
Concept explainers
The hydroxyl radical
(d) The radical is generated when sunlight hits water vapor. Calculate the maximum wavelength (in nm) required to break an
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of hydroxyl radical is to be drawn; the reason for radical’s high affinity for H atoms, enthalpy change for the given reaction, and the maximum wavelength required to break given bond in given compound are to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The standard enthalpy of a reaction is the enthalpy change that occurs under standard conditions.
The standard enthalpy of a reaction is determined using the equation as given below:
Here, the stoichiometric coefficients are represented by m for reactants and n for products, and enthalpy of formation at standard conditions is represented by
The standard enthalpy of formation is the amount of heat change that arises as a result of one mole of compound formation at the standard states from its integral elements.
The value of enthalpy of formation of an element is zero at its most stable state.
Bond Enthalpy is the energy required to break a bond of 1 mole of a substance. It is given in
The Lewis dot symbols contain dots, which give information about valence electrons.
According to Planck’s energy–frequency law, energy is given by:
Here, h is Planck’s constant,
Answer to Problem 146AP
Solution:
(a)
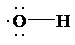
(b) The reason for radical
(c)
(d)
Explanation of Solution
a) Lewis structure for radical (OH)
The skeletal structure for
The number of valence electrons is as follows:
Now, only two electrons are used in bond formation. So, the number of remaining electrons is 5.
The oxygen atom has only one electron used in bond formation, so it will have 5 remaining electrons.
So, the Lewis structure for
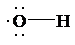
b) The radical has high affinity for H atom, refer table 8.6.
From table 8.6, the bond enthalpy of oxygen–hydrogen bond:
Since the value of oxygen–hydrogen bond is very high, the radical
Hence, the reason for radical
c) The enthalpy change for the following given reaction:
The enthalpy of reaction can be calculated as follows:
From table 8.6, the enthalpy of formation values are as follows:
Now, the standard enthalpy of the given reaction is as follows:
Substitute
Hence, the enthalpy of the given reaction from the bond enthalpy values is
d) The maximum wavelength (in nm) required to break an
From table 8.6, the bond enthalpy for oxygen–hydrogen bond is as follows:
This can be written as the energy of oxygen–hydrogen bond as
According to Planck’s energy–frequency law, energy is given as follows:
This can be written as follows:
Substitute
Hence, the maximum wavelength required to break the oxygen–hydrogen bond is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY
- EFFICIENTS SAMPLE READINGS CONCENTRATIONS Pigiadient) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) 58 6.274 3.898 301.7 151.2 14150 5.277 3.865 348.9 254.8 B 5.136 3.639 193.7 85.9 605 4.655 3.041 308.6 199.6 05 5.135 3.664 339.5 241.4 0139 4.676 3.662 160.6 87.6 90148 5.086 3.677 337.7 242.5 0092 6.348 3.775 464.7 186.4 PART3 5.081 3.908 223.5 155.8 5.558 3.861 370.5 257.1 4.922 3.66 326.6 242.9 4.752 3.641 327.5 253.3 50 5.018 3.815 336.1 256.0 84 4.959 3.605 317.9 216.6 38 4.96 3.652 203.8 108.7 $3 5.052 3.664 329.8 239.0 17 5.043 3.767 221.9 149.7 052 5.058 3.614 331.7 236.4 5.051 4.005 211.7 152.1 62 5.047 3.637 309.6 222.7 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 995 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 04 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 16 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 0.011 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 AVERAGE STDEV COUNT 95% CI Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH₃COCH₃) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH), applying heat to them produces an aldol condensation of the two compounds. If this is correct, draw the formula for the final product.arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A), what product(s) are obtained?arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardYou need to make a buffer by dissolving benzoic acid and sodium benzoate in water. What is the mass of benzoic acid that you would weigh out, in mg, to create 50 mL of a buffer at pH = 4.7 that will change pH no more than 0.10 units with the addition of 0.001 moles of acid or base? Enter just the answer without the units (mg) - just the number will do!arrow_forwardDraw the formula for 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride.arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardComplete the following reactions- hand written pleasearrow_forwardGive the organic product: O A O B Ос ○ D -NH–CH3 + CH3 CH3 NEN C ? A CH3 CH3 NH- CH3 B CH3 CH3 N=N- C CH3 CH3 N=NNH CH3 D CH3 N=N CH3 NHCH3 LNH CHOarrow_forward
- Finish the reaction- hand written pleasearrow_forwardGive the organic products: (benzyne) Br ? CH3 + K* :NH, liq NH3 HINT: Two products are formed. Each is a substituted aniline; they are isomers of each other. NH2 II I H₂N. CH3 CH3 III Select one: ○ A. I and II ○ B. I and III O C. I and IV O D. II and III O E. III and IV H₂N CH3 IV CH₂-NH2arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. Erase something Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
