
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The Lewis structures of the given molecules and ions are to be represented.
Concept Introduction:
In Lewis dot
In Lewis dot symbol, valence electrons are represented by dots.
Dots are placed above and below as well as to the left and right of symbol.
Number of dots is important in Lewis dot symbol but not the order in which the dots are placed around the symbol.
In writing symbol pairing is not done until absolutely necessary.
For metals, the number of dots represents the number of electrons that are lost when the atom forms a cation.
For second period non metals, the number of unpaired dots is the number of bonds the atom can form.
Atomic ions can also be represented by dot symbols, by simply adding (for anions) and subtracting (for cations) the appropriate number of dots from Lewis dot symbol.
Lewis structure is the representation of bonding and non-bonding electron pairs present in the outermost shell of all atoms present in the molecule.
The number of bonds formed by an atom in the molecule is determined by the valence electron pairs.
Answer to Problem 46QP
Solution:
(a)
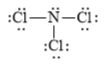
(b)
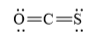
(c)
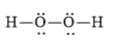
(d)
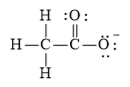
(e)
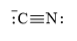
(f)
Explanation of Solution
a)
The electronic configuration of nitrogen and chlorine in
The nitrogen atom contains three valence electrons in its
The Lewis structure of
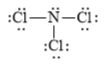
b)
The electronic configuration of oxygen, carbon, and sulfur in
Oxygen and sulfur atoms contain two valence electrons in their
The Lewis structure of
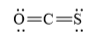
c)
The electronic configuration of oxygen and hydrogen in
The oxygen atom contains four valence electrons in its
The Lewis structure of
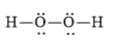
d)
The electronic configuration of oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen in
The carbon atom has a tendency to form four bonds because of the presence of four valence electrons in its outermost shell, hydrogen has a tendency to form one bond because of the presence of one electron in its outermost shell, and oxygen has a tendency to form two bonds due to the presence of two electrons in its outermost shell.
The Lewis structure of

e)
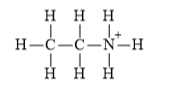
The electronic configuration of nitrogen and carbon in
Cyanide ion is composed of one triple bond of carbon and nitrogen atom. This species contains one lone pair on both carbon and nitrogen atoms.
The Lewis structure of
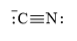
f)
The electronic configuration of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen in
Carbon atom has a tendency to form four bonds because of the presence of four valence electrons in its outermost shell, hydrogen has a tendency to form one bond because of the presence of one electron in its outermost shell, and nitrogen has tendency to form four bonds due to the presence of three electrons in its
The Lewis structure of

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY
- pls helparrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward35) Complete the following equation by drawing the line the structure of the products that are formed. Please note that in some cases more than one product is possible. You must draw all possible products to recive full marks! a. ethanol + 2-propanol + H2SO4 → b. OH conc. H2SO4 CH2 H3C CH + K2Cr2O7 C. d. H3C A pressure CH3 + H2 CH Pt catalystarrow_forward
- 21) The rate of reaction depends upon: a. the concentration and nature of reactants b. the temperature of the reaction C. whether or not a catalyst was used d. all of the above 22) A Maxwell-Boltzmann curve shows the distribution of molecular energies in a reaction system. When the temperature in this system is increased, the peak is a. higher and further to the right. b. higher and further to the left. c. lower and further to the right. d. lower and further to the left. 23) Which of the following correctly describes the reaction represented by the reaction below? CaCO3 (s) + energy → CaO (s) + CO2 (g) a. It is exothermic and the potential energy is greater in the reactants than the products. b. c. It is exothermic and the potential energy is greater in the products than the reactants. It is endothermic and the potential energy is greater in the products than the reactants. d. It is endothermic and the potential energy is equal for the products and reactants.arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward27) Draw the energy level diagram and write the full and shorthand electron configuration for a neutral sulfur atom.arrow_forward
- Indicate whether these compounds are isomers, enantiomers, or tautomers. OCH OCH محمد ممدarrow_forward30) Substance A to E below are listed with several of their properties. The identities of the substances are identified in random order below: Iron, ethane, ethanol, sodium nitrate, graphite First classify each substance as either a polar covalent compound, non-polar covalent compound, ionic compound, metallic solid, or network solid. Write your predictions in the sixth coloumn of the chart, under "type of substance." Then, identify the identity of the substance in the last coloumn. Substance Melting Point Boiling Point Solubility in H₂O Electrical Conductivity Type of Substance Identity of Substance (°C) (°C) as: Solid, Liquids, Solution A -182 -88 Insoluble No/No/- B 1538 2862 Insoluble Yes/Yes/- C 308 380 Soluble Yes/Yes/Yes Ꭰ 3456 Insoluble No/-/- E -114 78 Soluble No/No/Noarrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
- 28) Explain the process of galvanization. In your description, make sure to explain what metal is usually used for galvanization and why this metal used.arrow_forward29) Complete the following table Molecule H₂O NH3 Lewis Dot Diagram VSEPR Diagram Name of VSEPR Shapearrow_forward12) What is the best name to describe the shape of water molecule? a. Angular b. C. Tetrahedral Octahedral d. Trigonal pyramidal 13) Network solids are distinguished from metallic crystals in that: a. Network solids have charged ions, while metallic crystals do not. b. Network solids are composed of molecules, while metallic crystals only have one type of atom. C. Network solids are composed of non-metals. d. Network solids have much lower boiling points.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
