
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781292089034
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 59P
cis-4-Bromocyclohexanol and trans-4-bromocyclohexanol form the same elimination product but a different substitution product when they react with HO-.
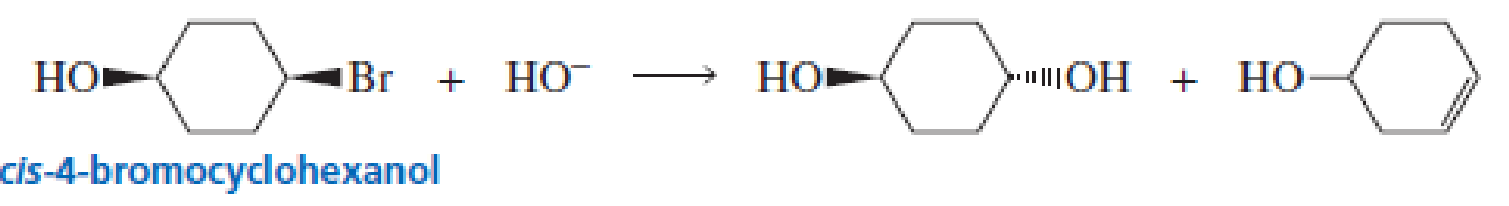
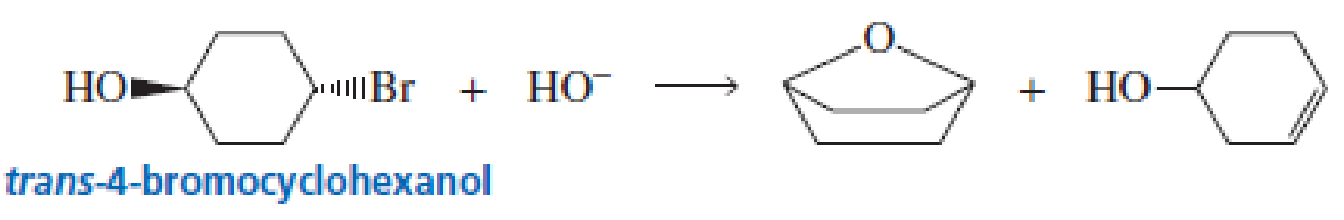
a. Why do they form the same elimination product?
b. Explain, by showing the mechanisms, why different substitution products are obtained.
c. How many stereoisomers does each of the elimination and substitution reactions form?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No wedge or dashes. Do proper structure. Provide steps and explanation.
10 Question (1 point)
Draw curved arrow notation to indicate the proton transfer between NaOH and CH3CO₂H.
2nd attempt
:0-
H
See Periodic Table
See Hint
Draw the products of the proton transfer reaction. Don't add a + sign between the
products.
Provide steps and explanation please.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 8.1 - Does increasing the energy barrier for an SN2...Ch. 8.1 - Arrange the following alkyl bromides in order from...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 7PCh. 8.2 - Which reaction in each of the following pairs...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 9PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 11PCh. 8.3 - Draw the substitution products that will be formed...Ch. 8.4 - Arrange the following alkyl halides in order from...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 14P
Ch. 8.5 - Which of the following reactions will go faster if...Ch. 8.6 - After a proton is removed from the OH group, which...Ch. 8.6 - Draw the product of each of the following...Ch. 8.9 - Prob. 20PCh. 8.9 - Prob. 21PCh. 8.11 - Why do the SN1/E1 reactions of tertiary alkyl...Ch. 8.11 - Prob. 23PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 24PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 25PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 26PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 27PCh. 8.12 - a In which solvent would tert-butyl bromide...Ch. 8.13 - What would be the best way to prepare the...Ch. 8 - Methoxychlor is an insecticide that was intended...Ch. 8 - Prob. 31PCh. 8 - Prob. 32PCh. 8 - Prob. 33PCh. 8 - Prob. 34PCh. 8 - Prob. 35PCh. 8 - Prob. 36PCh. 8 - Explain how the following changes would affect the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 38PCh. 8 - Draw the major product obtained when each of the...Ch. 8 - Which alkyl halide in Problem 39 can undergo an El...Ch. 8 - Prob. 42PCh. 8 - Prob. 43PCh. 8 - Prob. 44PCh. 8 - Prob. 45PCh. 8 - Starting with bromocyclohexane, how could the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 48PCh. 8 - Fill in the blanks in the following chemical...Ch. 8 - For each of the following alkyl halides, indicate...Ch. 8 - Prob. 51PCh. 8 - a. Explain why 1-bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane has...Ch. 8 - An ether can be prepared by an SN2 reaction of an...Ch. 8 - Give two sets of reactants (each set including an...Ch. 8 - Show how the following compounds could be...Ch. 8 - Prob. 56PCh. 8 - Prob. 57PCh. 8 - Draw the structures of the products obtained from...Ch. 8 - cis-4-Bromocyclohexanol and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - Prob. 61PCh. 8 - Prob. 62PCh. 8 - Prob. 63PCh. 8 - In which solventethanol or diethyl etherwould the...Ch. 8 - The pKa of acetic acid in water is 4.76. What...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. Experimental Procedure. a. How many (total) data plots are to be completed for this experiment? Account for each. b. What information is to be extracted from each data plot?arrow_forwardProvide the IUPAC name of the following molecule. Don't forget to include the proper stereochemistry where appropriate.arrow_forward3. 2. 1. On the graph below, plot the volume of rain in milliliters versus its height in centimeters for the 400 mL beaker. Draw a straight line through the points and label it "400 mL beaker." Volume (mL) 400 350 300 250 200 150 750 mL Florence Volume Versus Height of Water 400 mL beaker 100 50 0 0 2 3 4 5 Height (cm) 6 7 8 9 10 Explain why the data points for the beaker lie roughly on a straight line. What kind of relationship is this? How do you know? (see page 276 text) the design of the beaker is a uniform cylinder the volume of liquid increases evenly with its height resulting in a linear relationship. What volume would you predict for 10.0 cm of water? Explain how you arrived at your answer. Use the data table and the graph to assist you in answering the question. 4. Plot the volume of rain in milliliters versus its height in centimeters for the 250 mL Florence flask on the same graph. Draw a best-fit curve through the points and label it "250 mL Florence flask." oke camearrow_forward
- Show work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardIn the video, we looked at the absorbance of a certain substance and how it varies depending on what wavelength of light we are looking at. Below is a similar scan of a different substance. What color BEST describes how this substance will appear? Absorbance (AU) Violet Blue Green Orange 1.2 1.0- 0.8- 0.6- 0.4- 0.2 0.0 450 500 550 600 650 700 Wavelength (nm) violet indigo blue green yellow orange red Red O Cannot tell from this information In the above graph, what causes -450 nm wavelength of light to have a higher absorbance than light with a -550 nm wavelength? Check all that are true. The distance the light travels is different The different data points are for different substances The concentration is different at different times in the experiment Epsilon (molar absortivity) is different at different wavelengthsarrow_forward5. a. Data were collected for Trial 1 to determine the molar mass of a nonvolatile solid solute when dissolved in cyclo- hexane. Complete the table for the analysis (See Report Sheet). Record calculated values with the correct number of significant figures. B. Freezing Point of Cyclohexane plus Calculation Zone Unknown Solute 2. Mass of cyclohexane (g) 10.14 Part C.4 3. Mass of added solute (g) 0.255 C. Calculations 1. k; for cyclohexane (°C⚫ kg/mol) 20.0 2. Freezing point change, AT, (°C) 3.04 Part C.6 3. Mass of cyclohexane in solution (kg) 4. Moles of solute, total (mol) Show calculation. 5. Mass of solute in solution, total (g) 6. Molar mass of solute (g/mol) Show calculation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

07 Physical Properties of Organic Compounds; Author: Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UjlSgwq4w6U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY