
(a)
Interpretation:
The two expressions for Doppler broadening and Doppler half-width needs to be shown equivalent to each other.
Concept introduction:
The equation for the half-width for Doppler broadening Δλ0 of an atomic line can be used to study line broadening in a low − pressure laser-induced plasma.
Explanation of Solution
The change in wavelength at the center of the emission line can be represented as follows:
Here,
Similarly, the Doppler half-width can be calculated as follows:
Here,
Also,
(b)
Interpretation:
The half-width for Doppler broadening needs to be determined for 4s to 4p transition for nickel atom.
Concept introduction:
Doppler bordering is happened due to the Doppler effect caused by a distribution of velocities of atomic molecules.
Answer to Problem 8.12QAP
The half-width = 7934 nm and
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
The Doppler half-width can be calculated as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
The natural line width for the above transition needs to be determined, assuming that the lifetime of the excited state is
Concept introduction:
Natural line width is associated with the decay time (Natural life-time) and it is a minimum line width that does not contain effects such as collisional and Doppler broadening.
Answer to Problem 8.12QAP
Natural line width =
Explanation of Solution
Natural line width can be calculated as follows:
Putting the values,
(d)
Interpretation:
To show that the relativistic expression is consistent with the mentioned equation given for the low atomic speeds.
Concept introduction:
When compared with the
Explanation of Solution
When the atomic speed very low V is considerably small when compared to the c, that of the speed of light. Hence the above mentioned equation could be written as shown below. Hence, at low velocities, relativistic kinetic energy reduces to classical kinetic energy. No object with mass can achieve the speed of light because an infinite amount of energy input and an infinite amount of work is required to accelerate a mass to the speed of light.
(e)
Interpretation:
The speed of an iron atom the 4s to 4p transition at 385.9911 nm should be determined.
Concept introduction:
The rest wavelength of Nickel is 410 nm. The formula used is:
Answer to Problem 8.12QAP
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
(f)
Interpretation:
The fraction of a sample of iron atoms at 10,000 K that would have the velocity calculated in part e should be computed.
Concept introduction:
Natural line width is associated with the decay time. It is a minimum line width that does not contain effects such as collisional and Doppler broadening.
Answer to Problem 8.12QAP
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
(g)
Interpretation:
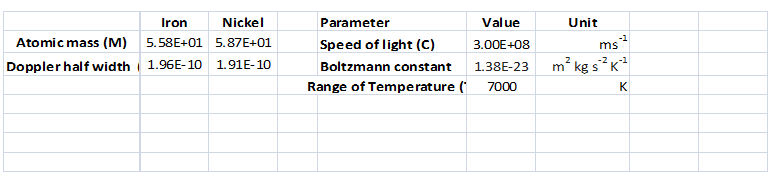
A spreadsheet should be created to calculate the Doppler half-width
Concept introduction:
Doppler bordering is happened due to the Doppler effect caused by a distribution of velocities of atomic molecules.
Answer to Problem 8.12QAP
Refer the spreadsheet
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation:
(h)
Interpretation:
The four sources of pressure broadening should be listed by consulting the paper by Gornushkin et al. (note 10).
Explanation of Solution
The interaction of the surrounding particles with the radiating atom is the major source of pressure line broadening, which causes a phase shift and a frequency disturbance.
The most important cases of interaction are:
- linear Starkeffect, p = 2;
- resonance interaction between identical particles, p = 3;
- quadratic Stark effect, p = 4,
- van der Waals interaction, p = 6.
The superposition problems are avoided by two approximations:
- ‘nearest neighbor approximation’, in this the considered interaction is interaction with the closest perturber.
- The impact or collision concept, in which moving perturbers act sequentially in time.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
- In a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both only if(A) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(B) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:2 or 2:1.arrow_forwardIn a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both.(1) Only if the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(2) If the initial quantities of A and B are in their stoichiometric ratios.arrow_forwardThere are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Calculate the measurement of uncertainty and provide the data in a spreadsheet table. Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32 152.87 151.24 153.26 152.02 152.90 152.87 151.49 152.46 152.58arrow_forward
- 1. Predict the organic product(s) of the following reactions. Assume excess of reagents unless otherwise noted. a) &l BH3 •THF b) 1) NaOH 2) H3O+ solve d) ala 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+ e) H2N سكر CuLi NH2 1) SOCI2 2) EtMgBr 3) H3O+ NC H3O+ Δarrow_forwardThere are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Summarise and report these results including an indication of measurement uncertainty. In both calculation samples calculate if an outlier is present, max value, number of samples, mean, standard deviation, g (suspect), g (critical) and t (critical). Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32…arrow_forwardIndicate the rate expressions for reactions that have order 0, 1, and 2.arrow_forward
- PROBLEMS Q1) Label the following salts as either acidic, basic, or neutral a) Fe(NOx) c) AlBr b) NH.CH COO d) HCOON (1/2 mark each) e) Fes f) NaBr Q2) What is the pH of a 0.0750 M solution of sulphuric acid?arrow_forward8. Draw all the resonance forms for each of the fling molecules or ions, and indicate the major contributor in each case, or if they are equivalent (45) (2) -PH2 سمة مدarrow_forwardA J то گای ه +0 Also calculate the amount of starting materials chlorobenzaldehyde and p-chloroacetophenone required to prepare 400 mg of the given chalcone product 1, 3-bis(4-chlorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one molar mass ok 1,3-bis(4-Chlorophenyl) prop-2-en-1-one = 277.1591m01 number of moles= 0.400/277.15 = 0.00144 moles 2 x 0.00 144=0.00288 moves arams of acetophenone = 0.00144 X 120.16 = 0.1739 0.1739x2=0.3469 grams of benzaldehyde = 0.00144X106.12=0.1539 0.1539x2 = 0.3069 Starting materials: 0.3469 Ox acetophenone, 0.3069 of benzaldehyde 3arrow_forward
- 1. Answer the questions about the following reaction: (a) Draw in the arrows that can be used make this reaction occur and draw in the product of substitution in this reaction. Be sure to include any relevant stereochemistry in the product structure. + SK F Br + (b) In which solvent would this reaction proceed the fastest (Circle one) Methanol Acetone (c) Imagine that you are working for a chemical company and it was your job to perform a similar reaction to the one above, with the exception of the S atom in this reaction being replaced by an O atom. During the reaction, you observe the formation of three separate molecules instead of the single molecule obtained above. What is the likeliest other products that are formed? Draw them in the box provided.arrow_forward3. For the reactions below, draw the arrows corresponding to the transformations and draw in the boxes the reactants or products as indicated. Note: Part A should have arrows drawn going from the reactants to the middle structure and the arrows on the middle structure that would yield the final structure. For part B, you will need to draw in the reactant before being able to draw the arrows corresponding to product formation. A. B. Rearrangement ΘΗarrow_forward2. Draw the arrows required to make the following reactions occur. Please ensure your arrows point from exactly where you want to exactly where you want. If it is unclear from where arrows start or where they end, only partial credit will be given. Note: You may need to draw in lone pairs before drawing the arrows. A. B. H-Br 人 C Θ CI H Cl Θ + Br Oarrow_forward
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning


