
A W 200 x 41.7 wide-flange beam (see Table F-l(b), Appendix F) is simply supported with a span length of 2.5 m (see figure). The beam supports a concentrated load of 100 kN at 0.9 m from support B. At a cross section located 0,7 m from the left-hand support, determine the principal stresses tr, and
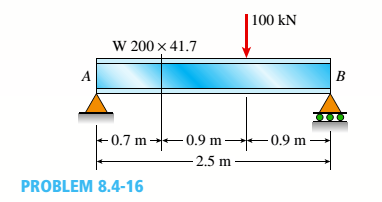
(a).
To find: Values of maximum stress and principal shear stress at top of beam.
Answer to Problem 8.4.16P
Values of principal stress :
Maximum shear stress
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Beam length
Point load
Dimensions of beam,
Concept Used:
Bending stress
Shear stress
Values of principal normal stress :
Maximum shear stress:
From equilibrium:
So, bending moment at point
Shear force at point
Moment of inertia:
First, moment of area at the top of beam shall be zero,
So, bending stress at top:
And shear stress at that point:
For this situation no stress in
Values of Principal and normal stress are given by following equation:
Maximum shear stress:
Conclusion:
Hence, we get:
Values of principal stress :
Maximum shear stress
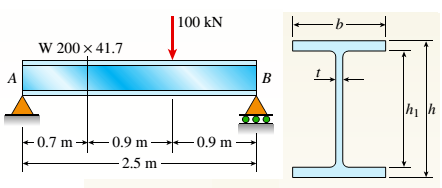
(b).
To find: The values of principal stress and principal stress at top of web.
Answer to Problem 8.4.16P
Values of principal stress:
Maximum shear stress:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Beam length
Point load
Dimensions of beam,
Concept Used:
Bending stress
Shear stress
Values of principal normal stress:
Maximum shear stress
From equilibrium:
So, bending moment at point
Shear force at point
Moment of inertia:
First, moment of area of flange:
So, bending stress at top of web:
And shear stress at that point ::
For this situation no stress in
Values of principal normal stress are given by following equation:
Maximum shear stress,
Conclusion:
Hence, we get:
Values of principal stress :
Maximum shear stress
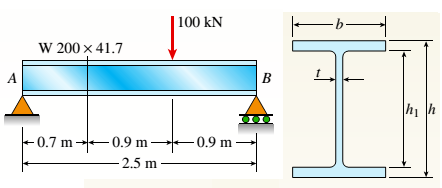
(c).
To find: Values of principal stress and maximum stress at neutral axis.
Answer to Problem 8.4.16P
Values of principal stress:
Maximum shear stress
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Beam length
Point load
Dimensions of beam:
Concept Used:
Bending stress
Shear stress
Principal normal stresses
Maximum shear stress
From equilibrium:
So, bending moment at point
Shear force at point
Moment of inertia,
First moment of area for the section above the neutral axis:
So, bending stress at neutral axis:
And shear stress at that point:
For this situation no stress in
Values of principal stress are given by following equation:
Maximum shear stress:
Conclusion:
Hence, we get:
Values of principal stress:
Maximum shear stress
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- A piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the change in the volume of the cylinder of the refrigerant-134a if the specific volume and enthalpy of R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and -10°C and at the final state of 90.4 kPa and 15°C are as follows: = 0.2418 m³/kg, h₁ = 247.77 kJ/kg 3 v2 = 0.2670 m³/kg, and h₂ = 268.18 kJ/kg The change in the volume of the cylinder is marrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device contains 0.87 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Use data from the tables. R-134a -10°C Determine the final pressure of the refrigerant-134a. The final pressure is kPa.arrow_forwardThe hydraulic cylinder BC exerts on member AB a force P directed along line BC. The force P must have a 560-N component perpendicular to member AB. A M 45° 30° C Determine the force component along line AB. The force component along line AB is N.arrow_forward
- ! Required information A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. The tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is given to be T₁ = 815 lb. A 15° 25° B T₂ Using trigonometry, determine the required tension T₂ in the right-hand portion if the resultant R of the forces exerted by the cable at A is to be vertical. The required tension is lb.arrow_forwardWhat are examples of at least three (3) applications of tolerance fitting analysis.arrow_forwardThe primary material used in the production of glass products is silica sand. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Which one of the following is the most common polymer type in fiber-reinforced polymer composites? thermosets thermoplastics elastomers none of the abovearrow_forwardA pattern for a product is larger than the actual finished part. True or Falsearrow_forwardIn the lost foam process, the pattern doesn’t need to be removed from the mold. True or Falsearrow_forward
- Tempering eliminates internal stresses in glass. True or Falsearrow_forwardThermoset polymers can be recycled with little to no degradation in properties. True or Falsearrow_forwardTwo forces are applied as shown to a hook support. The magnitude of P is 38 N. 50 N 25° DG a 터 Using trigonometry, determine the required angle a such that the resultant R of the two forces applied to the support will be horizontal. The value of a isarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
