
CHEMISTRY THE CENTRAL SCIENCE >EBOOK<
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780136873891
Author: Brown
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 69E
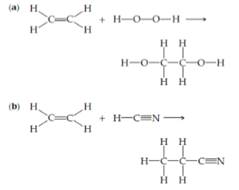
Using Table 8.3, estimate
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
identify the formal charge in the case.
below by indicating the magnitude,
sign, and location of the charge
magnitude and sign of formal charge
location of formal charge (atom
number):
N
None
Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
CHEMISTRY THE CENTRAL SCIENCE >EBOOK<
Ch. 8.2 - Which of the these elements is most likely to from...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.1.2PECh. 8.2 - Which of the following bond is the most polar? H-F...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.2.2PECh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.3.1PECh. 8.3 - Prob. 8.3.2PECh. 8.4 - Which of the following bonds is the most polar? a....Ch. 8.4 - Which of the following bonds is most polar: S-Cl,...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.5.1PECh. 8.4 - The dipole moment of chlorine monofluoride,...
Ch. 8.5 - Which of the these molecules has a Lewis structure...Ch. 8.5 -
How many valence electrons should appear in the...Ch. 8.5 - Compare the lewis symbol for neon the structure...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 8.7.2PECh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.8.1PECh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.8.2PECh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.9.1PECh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.9.2PECh. 8.6 - Which of the statements about resonance is true?...Ch. 8.6 - Prob. 8.10.2PECh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.11.1PECh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.11.2PECh. 8 - Prob. 1DECh. 8 - Prob. 1ECh. 8 - Prob. 2ECh. 8 - A portion of a two-dimensional "slab" of NaCl(s)...Ch. 8 - Prob. 4ECh. 8 - Prob. 5ECh. 8 - Incomplete Lewis structures for the nitrous acid...Ch. 8 - Prob. 7ECh. 8 - Prob. 8ECh. 8 - Prob. 9ECh. 8 - True or false: The hydrogen atom is most stable...Ch. 8 - Consider the element silicon, Si. Write its...Ch. 8 - Write the electron configuration for the element...Ch. 8 - Prob. 13ECh. 8 - What is the Lewis symbol for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Using Lewis symbols, diagram the reaction between...Ch. 8 - Use Lewis symbols to represent the reaction that...Ch. 8 - Predict the chemical formula of the ionic compound...Ch. 8 - Prob. 18ECh. 8 - Prob. 19ECh. 8 - Prob. 20ECh. 8 - Is lattice energy usually endothermic or...Ch. 8 - NaCI and KF have the same crystal structure. The...Ch. 8 - Prob. 23ECh. 8 - Prob. 24ECh. 8 - Consider the ionic compounds KF, NaCl, NaBr, and...Ch. 8 - Which of the following trends in lattice energy is...Ch. 8 - Energy is required to remove two electrons from Ca...Ch. 8 - Prob. 28ECh. 8 - Use data from Appendix C, Figure 7.10, and Figure...Ch. 8 - Prob. 30ECh. 8 - Prob. 31ECh. 8 - Prob. 32ECh. 8 - Using Lewis symbols and Lewis structures, diagram...Ch. 8 - Use Lewis symbols and Lewis structures to diagram...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35ECh. 8 - Prob. 36ECh. 8 - Prob. 37ECh. 8 - What is the trend in electronegativity going from...Ch. 8 - Prob. 39ECh. 8 - By referring only to the periodic table, select...Ch. 8 - which of the following bonds are polar? B-F,...Ch. 8 - Arrange the bonds in each of the following sets in...Ch. 8 - Prob. 43ECh. 8 - Prob. 44ECh. 8 - In the following pairs of binary compounds,...Ch. 8 - Prob. 46ECh. 8 - Prob. 47ECh. 8 - Write Lewis structures for the following: H2CO...Ch. 8 - Prob. 49ECh. 8 - Draw the dominant Lewis structure for the...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule...Ch. 8 - Prob. 52ECh. 8 - Prob. 53ECh. 8 - Prob. 54ECh. 8 - Prob. 55ECh. 8 - Prob. 56ECh. 8 - Prob. 57ECh. 8 - Prob. 58ECh. 8 - Prob. 59ECh. 8 - Prob. 60ECh. 8 - Prob. 61ECh. 8 - 8.62 For Group 3A-7A elements in the third row of...Ch. 8 - Draw the Lewis structures for each of the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 64ECh. 8 - In the vapor phase, BeCl2exists as a discrete...Ch. 8 -
8.66
Describe the molecule xenon trioxide, XeO3,...Ch. 8 -
8.67 There are many Lewis structures you could...Ch. 8 - Prob. 68ECh. 8 - Using Table 8.3, estimate H for each of the...Ch. 8 - Using Table 8.3, estimate H for the following...Ch. 8 - State whether each of these statements is true or...Ch. 8 - Prob. 72ECh. 8 - Prob. 73ECh. 8 - Prob. 74ECh. 8 - Prob. 75ECh. 8 - Prob. 76ECh. 8 - A new compound is made that has a C-C bond length...Ch. 8 - A new compound is made that has an N-N bond length...Ch. 8 - Prob. 79AECh. 8 - Prob. 80AECh. 8 - An ionic substance of formula MX has a lattice...Ch. 8 - Prob. 82AECh. 8 - Prob. 83AECh. 8 - Prob. 84AECh. 8 - Consider the collection of nonmetallic elements 0,...Ch. 8 - The substance chlorine monoxide, CIO(g), is...Ch. 8 -
[8.87]
a. using the electronegativities of Br...Ch. 8 - Prob. 88AECh. 8 - Although I3- is a known ion, F3- is not. a. Draw...Ch. 8 - Calculate the formal charge on the indicated atom...Ch. 8 - The hypochlorite ion, CIO- , is the active...Ch. 8 - Prob. 92AECh. 8 - a. Triazine, C3 H3N3, is like benzene except that...Ch. 8 - Prob. 94IECh. 8 - Prob. 95IECh. 8 - Prob. 96IECh. 8 - Prob. 97IECh. 8 - Prob. 98IECh. 8 - Prob. 99IECh. 8 - Prob. 100IECh. 8 - Prob. 101IECh. 8 - Prob. 102IECh. 8 -
8.103 The compound chloral hydrate, known in...Ch. 8 - Barium azide is 62.04% Ba and 37.96% N. Each azide...Ch. 8 - Acetylene (C2H2) and nitrogen (N2) both contain a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 106IECh. 8 - Prob. 107IECh. 8 -
8.108 Formic acid has the chemical formula...Ch. 8 - Prob. 109IECh. 8 - Prob. 110IE
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardA vial of Xe 133 gas (t 1/2 = 5.24 d) os ca;obrated fpr 22mCi @ 6:00am on March 1. What is its activity at 6:00 pm on march 8? what is mCI remainarrow_forwardMcLafferty Rearrangement: Label alpha (), beta (), and gamma () on the molecule. Draw mechanismarrows to describe the process of the rearrangement. What functional group is lost during the rearrangement? What new functional group is made from the ketone/aldehyde you started with? What stabilizing chemical theory causes (allows) rearrangement to happen?arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardIf a high molecular weight linear polyethylene is chlorinated by inducing the substitution of chlorine atoms by hydrogen, if 5% of all hydrogen atoms are replaced, what approximate percentage of chlorine by weight would the product have?arrow_forward
- O Macmillan Learning Chemistry: Fundamentals and Principles Davidson presented by Macmillan Learning Poly(ethylene terephthalate), known as PET or industrially as Dacron, is a polyester synthesized through a condensation reaction between two bifunctional monomers. The monomers, ethylene glycol and terepthalic acid, are given. Add bonds and remove atoms as necessary to show the structure of a two repeat unit portion of a longer polymer chain of PET. You may need to zoom out to see the complete structure of all four monomer units. Select Draw / || | C H 0 3 © Templates More ° ° ° || C CC - OH HO OH HOC - C Erase CC OH HO C C 〃 C H₂ Q2Qarrow_forwardc) + H₂Oarrow_forward으 b) + BF. 3 H2Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Calorimetry Concept, Examples and Thermochemistry | How to Pass Chemistry; Author: Melissa Maribel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nSh29lUGj00;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY