See Hint H A 5 F F Hr See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forward
- 03 Question (1 point) For the reaction below, draw both of the major organic products. Be sure to consider stereochemistry. > 1. CH₂CH₂MgBr 2. H₂O 3rd attempt Draw all four bonds at chiral centers. Draw all stereoisomers formed. Draw the structures here. e 130 AN H See Periodic Table See Hint P C Brarrow_forwardYou may wish to address the following issues in your response if they are pertinent to the reaction(s) you propose to employ:1) Chemoselectivity (why this functional group and not another?) 2) Regioselectivity (why here and not there?) 3) Stereoselectivity (why this stereoisomer?) 4) Changes in oxidation state. Please make it in detail and draw it out too in what step what happens. Thank you for helping me!arrow_forward1) Chemoselectivity (why this functional group and not another?) 2) Regioselectivity (why here and not there?) 3) Stereoselectivity (why this stereoisomer?) 4) Changes in oxidation state. Everything in detail and draw out and write it.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
