
(a)
Interpretation:
The configuration of the substitution products formed from the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
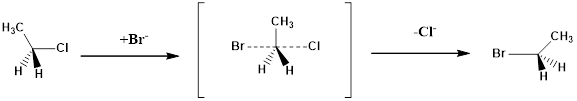
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
Solvolysis: The reaction is defined as solvolysis reaction if solvent acts as nucleophile in the given reaction.
Configuration of a molecule: The configurations of a molecule arise due to the spatial arrangement of atoms. The configuration can be assigned by following CIP rules as follows.
Assign numbering to the groups which are bonded to the chiral carbon based on the molecular weight and electronegativity.
If the sequence of the numbering follows clockwise direction the chiral atom is assigned as R configuration.
If the sequence of the numbering follows anticlockwise direction the chiral atom is assigned as S configuration.
(b)
Interpretation:
The configuration of the substitution products formed from the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
Transition State: The state which defines the highest potential energy with respect to reaction co-ordinate between reactant and product. It is usually denoted by using the symbol ‘≠’.
Nucleophile: donates pair of electrons to positively charged substrate resulting in the formation of
Configuration of a molecule: The configurations of a molecule arise due to the spatial arrangement of atoms. The configuration can be assigned by following CIP rules as follows.
Assign numbering to the groups which are bonded to the chiral carbon based on the molecular weight and electronegativity.
If the sequence of the numbering follows clockwise direction the chiral atom is assigned as R configuration.
If the sequence of the numbering follows anticlockwise direction the chiral atom is assigned as S configuration.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
- 0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward9arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole



