
To determine:The shape of
Concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution:
Trigonal pyramid.
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure of

It has three bonds and one pair of lone electrons. So, its shape is trigonal pyramid.
(c)
To determine:The shape of
Concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution:
Linear.
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure of
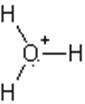
It has two bonds and three pairs of lone electrons. So, its shape is linear.
(d)
To determine:The shape of
. Concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution:
Octahedral.
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure of
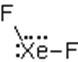
It has six bonds and no lone pair of electrons. So, its shape is octahedral.
(e)
To determine:The shape of
. Concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution:
Square pyramidal.
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure of
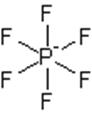
It has five bonds and one pair of lone electrons. So, its shape is square pyramidal.
(f)
To determine:The shape of
Concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution:
Tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
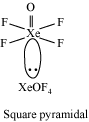
The electron dot structure of

It has four bonds and no lone pair of electrons. So, its shape is tetrahedral.
(g)
To determine:The shape of
. Concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution: Tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure of
It has four bonds and no lone pair of electrons. So, its shape is tetrahedral.
(h)
To determine:The shape of
Concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution: Tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure of

It has four bonds and no lone pair of electrons. So, its shape is tetrahedral.
(i)
To determine:The shape of
. .concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution: Square planar.
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure of
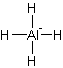
It has four bonds and two pairs of lone electrons. So, its shape is square planar.
(j)
To determine:The shape of
Concept Introduction:
- To predict the shapes, we have to considerer the special distribution of the atoms and the pairs of free electrons.
- The pairs of free electrons are those do not form part of bonds between atoms.
- The electron dot structure shows the valence electrons distribution around the atoms.
| Number of bonds | Number of pairs of free electrons | Shapes |
| 2 | 0 | Linear |
| 2 | 3 | Linear |
| 2 | 1 | Bent |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | 1 | Square pyramidal |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
| 6 | 0 | Octahedral |
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Solution: Trigonal planar.
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure of

It has three bonds and no lone pair of electrons. So, its shape is trigonal planar.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Chemistry with eText -- Access Card Package (7th Edition)
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





