
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 8.5.19P
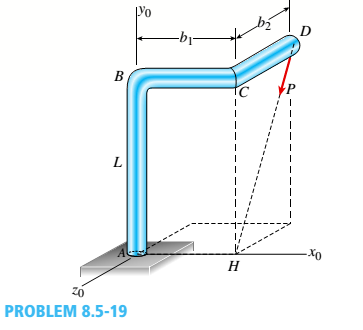
A bracket ABCD having a hollow circular cross section consists of a vertical arm AB{L = 6 ft), a horizontal arm BC parallel to the v0 axis, and a horizontal arm CD parallel to the -0 axis (see figure). The arms BC and CD have lengths b}= 3.6 ft and b2= 2,2 ft, respectively. The outer and inner diameters of the bracket are d-, = 7,5 in. and dx= 6,8 in. An inclined load P = 2200 lb acts at point D along line DH. Determine the maximum tensile, compressive, and shear stresses in the vertical arm
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 3 (10 pts). When using linear shape functions to solve the multiphysics thermoelastic problem considered in class, we found that the stress in the rod is affected by unphysical oscillations like the following plot(a) [10pts] What is the origin of this issue and how can we fix it?
Z6 please help on the attached question.
Z5 please help on the attached question.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 8 - A spherical balloon is filled with a gas. The...Ch. 8 - A spherical balloon with an outer diameter of 500...Ch. 8 - A large spherical tank (see figure) contains gas...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem if the internal...Ch. 8 - A hemispherical window (or viewport) in a...Ch. 8 - A rubber ball (sec figure) is inflated to a...Ch. 8 - (a) Solve part (a) of the preceding problem if the...Ch. 8 - A spherical steel pressure vessel (diameter 500...Ch. 8 - A spherical tank of diameter 48 in. and wall...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem for the following...
Ch. 8 - A spherical stainless-steel tank having a diameter...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem if the diameter is 480...Ch. 8 - : A hollow, pressurized sphere having a radius r =...Ch. 8 - A fire extinguisher tank is designed for an...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.3.2PCh. 8 - A scuba t a n k (see fig ure) i s bci ng d e...Ch. 8 - A tall standpipc with an open top (see figure) has...Ch. 8 - An inflatable structure used by a traveling circus...Ch. 8 - A thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of a...Ch. 8 - A strain gage is installed in the longitudinal...Ch. 8 - A circular cylindrical steel tank (see figure)...Ch. 8 - A cylinder filled with oil is under pressure from...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem if F =90 mm, F = 42...Ch. 8 - A standpipe in a water-supply system (see figure)...Ch. 8 - A cylindrical tank with hemispherical heads is...Ch. 8 - : A cylindrical tank with diameter d = 18 in, is...Ch. 8 - A pressurized steel tank is constructed with a...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem for a welded Tank with...Ch. 8 - A wood beam with a cross section 4 x 6 in. is...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.4.2PCh. 8 - A simply supported beam is subjected to two point...Ch. 8 - A cantilever beam with a width h = 100 mm and...Ch. 8 - A beam with a width h = 6 in. and depth h = 8 in....Ch. 8 - Beam ABC with an overhang BC is subjected to a...Ch. 8 - A cantilever beam(Z, = 6 ft) with a rectangular...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem for the following...Ch. 8 - A simple beam with a rectangular cross section...Ch. 8 - An overhanging beam ABC has a guided support at A,...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem if the stress and...Ch. 8 - A cantilever wood beam with a width b = 100 mm and...Ch. 8 - . A cantilever beam (width b = 3 in. and depth h =...Ch. 8 - A beam with a wide-flange cross section (see...Ch. 8 - A beam with a wide-flange cross section (see...Ch. 8 - A W 200 x 41.7 wide-flange beam (see Table F-l(b),...Ch. 8 - A W 12 x 35 steel beam is fixed at A. The beam has...Ch. 8 - A W 360 x 79 steel beam is fixed at A. The beam...Ch. 8 - A W 12 X 14 wide-flange beam (see Table F-l(a),...Ch. 8 - A cantilever beam with a T-section is loaded by an...Ch. 8 - Beam A BCD has a sliding support at A, roller...Ch. 8 - , Solve the preceding problem using the numerical...Ch. 8 - A W 12 x 35 steel cantilever beam is subjected to...Ch. 8 - A W 310 x 52 steel beam is subjected to a point...Ch. 8 - A solid circular bar is fixed at point A. The bar...Ch. 8 - A cantilever beam with a width h = 100 mm and...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem using the following...Ch. 8 - A cylindrical tank subjected to internal...Ch. 8 - A cylindrical pressure vessel having a radius r =...Ch. 8 - A pressurized cylindrical tank with flat ends is...Ch. 8 - A cylindrical pressure vessel with flat ends is...Ch. 8 - The tensional pendulum shown in the figure...Ch. 8 - The hollow drill pipe for an oil well (sec figure)...Ch. 8 - Solve the preceding problem if the diameter is 480...Ch. 8 - . A segment of a generator shaft with a hollow...Ch. 8 - A post having a hollow, circular cross section...Ch. 8 - A sign is supported by a pole of hollow circular...Ch. 8 - A sign is supported by a pipe (see figure) having...Ch. 8 - A traffic light and signal pole is subjected to...Ch. 8 - Repeat the preceding problem but now find the...Ch. 8 - A bracket ABCD having a hollow circular cross...Ch. 8 - A gondola on a ski lift is supported by two bent...Ch. 8 - Beam A BCD has a sliding support at A, roller...Ch. 8 - A double-decker bicycle rack made up of square...Ch. 8 - A semicircular bar AB lying in a horizontal plane...Ch. 8 - Repeat Problem 8.5-22 but replace the square tube...Ch. 8 - An L-shaped bracket lying in a horizontal plane...Ch. 8 - A horizontal bracket ABC consists of two...Ch. 8 - , An arm A BC lying in a horizontal plane and...Ch. 8 - A crank arm consists of a solid segment of length...Ch. 8 - A moveable steel stand supports an automobile...Ch. 8 - A mountain bike rider going uphill applies a force...Ch. 8 - Determine the maximum tensile, compressive, and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.5.32PCh. 8 - A plumber's valve wrench is used to replace valves...Ch. 8 - A compound beam ABCD has a cable with force P...Ch. 8 - A steel hanger bracket ABCD has a solid, circular...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A particle, starting from rest, travels along a straight track and for 14 s has an acceleration as shown. Draw the v-t graph that describes the motion and find the distance traveled in 14 S. a 8 11 уг (0.8) 11 ут (6,8 6. 4+ 2 *2 Ye (1.0) t 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 dre dec dec decarrow_forwardMechanical engineering,Use paper sheet. No chatgpt.arrow_forwardMechanical engineering question.arrow_forward
- correct answer only. I will upvote.arrow_forwardCorrect answer only. I will upvote.arrow_forwardI really don't know how to approach this problem i've tried approaching it with some of the torsional stress equations I know but i'm comming up with awnsers that don't make any sence can you please help me with this?arrow_forward
- I tried this problem and don't know what I did wrong or how else I could approach it can you please help me out?arrow_forwardQ3: An engine produce 750 kW power and uses gaseous C12H26 as a fuel at 25 C; 200% theoretical air is used and air enters at 500 K. The products of combustion leave at 800 K. The heat loss from the engine is 175 kW. Determine the fuel consumption for complete combustion.arrow_forwardQu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures. show all work step by step problems formula material sciencearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Torsion; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1YTKedLQOa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY